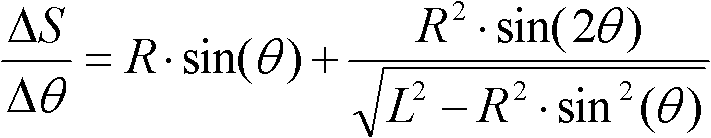Method for accurately finding upper dead point of crank connecting rod pressing machine
A technology of crank connecting rod and press, applied in the direction of press, punching machine, manufacturing tool, etc., can solve the problems of low efficiency, affecting processing accuracy, many human factors, etc., and achieve the effect of simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
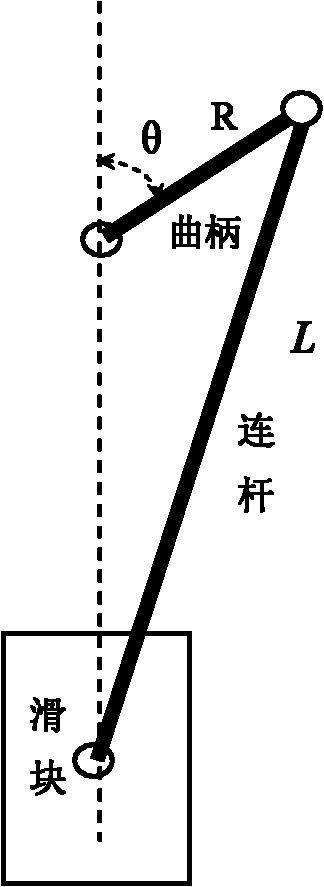
[0018] The application object of the present invention is a crank-connecting rod press. The crank-connecting rod press controls the rotation of a servo motor or an ordinary AC asynchronous motor. The motor drives the crank, and transmits the eccentric rotational power of the crank to the slider through the connecting rod to realize For the up and down movement of the slider, an angle measuring device is installed on the rotation axis of the crank without a fixed slider position measuring device installed on the slider side. Such as figure 1 , R is the radius of the crank, L is the length of the connecting rod, θ is the difference between the current angle of the crank and the top dead center.
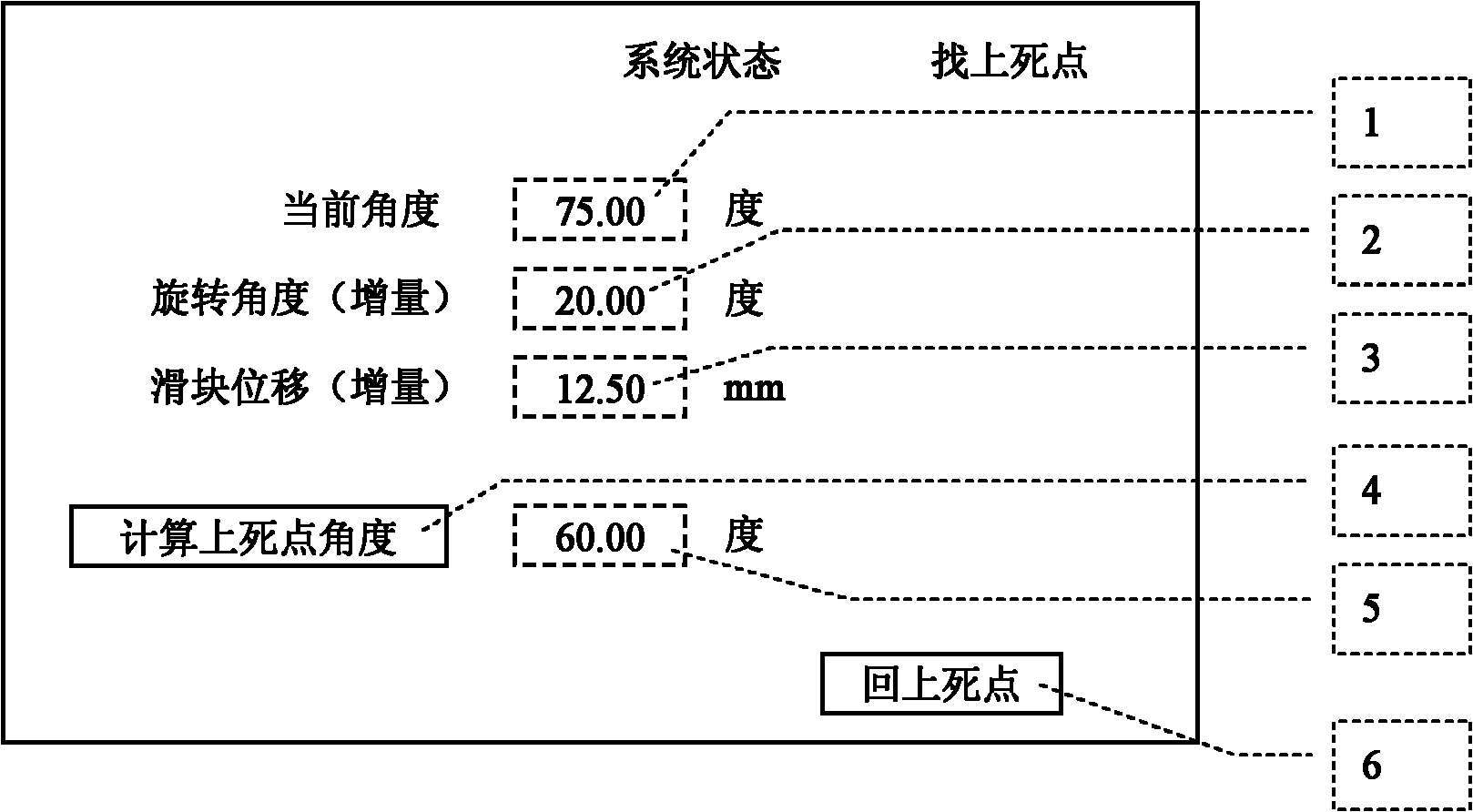
[0019] The following components are set on the crank press: motion control component, which controls the crank to rotate freely according to the angle; displacement measurement component, which measures the distance difference between the two upward or downward movements of the slider; ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com