Substrate structure and manufacturing method thereof
A manufacturing method and substrate technology, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, electrical solid-state devices, etc., can solve the problem of low thermal resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
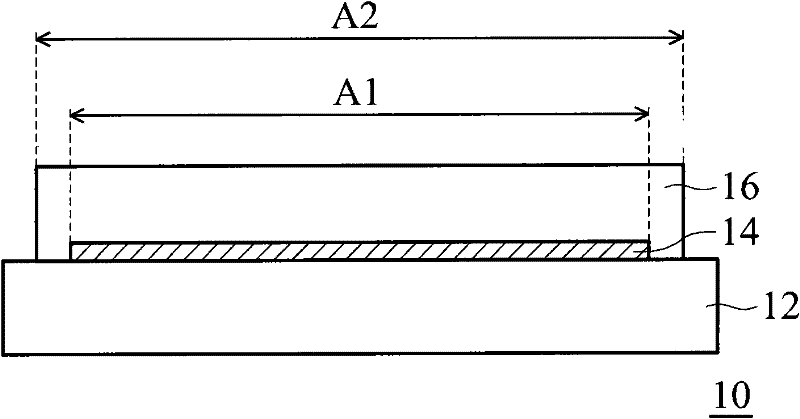
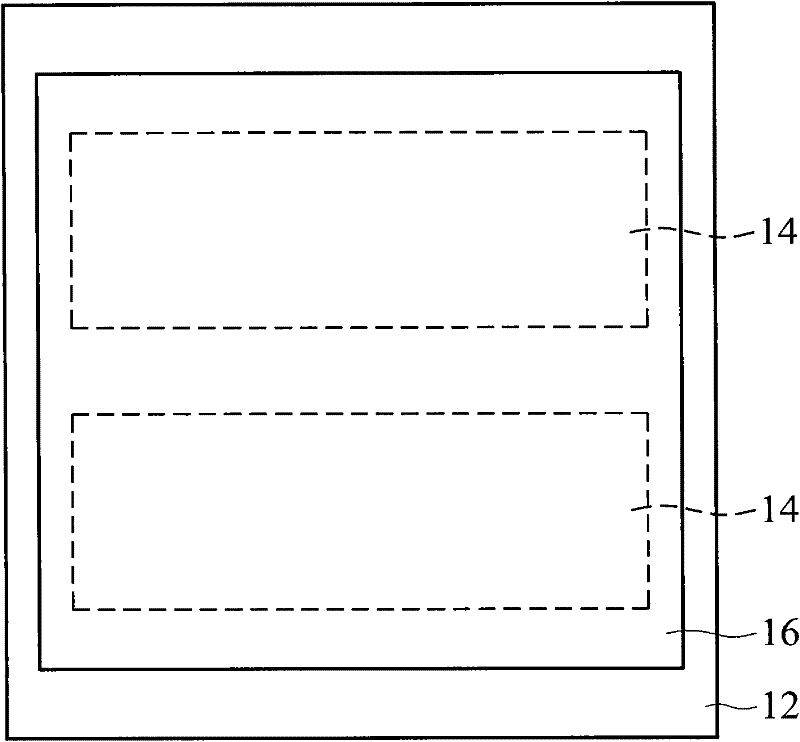
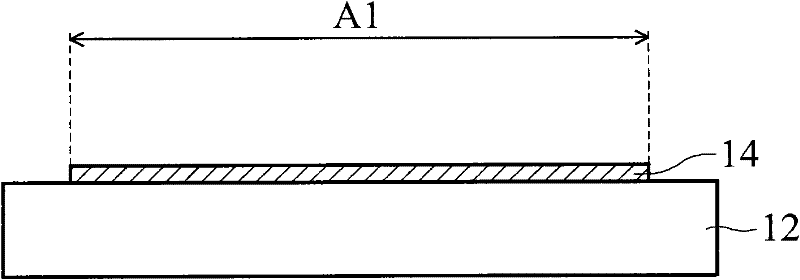
[0043] Fabrication of polyimide B1317-BAPPm(BB) / Topas(X=50, Y=50) / glass substrate structure
[0044] First, prepare Topas solutions with different solid content (1%, 3%, 6%, 7%, 8%). Afterwards, the Topas solution was coated on different glass support carriers to form a wet Topas film. The thickness of the wet Topas film is 30 μm, 60 μm, 90 μm, and 120 μm, respectively. After baking at 50°C for 5 minutes and 300°C for 1 hour, apply a polyimide substrate material (containing 1% adhesion promoter) on the Topas film. After baking again, perform a release test, and the results are shown in Table 1.
[0045] Table I
[0046] Topas solid content
Embodiment 2
[0048] Fabrication of polyimide B1317-BAPPm(BB) / Arton(X=50, Y=50, R=H) / glass substrate structure
[0049] First, prepare Arton solutions with different solid content (5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25%). Afterwards, the above-mentioned Arton solution was coated on different glass support carriers to form a wet Arton film. The thickness of the wet Arton film is 30 μm, 60 μm, 90 μm, and 120 μm, respectively. After baking at 50°C for 5 minutes and 300°C for 1 hour, apply a polyimide substrate material (containing 1% adhesion promoter) on the Arton film. After baking again, a release test was performed, and the results are shown in Table 2.
[0050] Table II
[0051] Arton solid content
Embodiment 3
[0053] The production of parylene release layer
[0054] Put the parylene dimer (parylene dimer) into the thermal evaporation equipment, put the pre-washed glass (15cm*15cm) into the sample chamber, and cover the glass with a hollow (8cm*8cm) gasket After vacuuming, heat to 150°C to vaporize the precursor of parylene, and then heat to 650°C to crack the raft door and open the raft door to the sample chamber, and polymerize and deposit at room temperature without being covered by gaskets. In the glass area, an 8cm*8cm release film is formed.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com