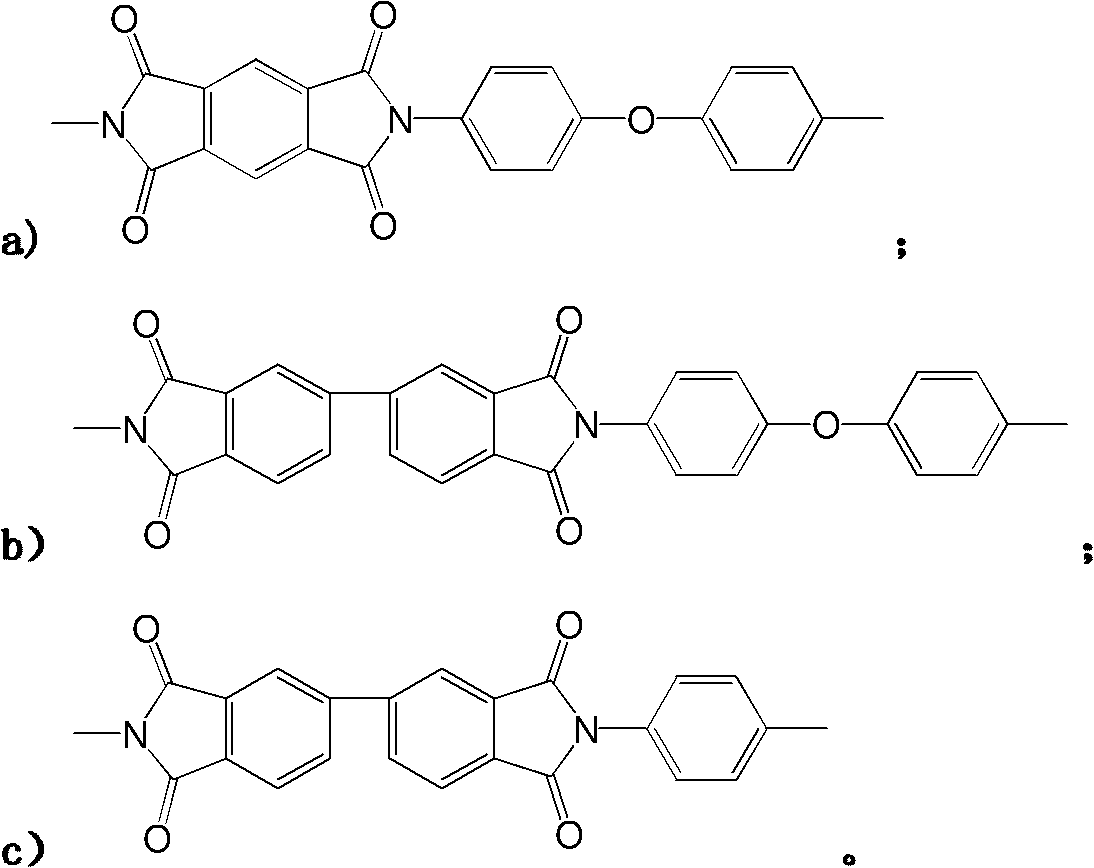
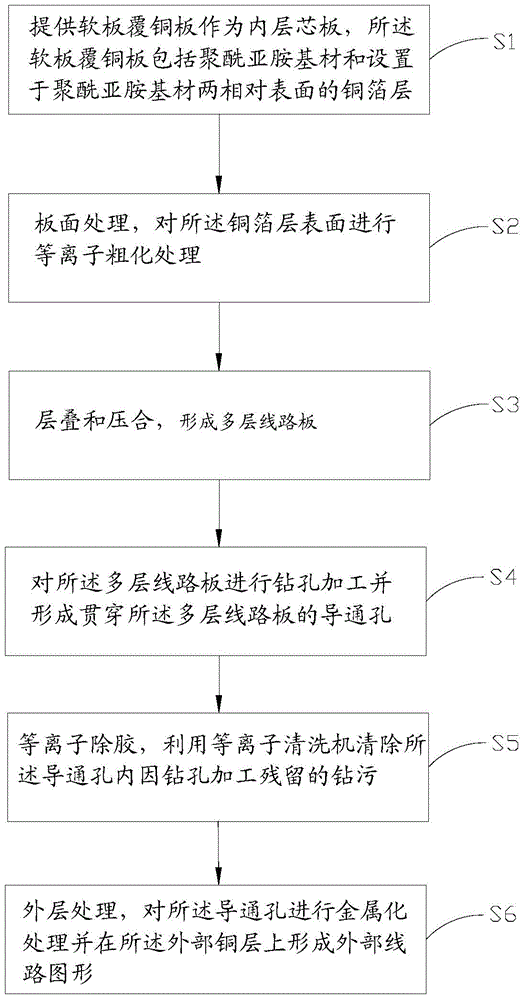
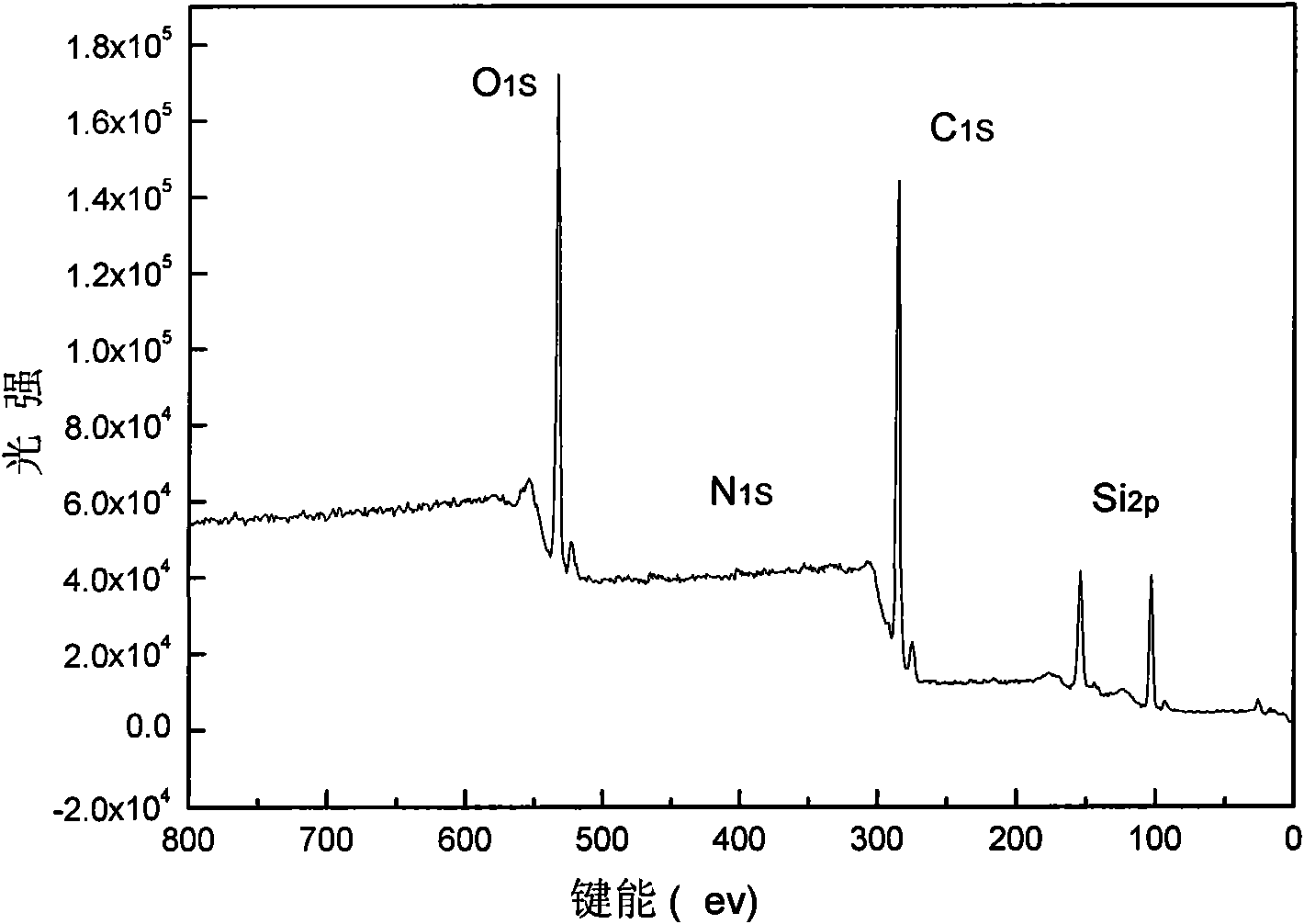
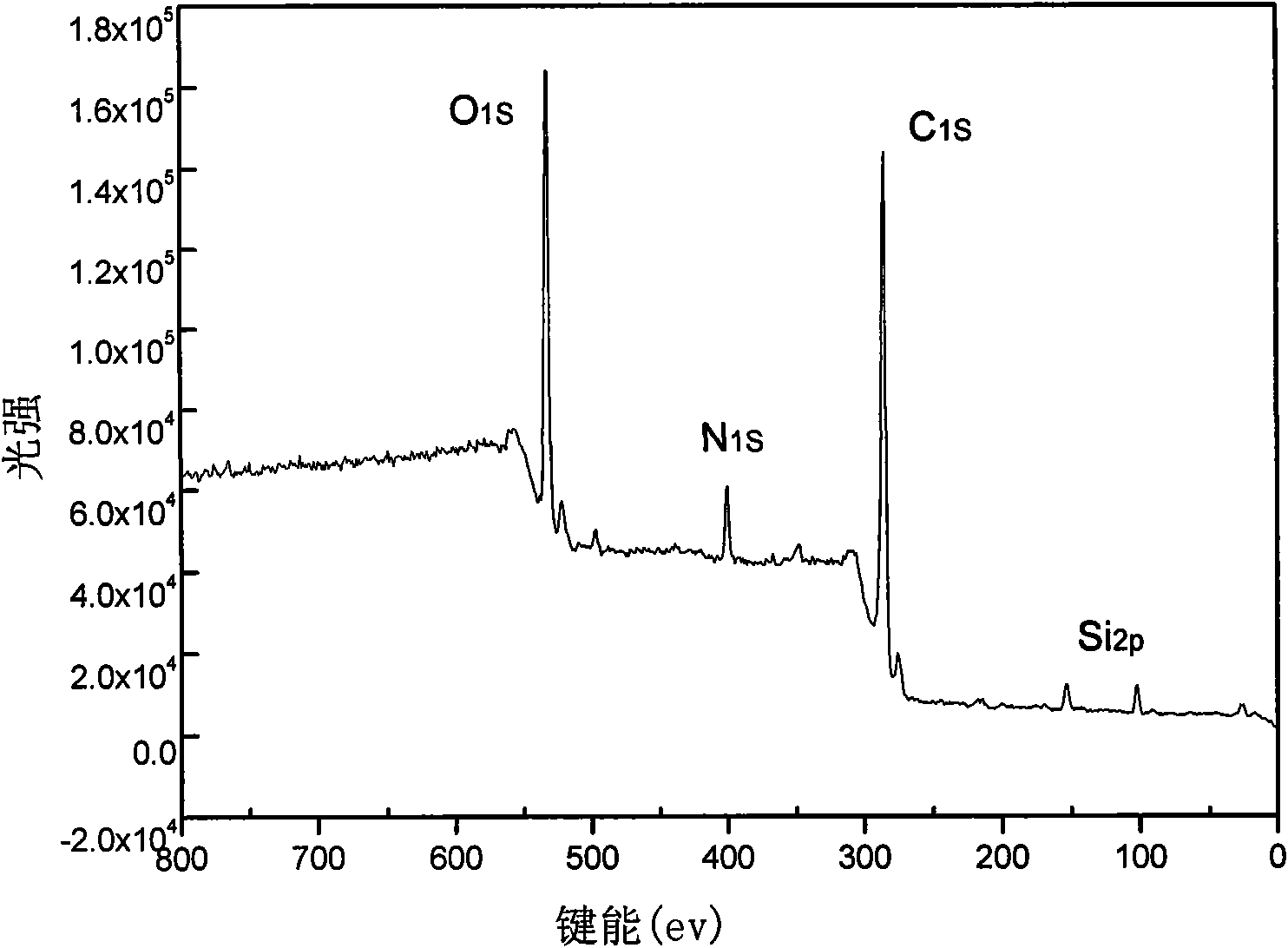
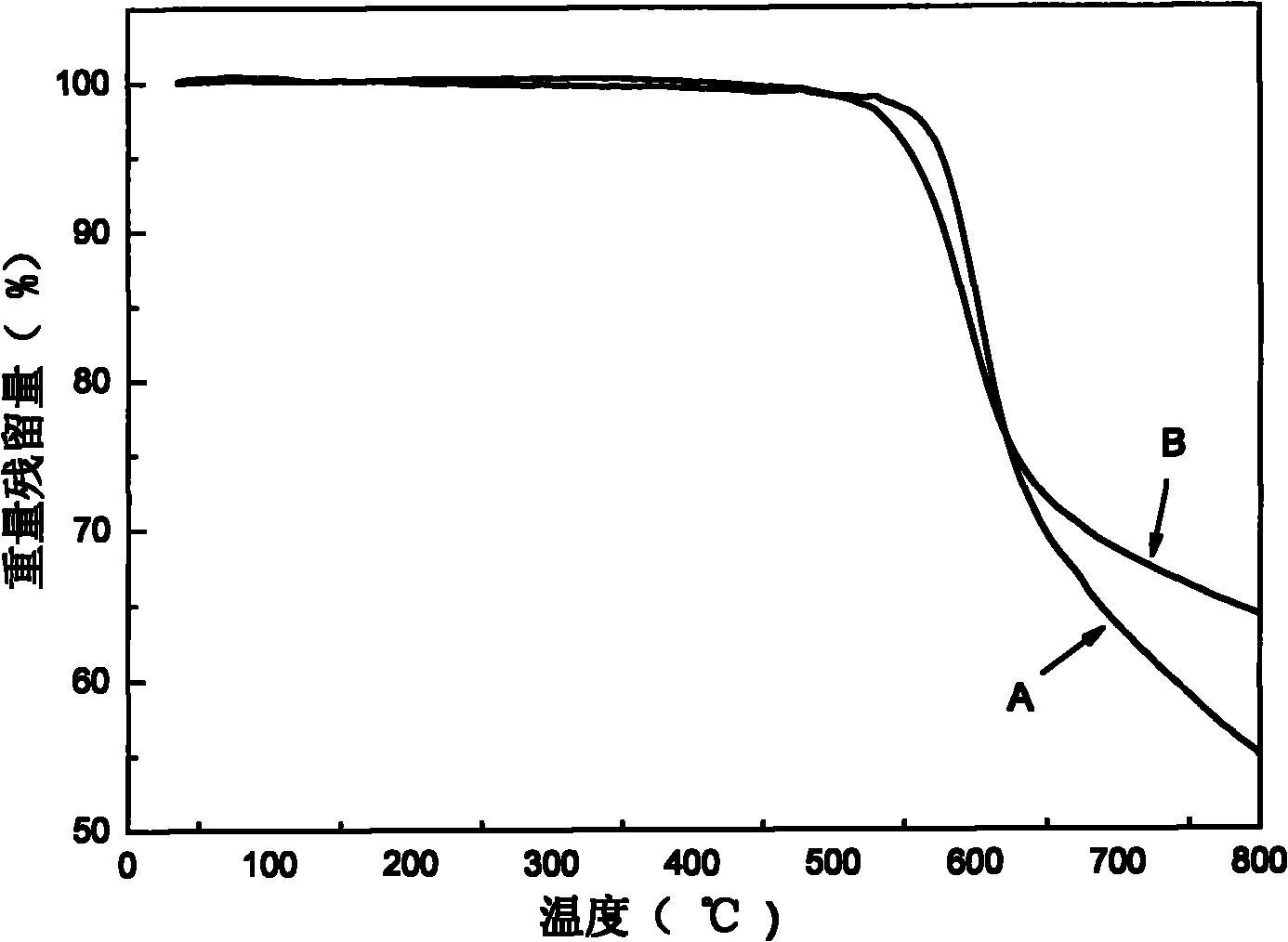
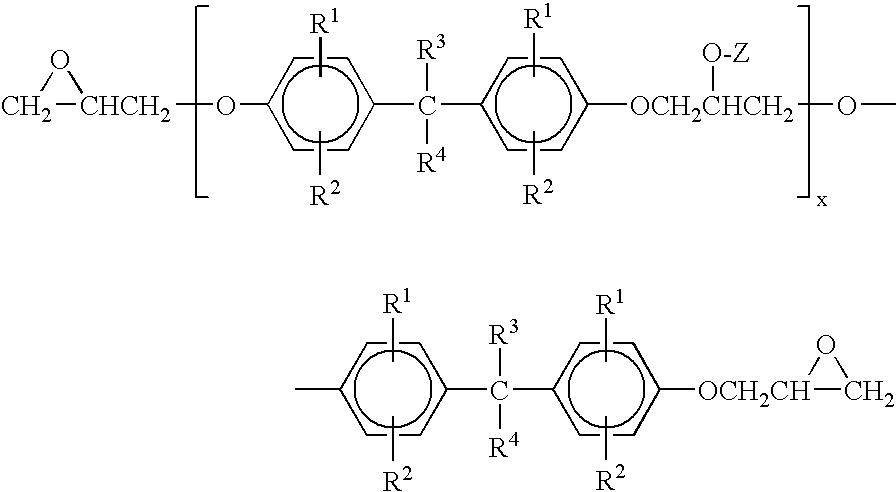Patents
Literature
323 results about "Polyimide substrate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
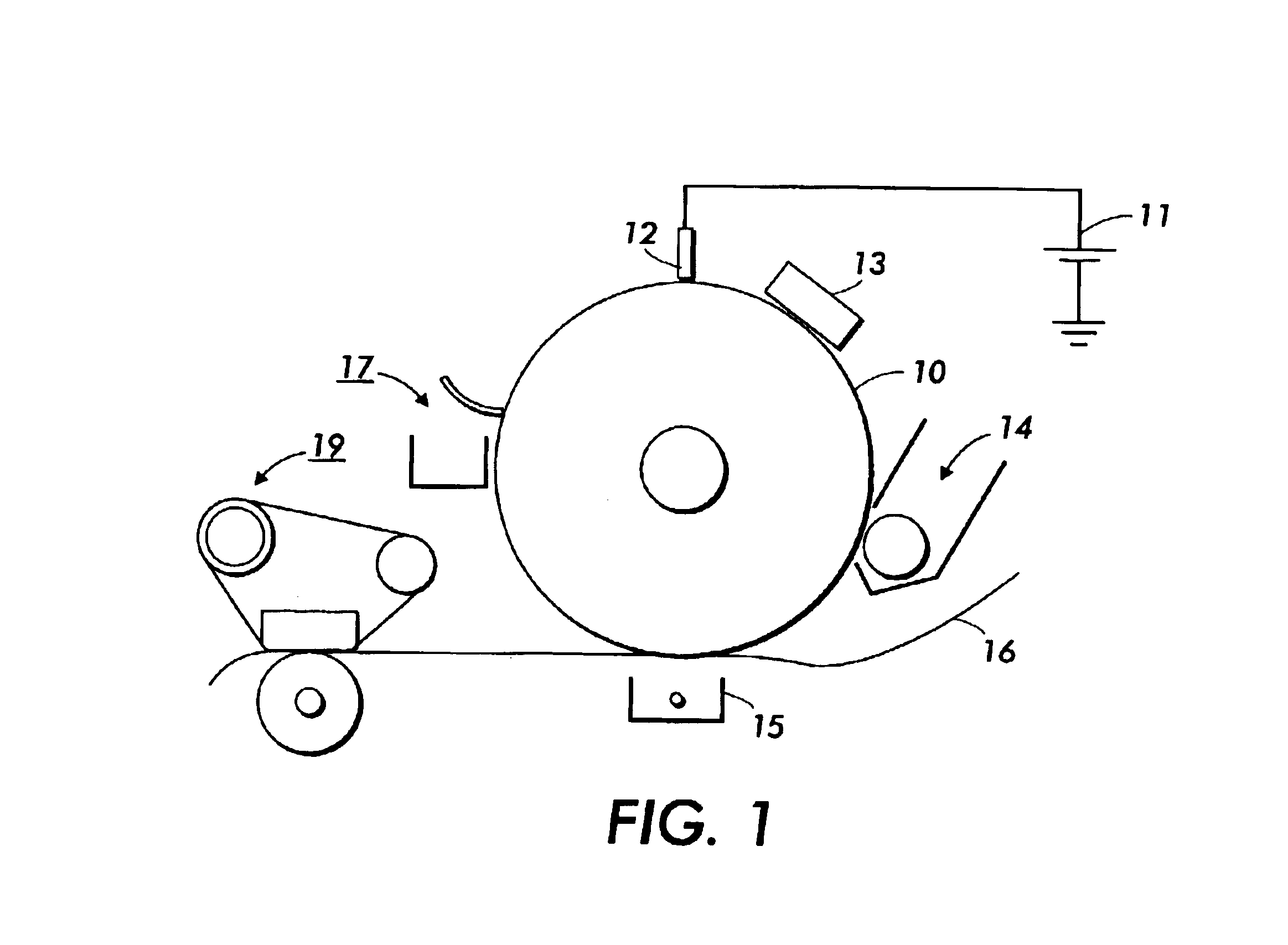
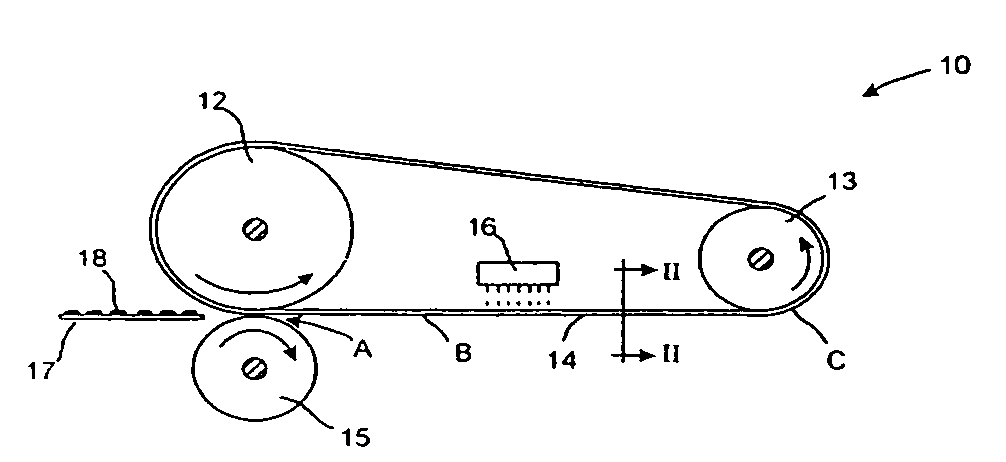
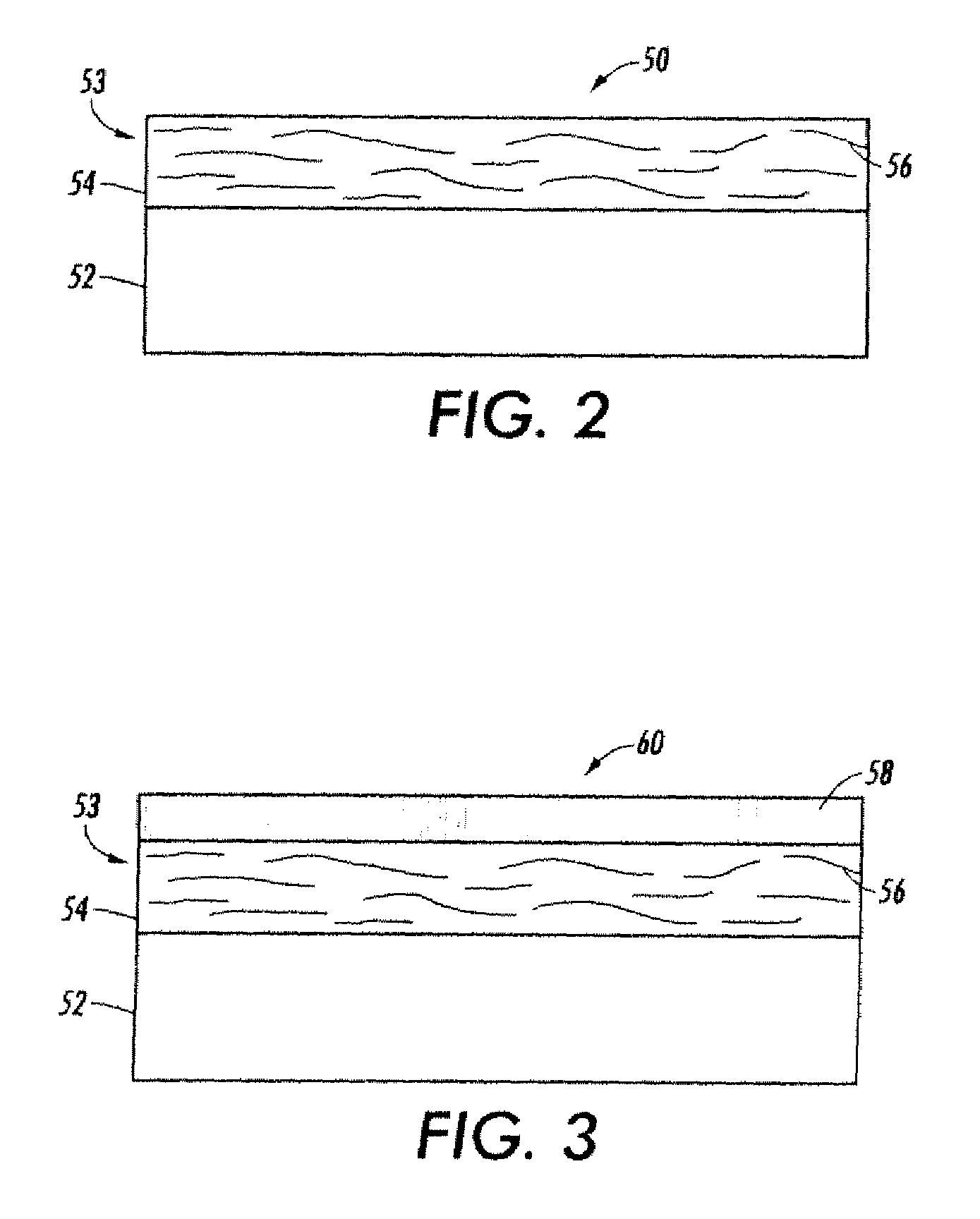
Fuser member having fluorocarbon outer layer
InactiveUS6927006B2Synthetic resin layered productsElectrographic process apparatusPolyimide substrateFluorocarbon
A fuser member having a polyimide substrate, and thereover, an outer layer with from about 61 to about 99 volume percent fluorocarbon.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Flexible substrate, flexible AMOLED (Active Matrix/Organic Light Emitting Diode) and flexible PMOLED (Passive Matrix/Organic Light Emitting Diode)
InactiveCN102223760AHigh transparencyExcellent water and oxygen barrier propertiesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPolyimide substrateActive matrix
The invention discloses a flexible substrate, which comprises a polyimide substrate, wherein an inorganic layer is arranged on the polyimide substrate and is provided with at least one polyimide layer; and inorganic layers are also respectively arranged on the polyimide layers. The inorganic layers and the PI (Polyimide) layers form an alternating structure; the PI layers have favorable transparency and play a role of flattening; and the inorganic layers have excellent performances for resisting water and oxygen, and the like, so that the flexible substrate has the advantages of favorable flatting performance, low water and oxygen transmissivity, strong adhesion property, and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN DANBANG INVESTMENT GROUP
Adhesive for bonding polyimide resins
ActiveUS20120321879A1Film/foil adhesivesSynthetic resin layered productsPolyimide substratePolymer science
One embodiment relates to an, article and a method for producing an article including a plurality of substrates, and an adhesive bonded between at least two of the plurality of substrates. The adhesive can include a polycarbonate copolymer that includes reacted resorcinol, siloxane, and bisphenol-A. Another embodiment relates to an article having a first polyimide substrate, a second polyimide substrate, and an adhesive bonded between the first substrate and the second substrate. The article can have a 2 minute integrated heat release rate of less than or equal to 65 kilowatt−minutes per square meter (kW−min / m2) and a peak heat release rate of less than 65 kilowatts per square meter (kW / m2) as measured using the method of FAR F25.4, in accordance with Federal Aviation Regulation FAR 25.853(d).
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
Light activatable polyimide compositions for receiving selective metalization, and methods and compositions related thereto
InactiveUS20060083939A1Material nanotechnologySynthetic resin layered productsPolyimide substrateElectrically conductive
The present invention relates generally to polyimide composites having dispersed in the polyimide base matrix, useful spinel crystal fillers wherein the composite has a visible-to-infrared light extinction coefficient between and including 0.05 and 0.60 microns−1. The composite polyimides formed therefrom are typically used to make circuits having fine electrically conductive pathways adjacent to the polyimide substrate. These fine electrically conductive pathways are typically formed on the substrate using an electro-less metal plating step. First, the surface of the polyimide composite is light activated, typically by using a laser beam, then the light activated portions are plated to form thin lines, or pathways, on the film's surface.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Flexible impact sensors and methods of making same
InactiveUS20100126273A1Cost-effectiveEasy to processAcceleration measurement using interia forcesVacuum evaporation coatingPolyimide substrateNanoparticle
Flexible impact sensors are provided which are constructed of flexible polyimide substrate, electrodes and a pressure-sensitive electrically conductive polymer composite layer having conductive nanoparticles. Dual-purpose impact and temperature sensors are also described. Methods of making flexible impact sensors are disclosed.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Polyimide substrate bonded to other substrate
InactiveUS20100035052A1Securely holdLamination ancillary operationsDecorative surface effectsAdhesivePliability
Polyimide substrates are bonded to germanium wafers having an epitaxially grown III-V layer and a metal layer. The polyimide substrate and the Ge wafer are subsequently thinned by grinding and etching to reach a final thickness of 25 μms Ge on 25 μms adhesive layer on 50 μms polyimide substrate. The choice of adhesive is of paramount importance. There are several requirements for the adhesive layer to act as a permanent carrier of the thin fragile multijunction solar cell. The adhesive must remain flexible after curing and have a low CTE. It is desired to use an adhesive that cures without the addition of heat, preferably at room temperature. Furthermore, the adhesive layer should have a uniform thickness preferably less than 25 μms (1 mil) and be void-free. It is desired to use a clear adhesive which does not contain any particles in order to obtain a smooth uniform void-free bondline. However, clear adhesives have CTE's that are larger than 80 ppm / ° C. and which can be as high as 200 ppm / ° C. or more above the glass transition temperature. This is especially problematic for hard adhesives. The ideal adhesive is applied at room temperature but must withstand up to 250° C. during post-bond metallization of the front side of the solar cell. Another important parameter, which affects the ability to spread a liquid adhesive over a 4″ area is the viscosity. Some adhesives, like paste, may have favorable properties but are too thick to spread evenly over a 4″ wafer. Ideally the adhesive is applied either by spinning or spraying. These represent a set of conflicting requirements. There is not one adhesive that has all the desired properties. A thin bonded wafer is demonstrated which has an epi-layer and a metal layer.
Owner:FARAH JOHN
Polymide substrate bonded to other substrate
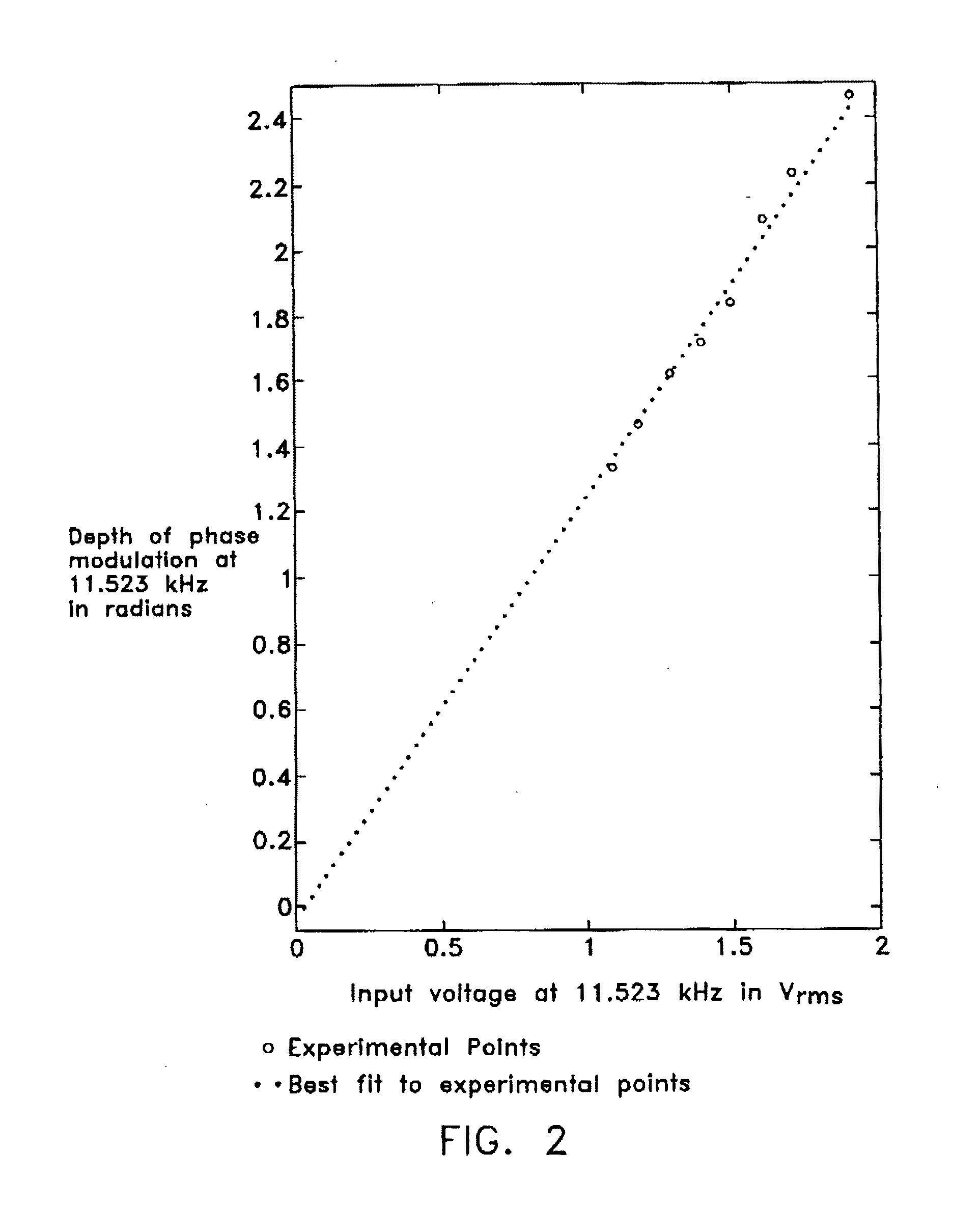
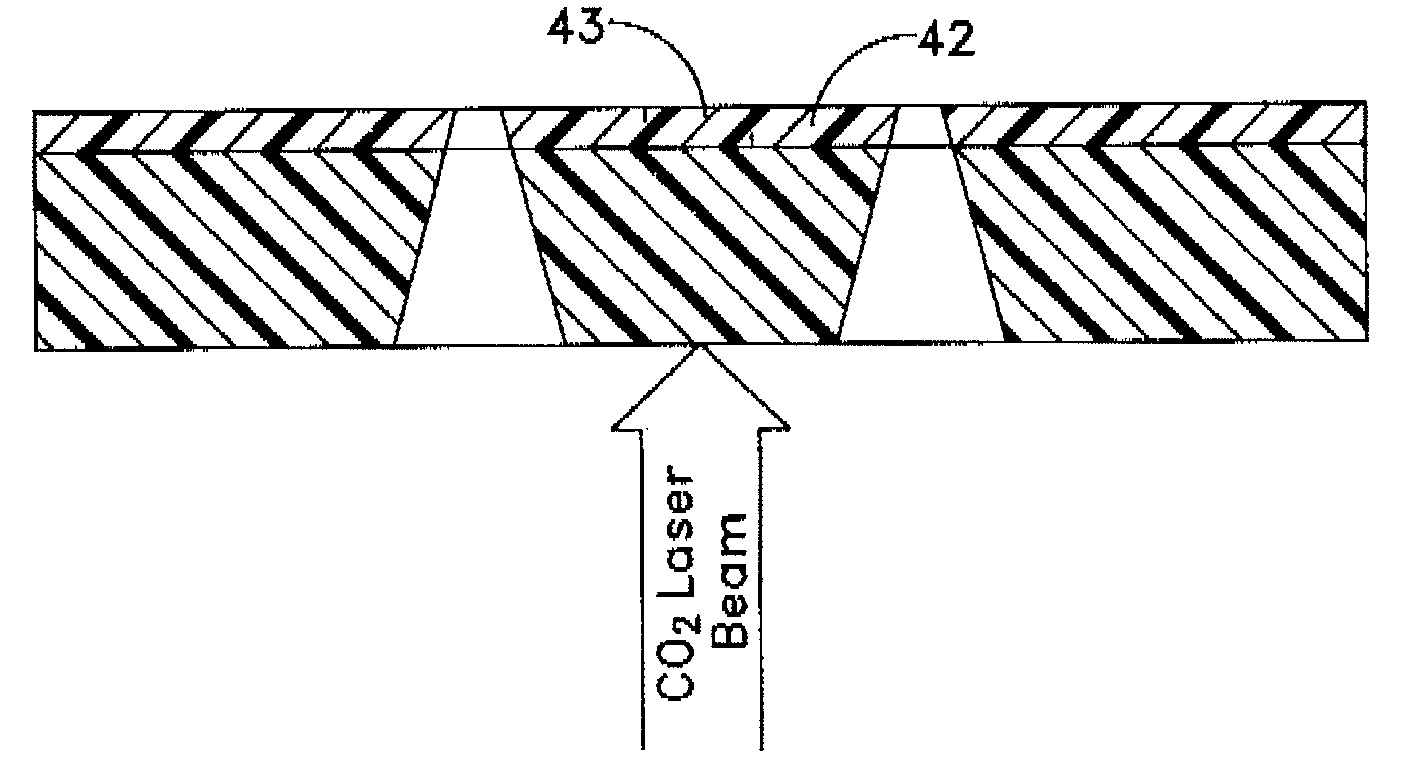
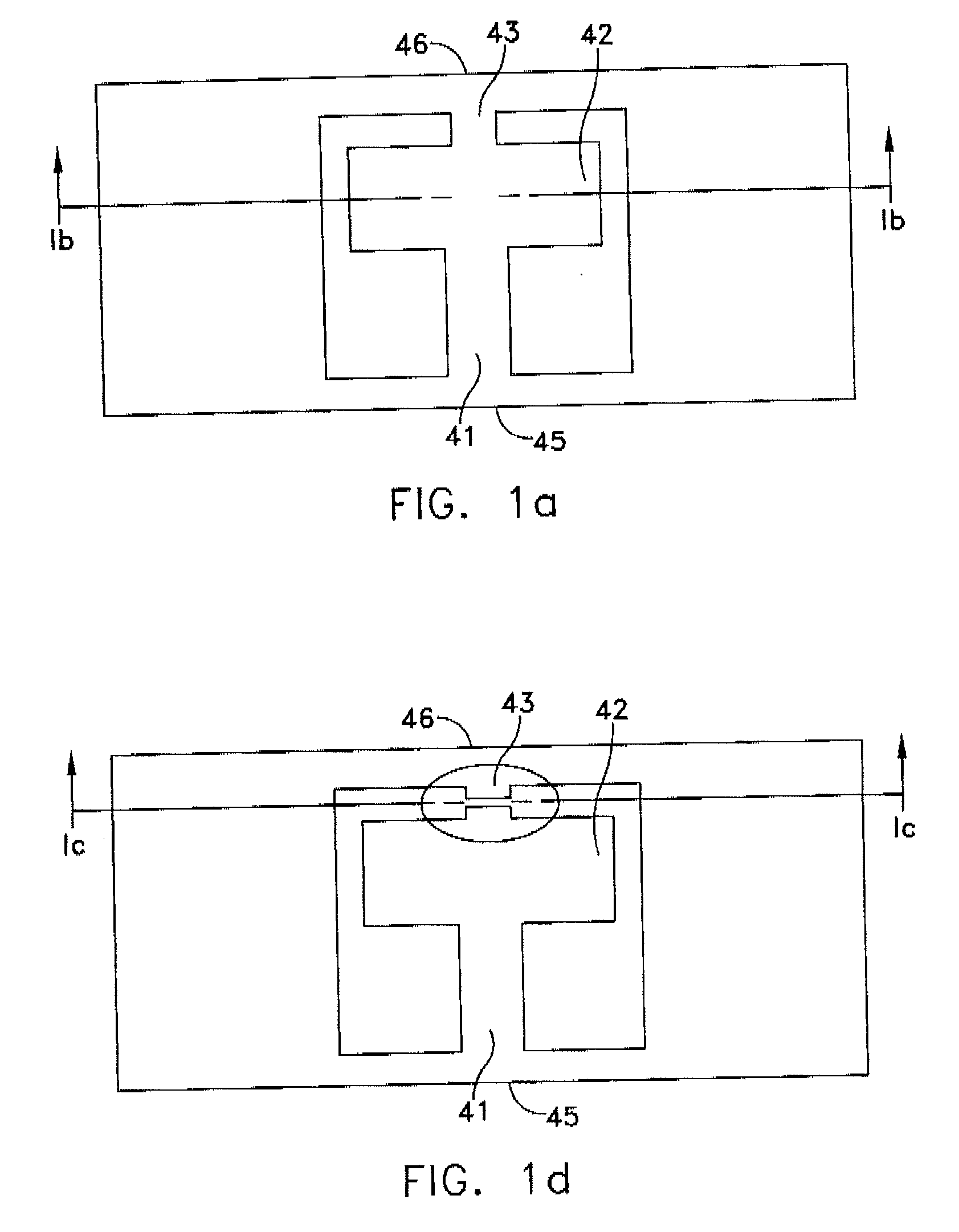
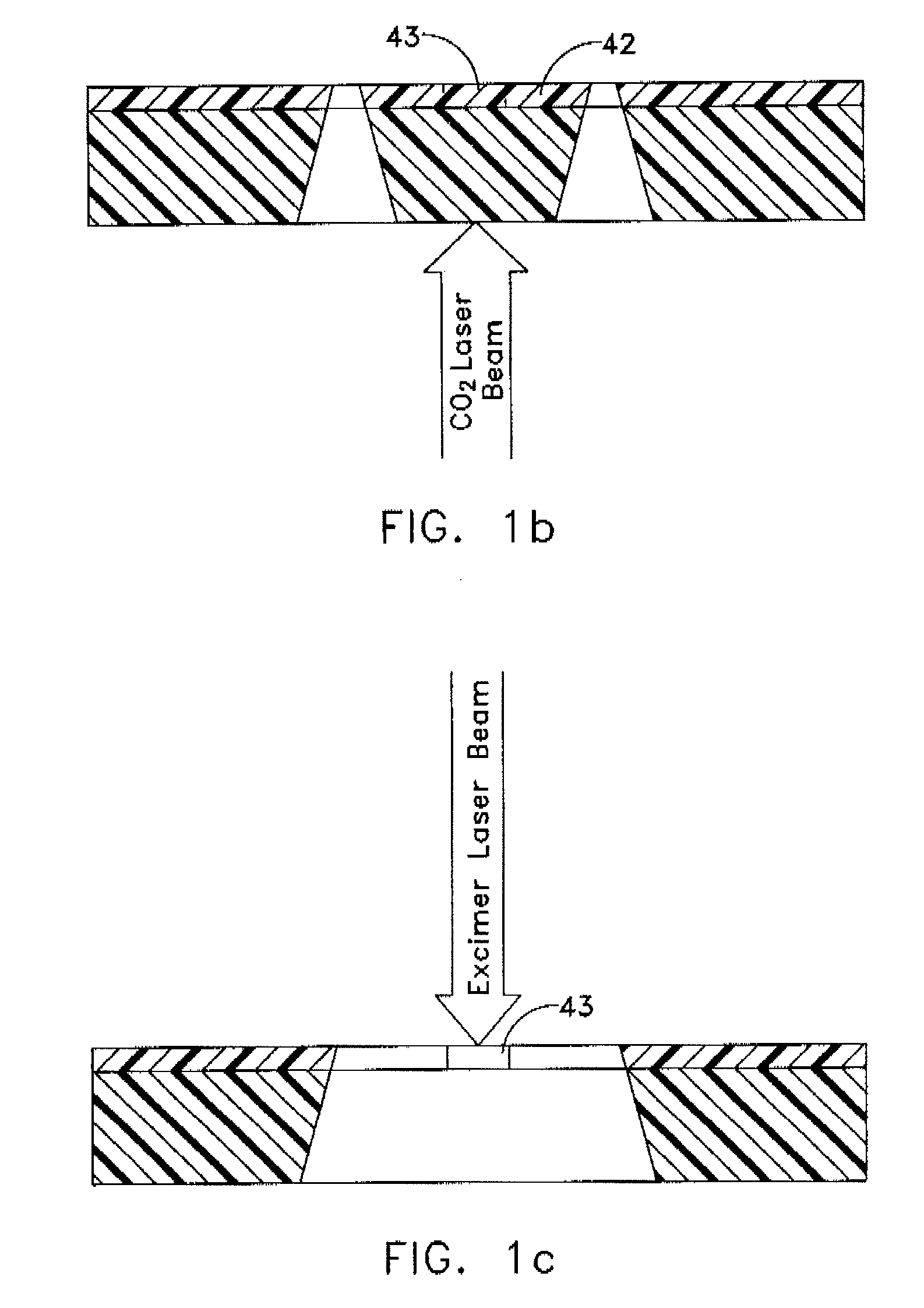
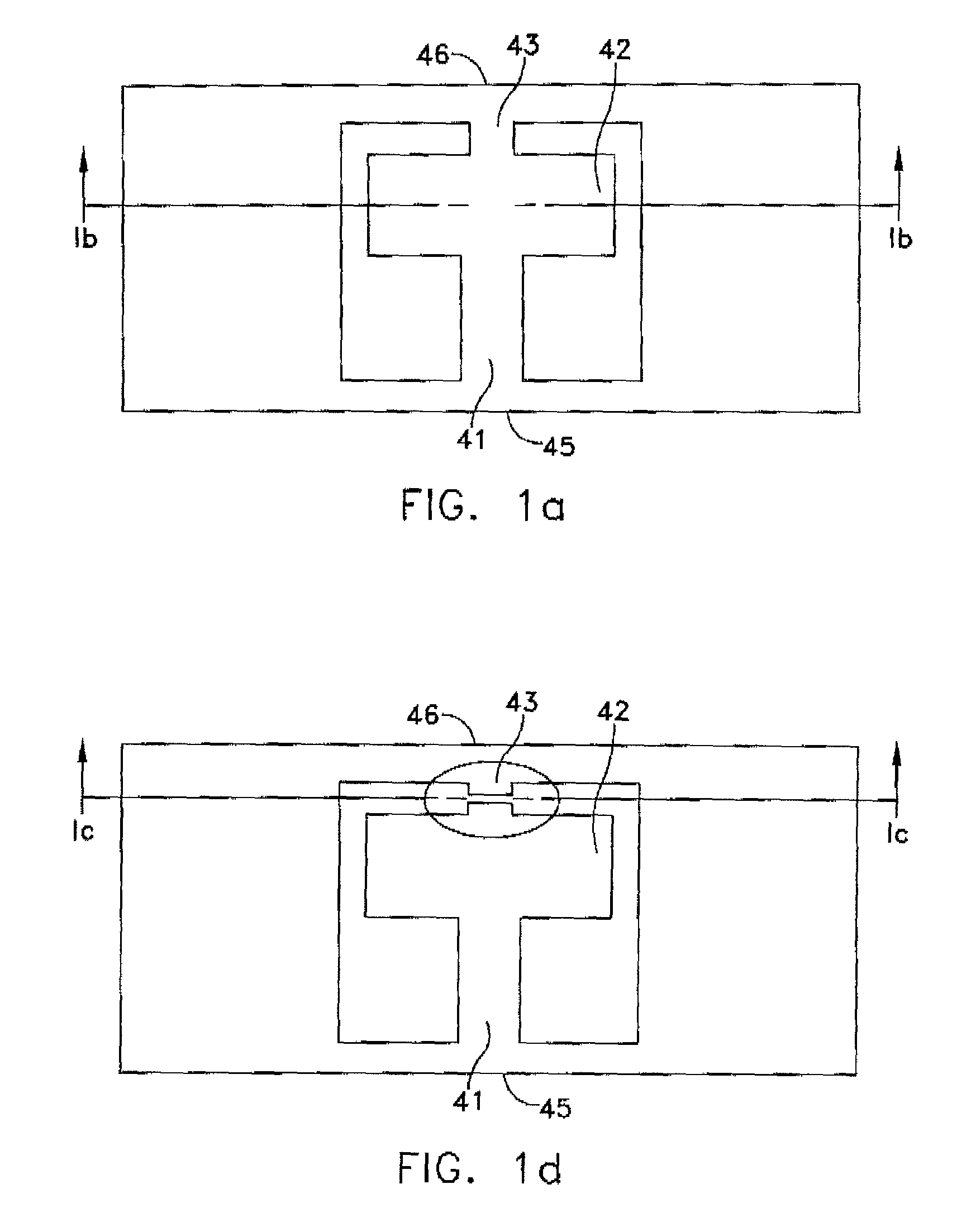
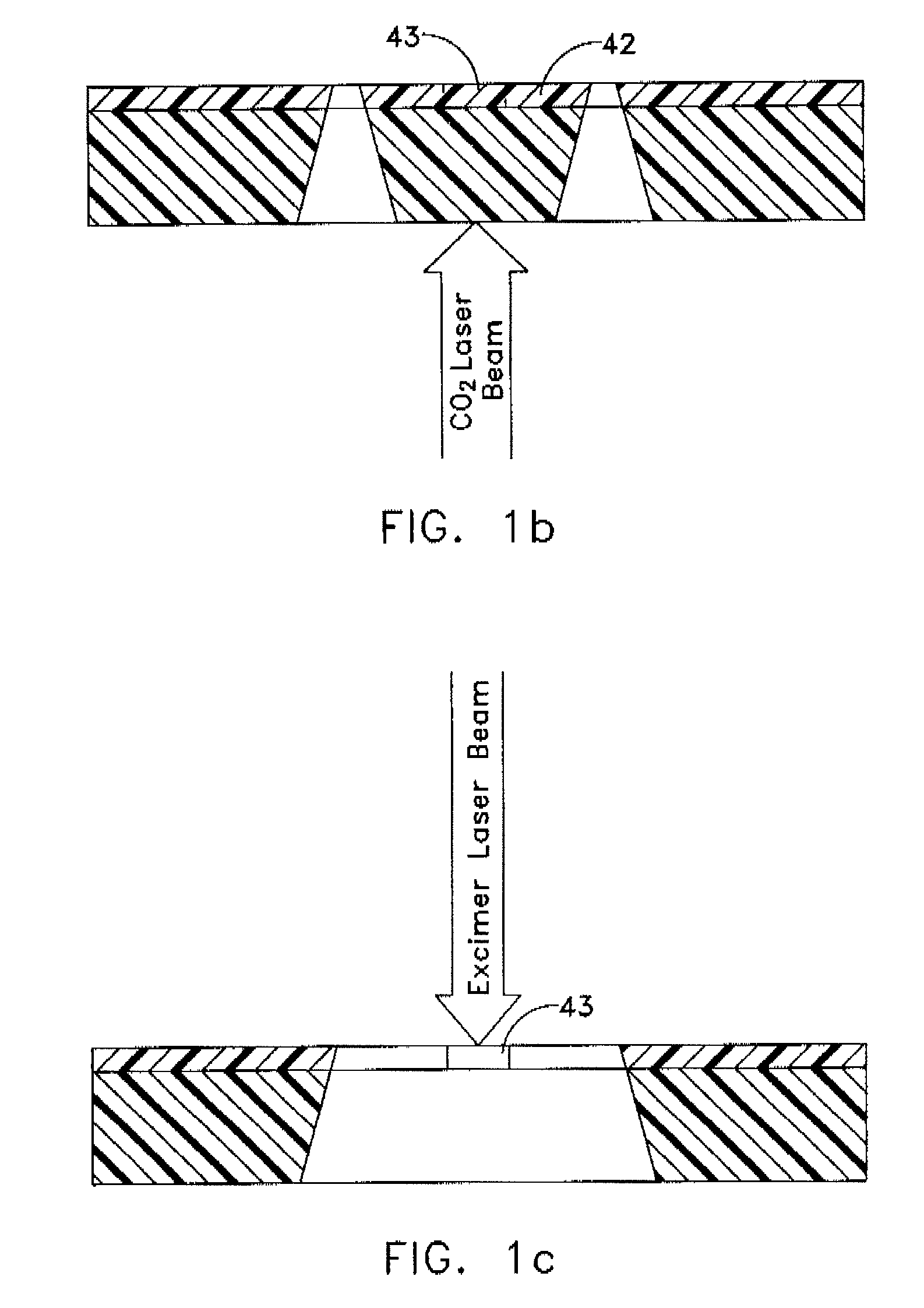
Polyimide substrates, and polymer laminates for optical and electronic applications are described. Single or multi-layer waveguide structures are deposited on the polyimide substrates. Laminates including polymer or a hybrid organic / inorganic waveguiding film can be deposited on a polished polyimide substrate. The laminate can also include piezoelectric and metallic layers. Micromachined optical devices, such as cantilevered waveguide are fabricated by laser ablation using a combination of IR and UV lasers. A fiber-to-waveguide coupler with a laser-machined groove for holding the fiber is also disclosed. Holes are drilled with excimer and YAG laser in the polyimide substrate and metallized to provide continuous electrical contact between both sides of the substrate. Metallized polyimide substrates are bumped and stacked to provide high density interconnects. The polyimide substrate is bonded to a semiconductor wafer. Thin SOI or epitaxially grown layer with devices is transferred to the polyimide substrate by grinding and etching the semiconductor wafer.
Owner:FARAH JOHN
Flexible temperature differential power generation micro-unit structure
InactiveCN103178754AFlexibleAvoid failureGenerators/motorsThermoelectric devicesPolyimide substrateMicro devices
The invention discloses a flexible temperature differential power generation micro-unit structure. The flexible temperature differential power generation micro-unit structure is characterized in that a plurality of insulating hard films which are equidistantly distributed to form a layer are deposited on the upper surface of a polyimide substrate, a P-type film thermoelectric arm and an N-type film thermoelectric arm which are parallel to each other are respectively arranged on two upper sides of each insulating hard film, the length and the width of each P-type film thermoelectric arm are equal to those of each N-type film thermoelectric arm, one end of each P-type film thermoelectric arm is connected with one end of the corresponding N-type film thermoelectric arm by a conducting wire, the other end of each P-type film thermoelectric arm is connected with the other end of the adjacent front N-type film thermoelectric arm by a conducting wire, the other end of each N-type film thermoelectric arm is connected with the other end of the adjacent rear P-type film thermoelectric arm, and the same procedure is sequentially repeatedly carried out, so that the flexible temperature differential power generation micro-unit structure is formed. The flexible temperature differential power generation micro-unit structure has the advantages that the flexible temperature differential power generation micro-unit structure is flexible and can deform in multiple directions, the insulating hard films can prevent bismuth telluride thermoelectric materials with poor ductility from being broken when a temperature differential power generation unit structurally deforms, and failure is prevented; and the flexible temperature differential power generation micro-unit structure is mainly used for supplying power for implanted medical micro-devices, and has popularization and application value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
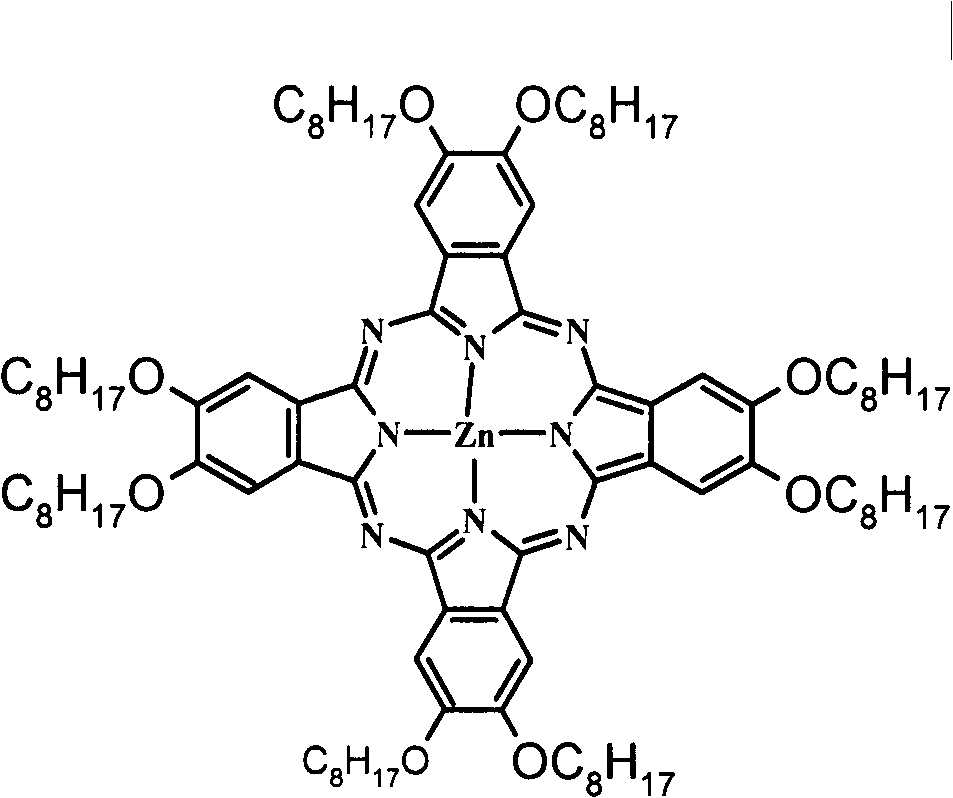
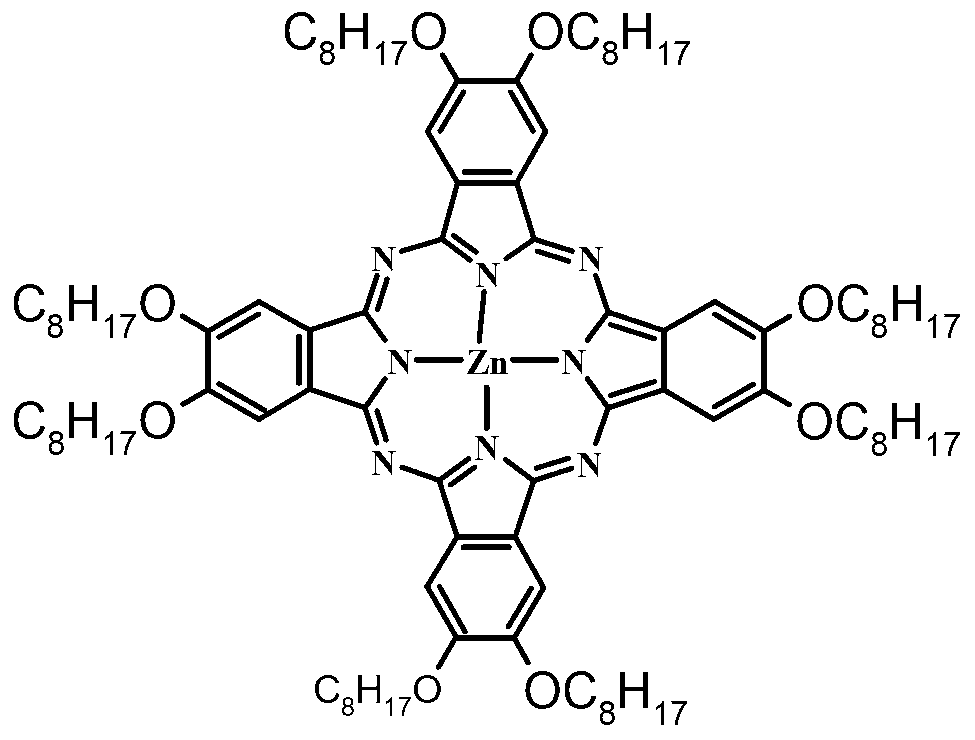
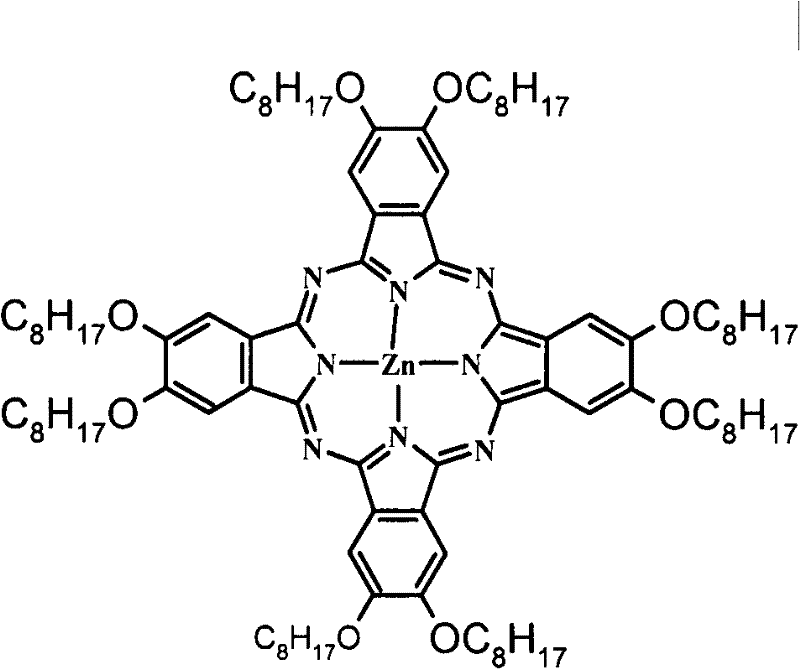
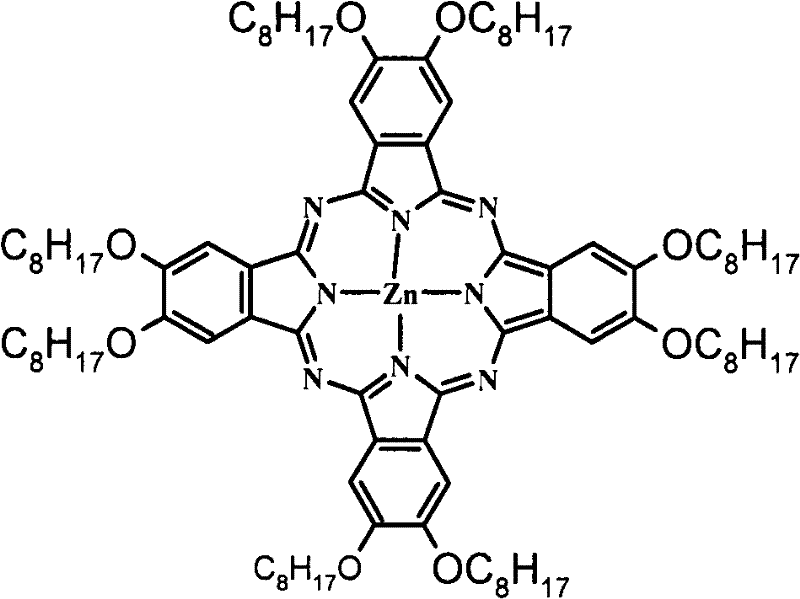
Application of zinc phthalocyanine complex as ink in micro-contact printing
InactiveCN102516841BReduce bloatReduce distortionInksOther printing apparatusMicrocontact printingPolyimide substrate
The invention discloses application of a zinc phthalocyanine complex as ink in micro-contact printing. The 2-propyl alcohol solution of 8(Octanohydroxamic)-zinc phthalocyanine serves as micro-contact printing ink; the pattern of a Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) seal is transferred to the surface of carboxylation polyethylene terephthalate, polyethylene naphthalate or polyimide substrate; and a delicate metal pattern is obtained on the substrate with a chemical plating method. The application of the zinc phthalocyanine complex as the ink in the micro-contact printing has the beneficial effect that the common phenomena of pattern inflation and pattern torsion in the micro-contact printing can be reduced by the phthalocyanine metal complex ink, and the phthalocyanine metal complex ink has a lowpreparation cost and great potential in the industrial application and is stable.
Owner:GUANGXI TEACHERS EDUCATION UNIV
Manufacturing method of resistance strain gage based on ion beam technology
InactiveCN101614522ASimple processImprove yieldDecorative surface effectsPhotomechanical apparatusPolyimide substrateSputtering
The invention relates to a manufacturing method of a resistance strain gage based on an ion beam technology. The method comprises the following steps: coating polyimide glue solution on the surface of a high temperature silicon rubber substrate by adopting a DC plasma sputtering technology and a plasma etching technology, hot solidifying the polyimide glue solution to form a flexible polyimide substrate, then peeling off, solidifying to obtain a flexible substrate film with needed strain property requirement, sputtering a resistance alloy film on the polyimide surface of the flexible substrate and finally manufacturing the resistance strain gage by a photoengraving and etching process. The invention has simple process, high rate of finished products, controllable components of the resistance alloy film, adjustable alloy components as required, high image resolution, favorable property of manufactured material, and the like.
Owner:SHAANXI ELECTRICAL APPLIANCE RES INST
Copper-alloy foil to be used for laminate sheet
InactiveUS20020155021A1Improve adhesionImprove surface roughnessSynthetic resin layered productsPrinted circuit aspectsPolyimide substrateSurface roughness
A copper alloy foil to be used in a printed board comprising a polyimide substrate is provided. The copper foil is not subjected to roughening plating and has hence fine surface roughness and can be directly bonded with the polyimide substrate. The copper alloy contains (a) one or more of the additive elements of from 0.01 to 2.0% of Cr and from 0.01 to 1.0% of Zr, or (b) from 1.0 to 4.8% of Ni and from 0.2 to 1.4% of Si. The surface roughness in terms of the ten-point average surface-roughness (Rz) is 2 mum or less, the 180° peeling strength is 8.0 N / cm or more. The alloy (a) has 600 N / mm2 or more of tensile strength, and 50% ICAS or more of electric conductivity. The alloy (b) has 650 N / mm2 or more of tensile strength, and 50% ICAS or more of electric conductivity.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CO LTD
Epoxy primer layer for fuser belts
InactiveUS20070026226A1High glossFacilitated releaseSynthetic resin layered productsRecord information storageEpoxyPolyimide substrate
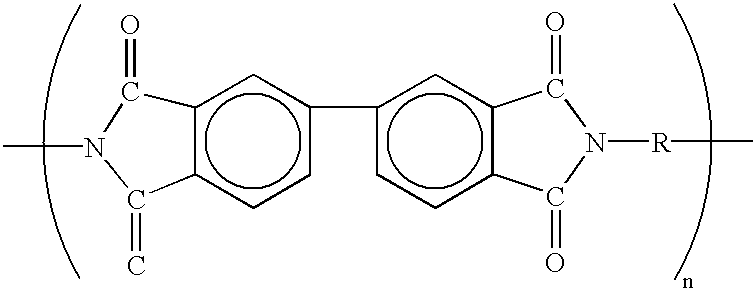
A fuser belt comprising in order a substrate comprising a polyimide substrate, an epoxy primer layer comprising an epoxy resin having the following structure: where R1 and R2 are each independently H or an alkyl group containing 1 to about 4 carbon atoms, and R3 and R4 are each independently H, F, or an alkyl group containing 1 to about 4 carbon atoms, Z is a carbonyl cross-linking group, and x is an integer from 1 to about 10 and said epoxy priming layer also comprising an anhydride crosslinking agent cyclic mono anhydride or dianhydride having the following structure: and mixture thereof where R is an alkyl group containing 6 to about 8 carbon atoms and a toner release layer comprising a silsesquioxane.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
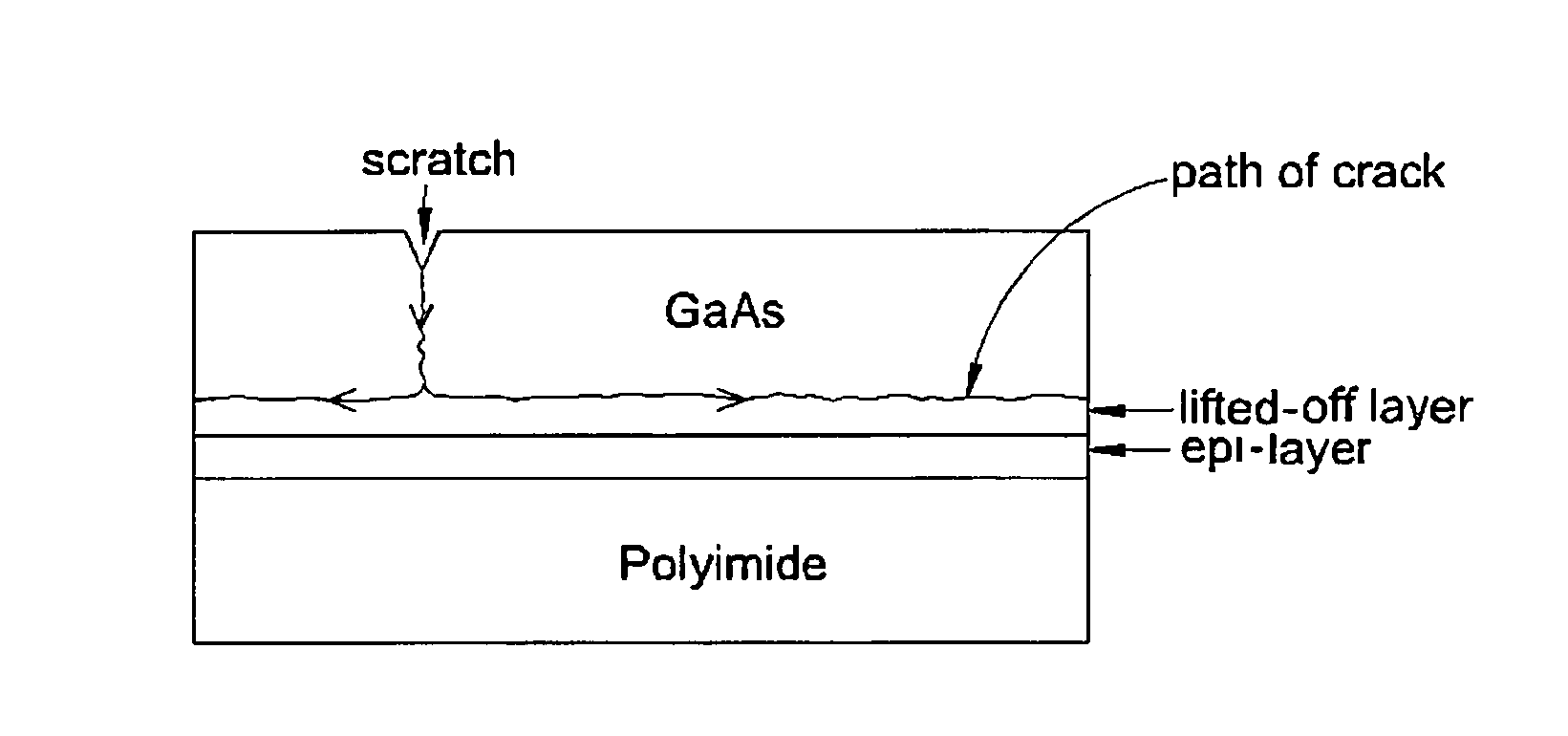
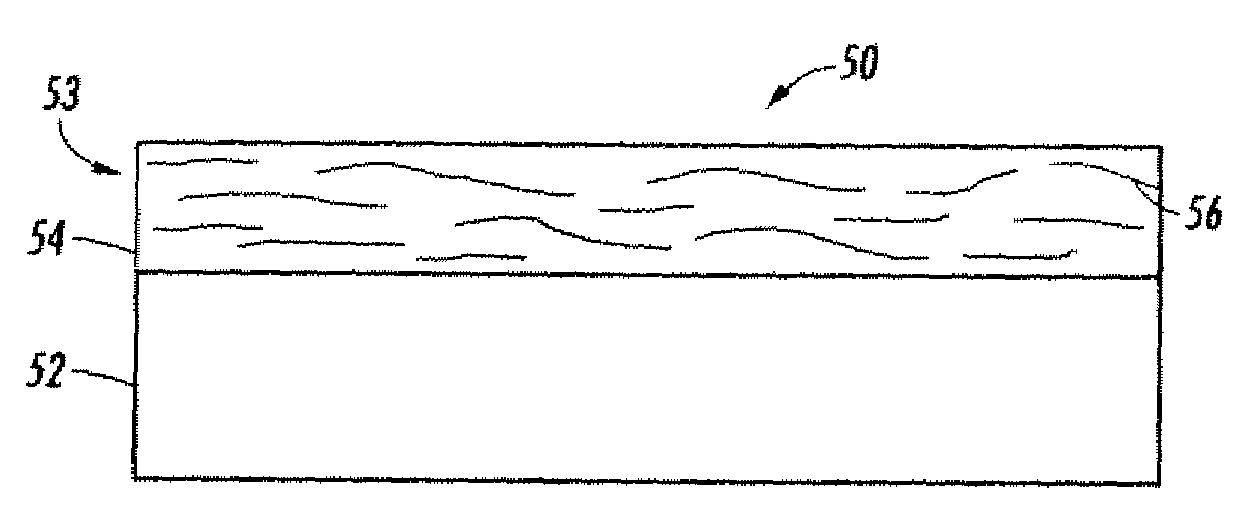
Rapid Thinning of GaN and SiC Substrates and Dry Epitaxial Lift-off
InactiveUS20150258769A1Minimize post lift-off polishingAvoid wasting substrate materialPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsEtchingCopper plating
An epitaxially grown layer III-V solar cell is separated from the growth substrate by propagating a crack close to the epi / wafer interface. The crack is driven by the elastic strain energy built up due to thermal stresses between GaAs and polyimide by cooling below room temperature. A GaAs wafer is bonded to a polyimide substrate on the epi-side and scribed on the opposite side. The crack is initiated from the scratch and guided along the interface using an epitaxially grown sacrificial layer with lower fracture toughness under the solar cell. No expensive ion implantation or lateral chemical etching of a sacrificial layer is needed. The active layer is transferred wafer-scale to inexpensive, flexible, organic substrate. The process allows re-using of the wafer to grow new cells, resulting in savings in raw materials and grinding and etching costs amounting to up to 30% of the cost of the cell. Several cells are integrated on a common blanket polyimide sheet and interconnected by copper plating. The blanket is covered with a transparent spray-on polyimide that replaces the cover glass. The solar cell is stress-balanced to remain flat on orbit.Wide bandgap materials, such as Gallium Nitride (GaN) and Silicon Carbide (SiC) are very promising for light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and power electronics. These materials are extremely hard and difficult to machine and very expensive. The lack of good quality bulk GaN substrates with a smooth surface at a reasonable price is hampering the development of vertical devices.A rapid thinning technique is presented by lifting-off a 20-70 μm thick layer from the surface within a fraction of a second, which leaves the surface shiny and smooth. The savings in lapping and polishing add up to 60%, when this technique is incorporated in the crystal manufacturing process. This technology also has application for backside thinning where the savings are even larger.
Owner:FARAH JOHN
Carbon nanotubes for transfer belt applications
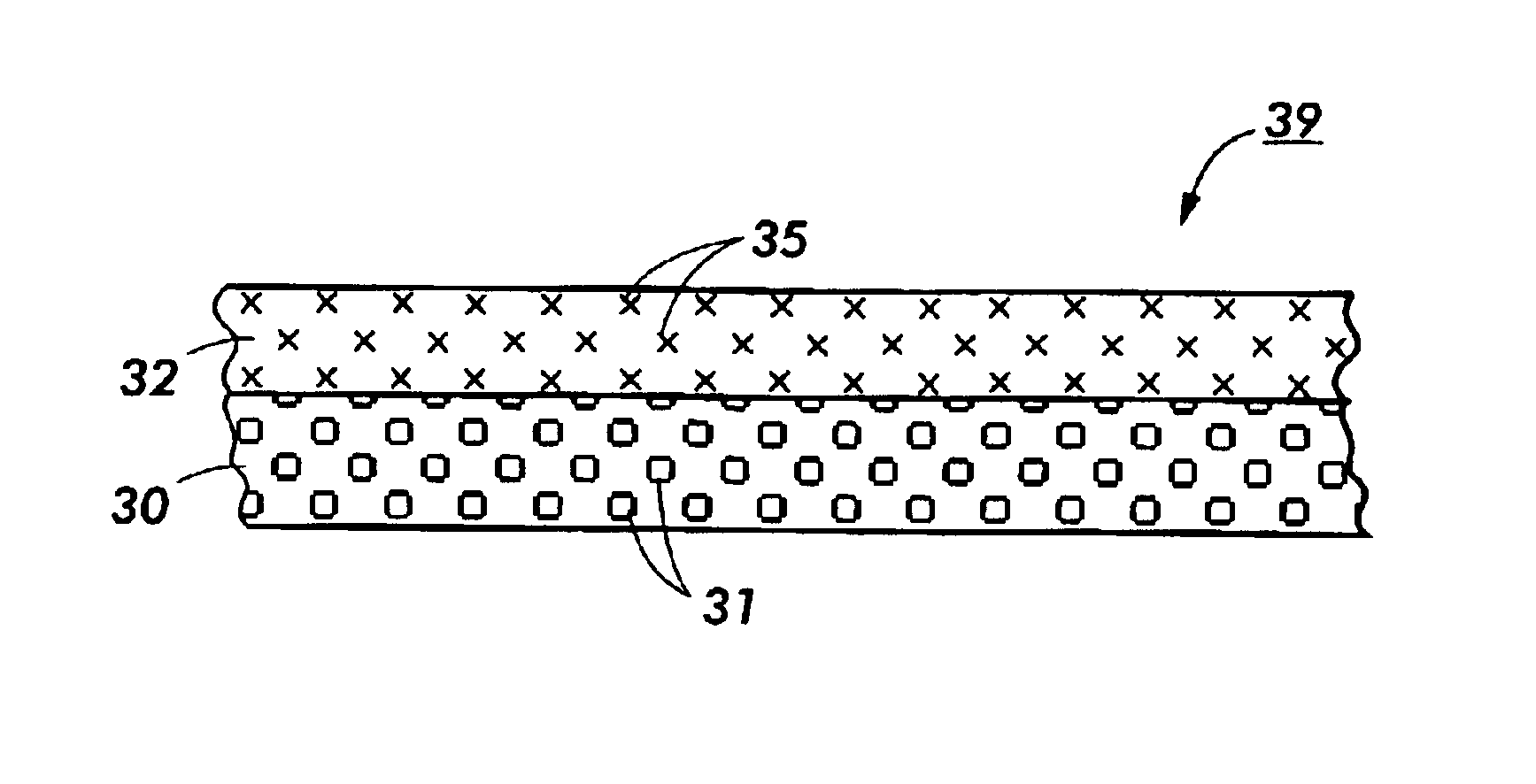
A xerographic transfer member includes a resistive, electrically relaxable, polyimide substrate, and a conformance resistive layer that includes a fluoroelastomer composite. The fluoroelastomer composite includes a cross-linked fluoropolymer, a plurality of carbon nanotubes, and exhibits a resistivity from about 107 ohm-cm to about 1013 ohm-cm.
Owner:XEROX CORP
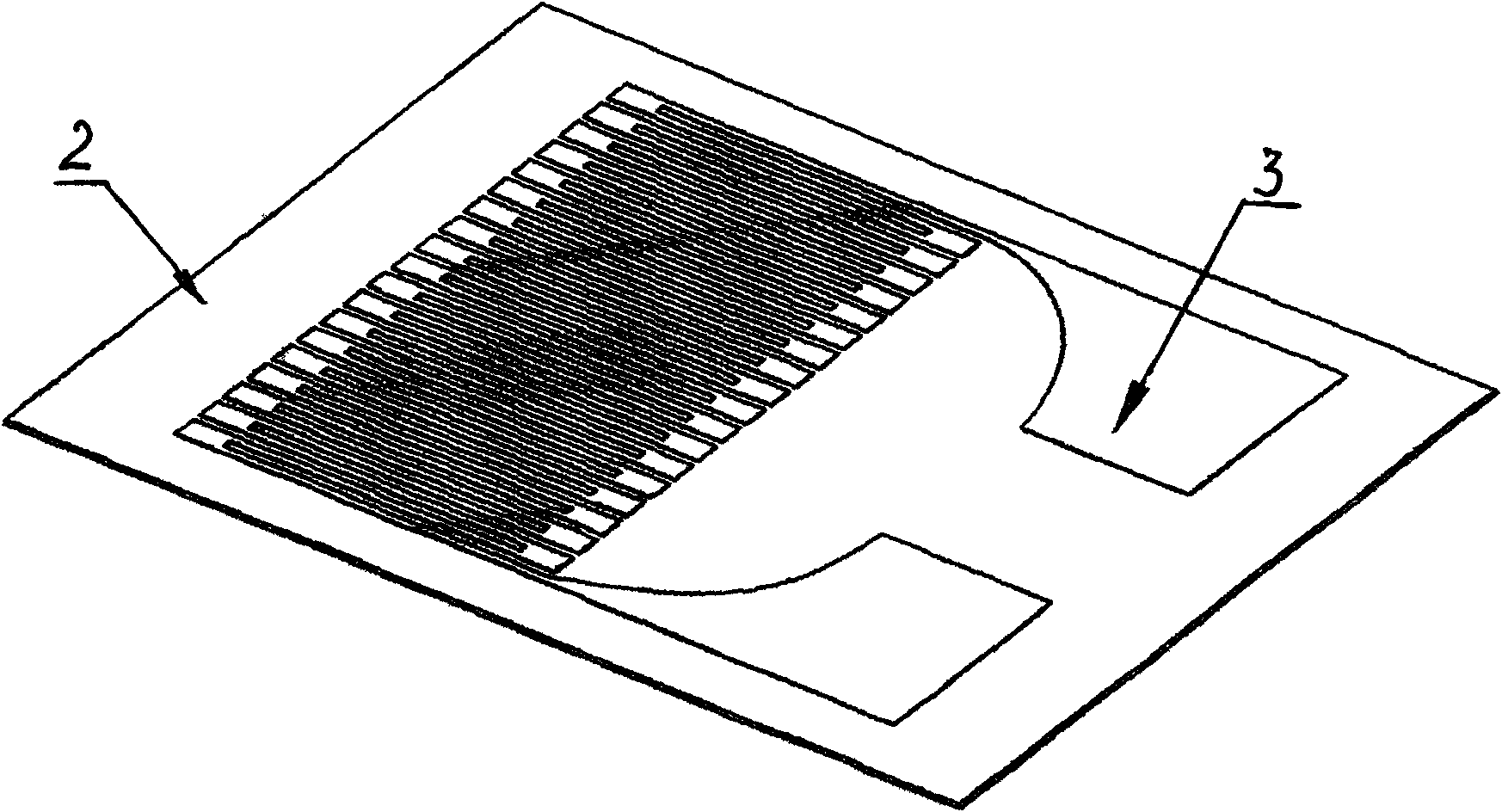
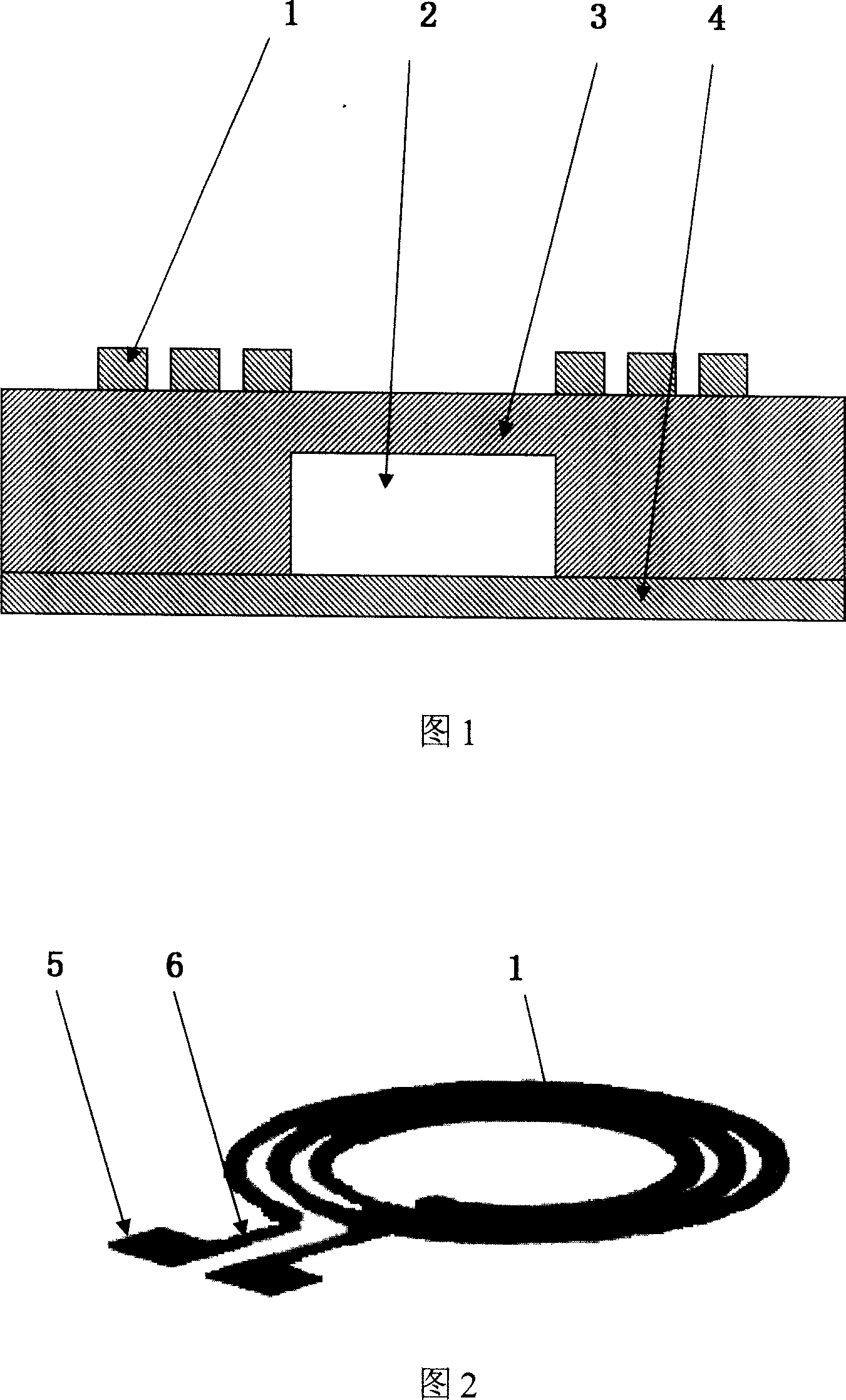
A plane NMR micro-coils micro detector
InactiveCN1971259AHigh sensitivityHigh resolutionAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMeasurements using NMRPolyimide substrateNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
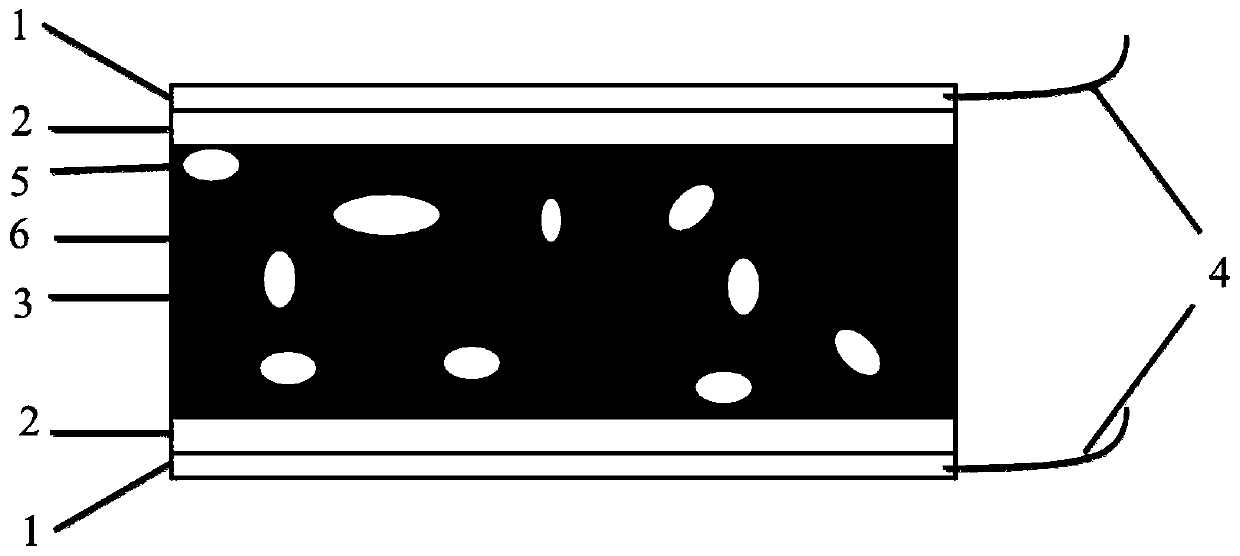
A plane nuclear magnetic resonance micro coil micro detector is disclosed that consists of plane nuclear magnetic resonance micro coil [1] and micro flow channel structure [2]. It adopts the integral design; the plane nuclear magnetic resonance micro coil [1] is processed on the surface of the polyimides substrate [3], the micro flow channel structure [2] is rectangle structure and processed on the other surface of the polyimides substrate [3], it is embedded in the inner of the polyimides substrate [3] which is under the plane nuclear magnetic resonance micro coil [1] by the polyimides slice [4]. When it is working, the plane nuclear magnetic resonance micro coil works as the radio-frequency exciter and the signal receiver at the same time, and actuates the sample to be measured to generate the NMR signal and obtain the NMR wave spectrum. The invention can fulfill the detecting requirements of lossless and real-time, the molecular structure and information of images-structure of detecting sample can be supplied. It can be used in fields of analysis detection of tiny sample, real-time dynamic monitoring of chemical reaction, and biological texture and growth status of cell.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Polymide substrate bonded to other substrate
Polyimide substrates, and polymer laminates for optical and electronic applications are described. Single or multi-layer waveguide structures are deposited on the polyimide substrates. Laminates including polymer or a hybrid organic / inorganic waveguiding film can be deposited on a polished polyimide substrate. The laminate can also include piezoelectric and metallic layers. Micromachined optical devices, such as cantilevered waveguide are fabricated by laser ablation using a combination of IR and UV lasers. A fiber-to-waveguide coupler with a laser-machined groove for holding the fiber is also disclosed. Holes are drilled with excimer and YAG laser in the polyimide substrate and metallized to provide continuous electrical contact between both sides of the substrate. Metallized polyimide substrates are bumped and stacked to provide high density interconnects. The polyimide substrate is bonded to a semiconductor wafer. Thin SOI or epitaxially grown layer with devices is transferred to the polyimide substrate by grinding and etching the semiconductor wafer.
Owner:FARAH JOHN
Composite film based on glassy carbon and graphene and preparation method thereof
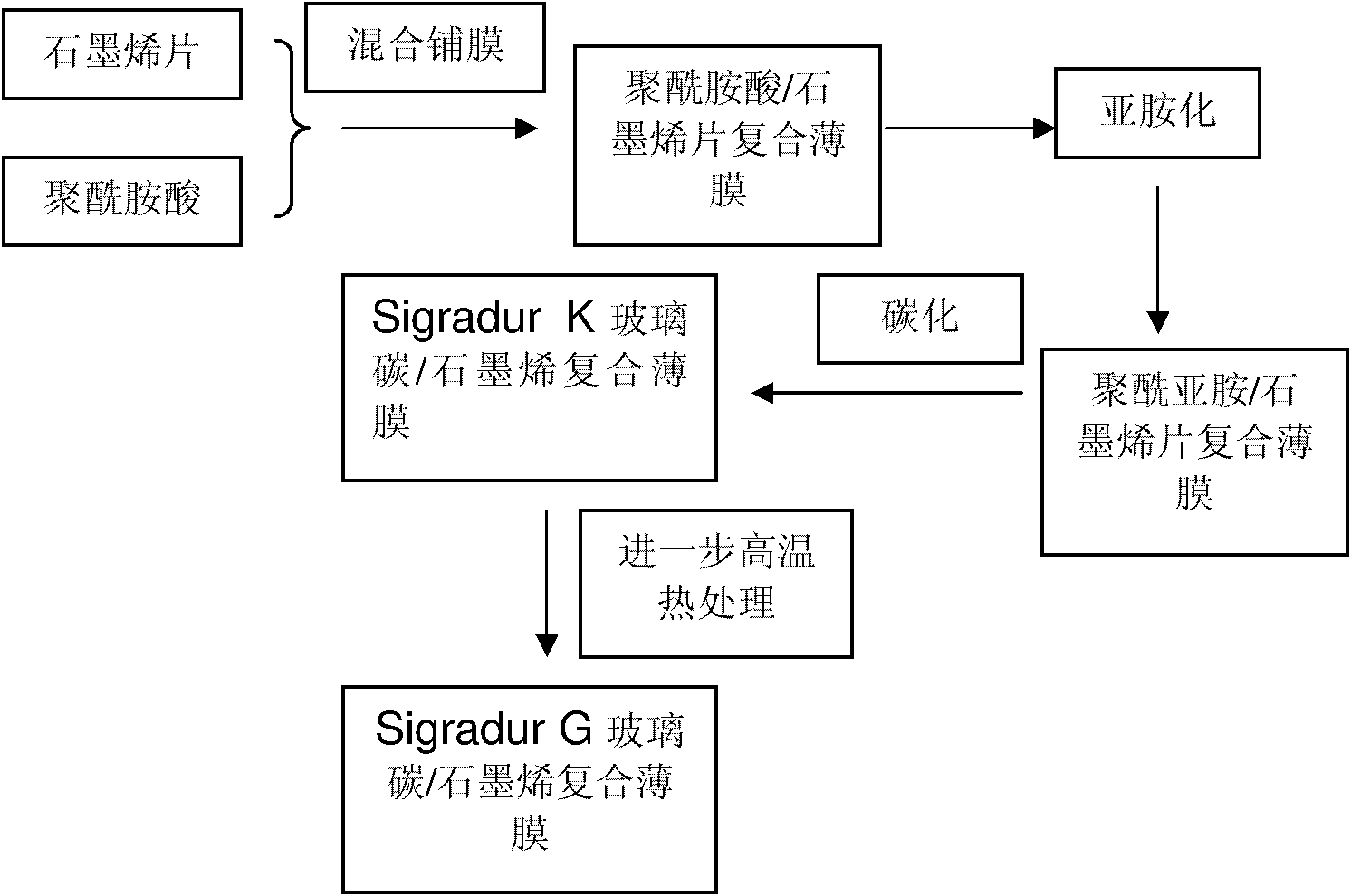
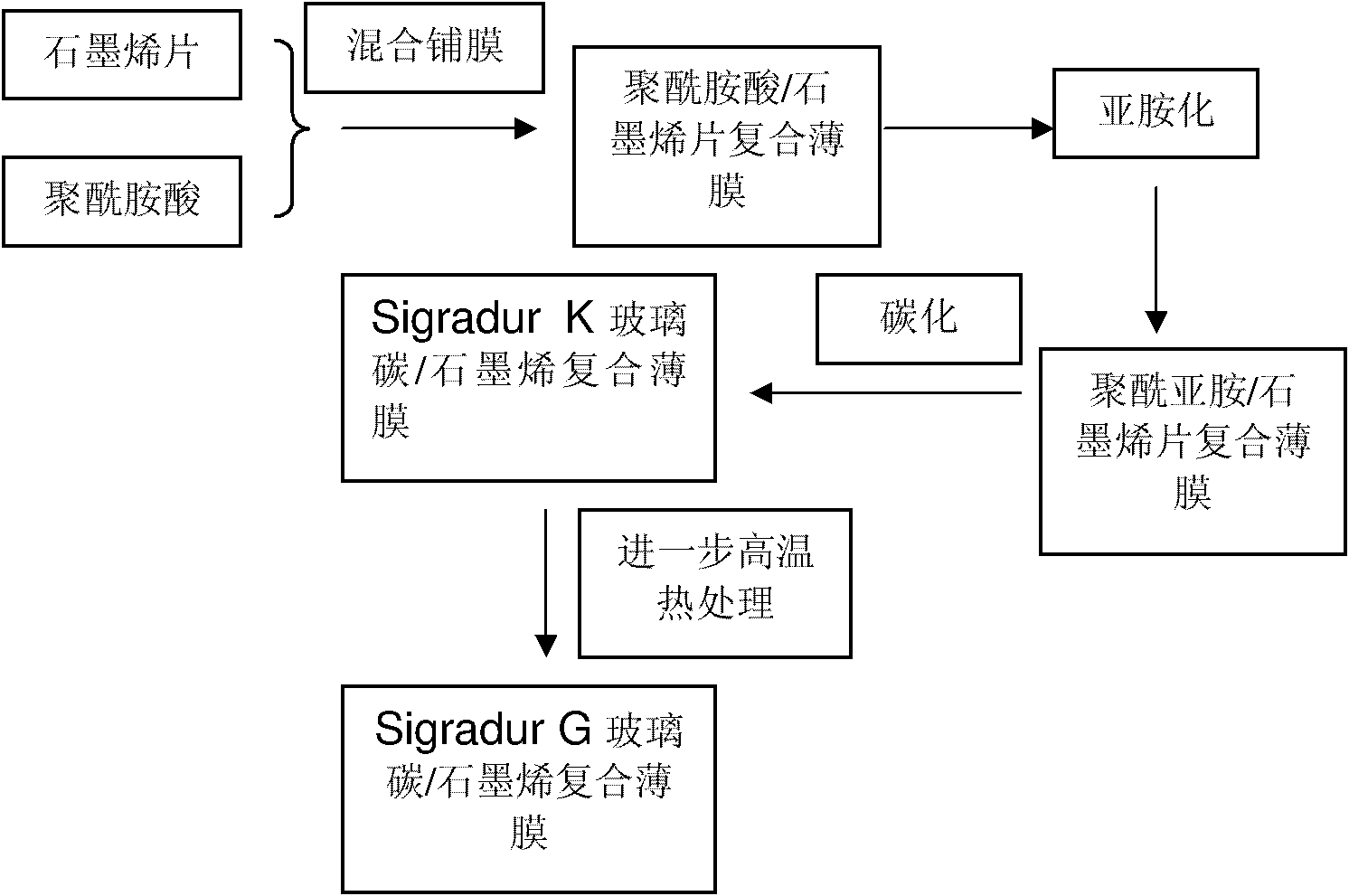
The invention belongs to the technical field of composite materials and relates to a composite film based on glassy carbon and graphene and a preparation method thereof. A composite film precursor comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 0.1 to 50 percent of graphene sheet and 99.9 to 50 percent of polyimide substrate. The preparation method comprises the following step of: carrying out carbonization on a polyimide precursor film at the temperature of less than 2500 DEG C to obtain the composite film based on the glassy carbon and the graphene. The flexural strength of the prepared composite film can reach more than 600MPa.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Manufacturing method of metal-coated polyimide substrate
ActiveCN101350315AReduce dispersionImprove failure rateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingConductive pattern formationPolyimide substrateSurface resistivity
The invention provides a metal faced polyimide base plate manufacturing method capable of reducing the dimensional change dispersibility while heating the metal faced polyimide base plate, jointing stably under the endured heat quantity when used as COF and improving the qualification rate. The method comprises: a sputtering process for forming a metal coat on the polyimide sheet surface and an electroplating process for forming metallic conductor on the obtained metal coat by a continuous electroplating equipment. The invention is characterized in satisfying the (1) and (2) condition: (1) in the sputtering process, the surface resistivity of the formed metal coat is kept between 0.1 / m2 and 1.0 / m2; (2) in the electroplating process, the average cathode current density of all the electroplating bath is controlled between 1A / dm2 and 3A / dm2, and the ratio of the maximum of the cathode current density of all the electroplating bath to the minimum of that is controlled between 1 and 5, while the sheet conveying velocity is adjusted to 80-300m / h.
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL MINING CO LTD
Force sensing resistor (FSR) with polyimide substrate, systems, and methods thereof
ActiveUS20180272232A1Input/output for user-computer interactionVideo gamesPolyimide substrateElectrical resistance and conductance
A force sensing resistor (FSR) that is constructed with a first substrate made of polyimide disposed underneath a second substrate that is resistive and flexible. A handheld controller for an electronic system may include the FSR having a first substrate made of polyimide. The FSR may be mounted on a planar surface of a structure within the controller body, such as a structure mounted within a handle of the controller body, and / or a structure that is mounted underneath at least one thumb-operated control that is included on a head of the controller body. The FSR may be configured to measure a resistance value that corresponds to an amount of force applied to an outer surface of the handle and / or an amount of force applied to the at least one thumb-operated control.
Owner:VALVE
Device capable of thermally cooling while electrically insulating
InactiveUS20090229809A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSynthetic resin layered productsPolyimide substrateAcrylic polymer
The present disclosure relates to a device for thermally cooling while electrically insulating. The device contains a first adhesive layer, polyimide substrate, a second adhesive layer and a heat sink. The first adhesive layer and the second adhesive layer are a vinyl or acrylic polymer. The polyimide substrate has at least two polyimide layers. The polyimide layers are derived from at least one aromatic dianhydride and at least one aromatic diamine. The adhesive layers and the polyimide layers may contain thermally conductive fillers, light absorbing pigments or mixtures of both.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
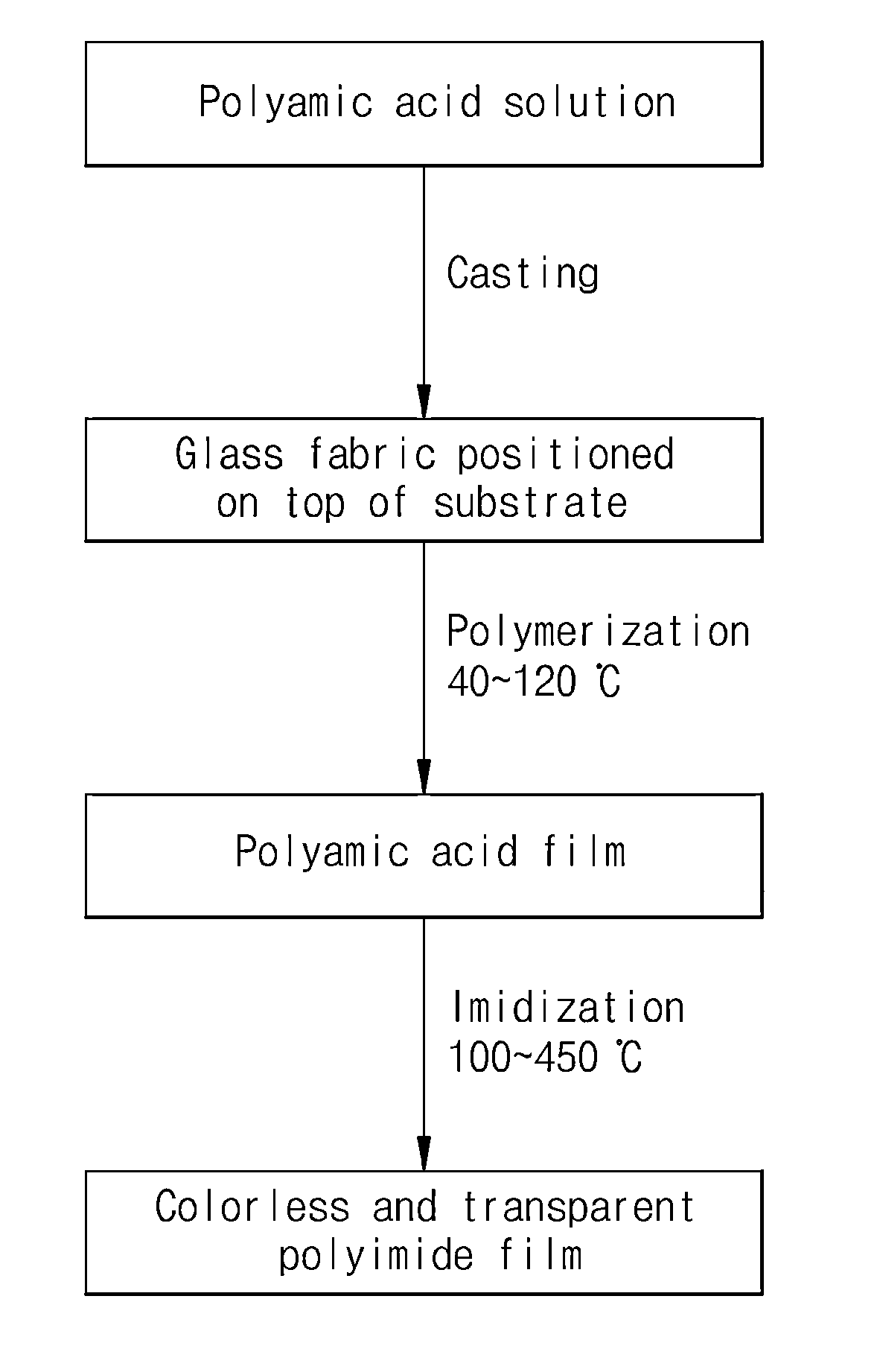
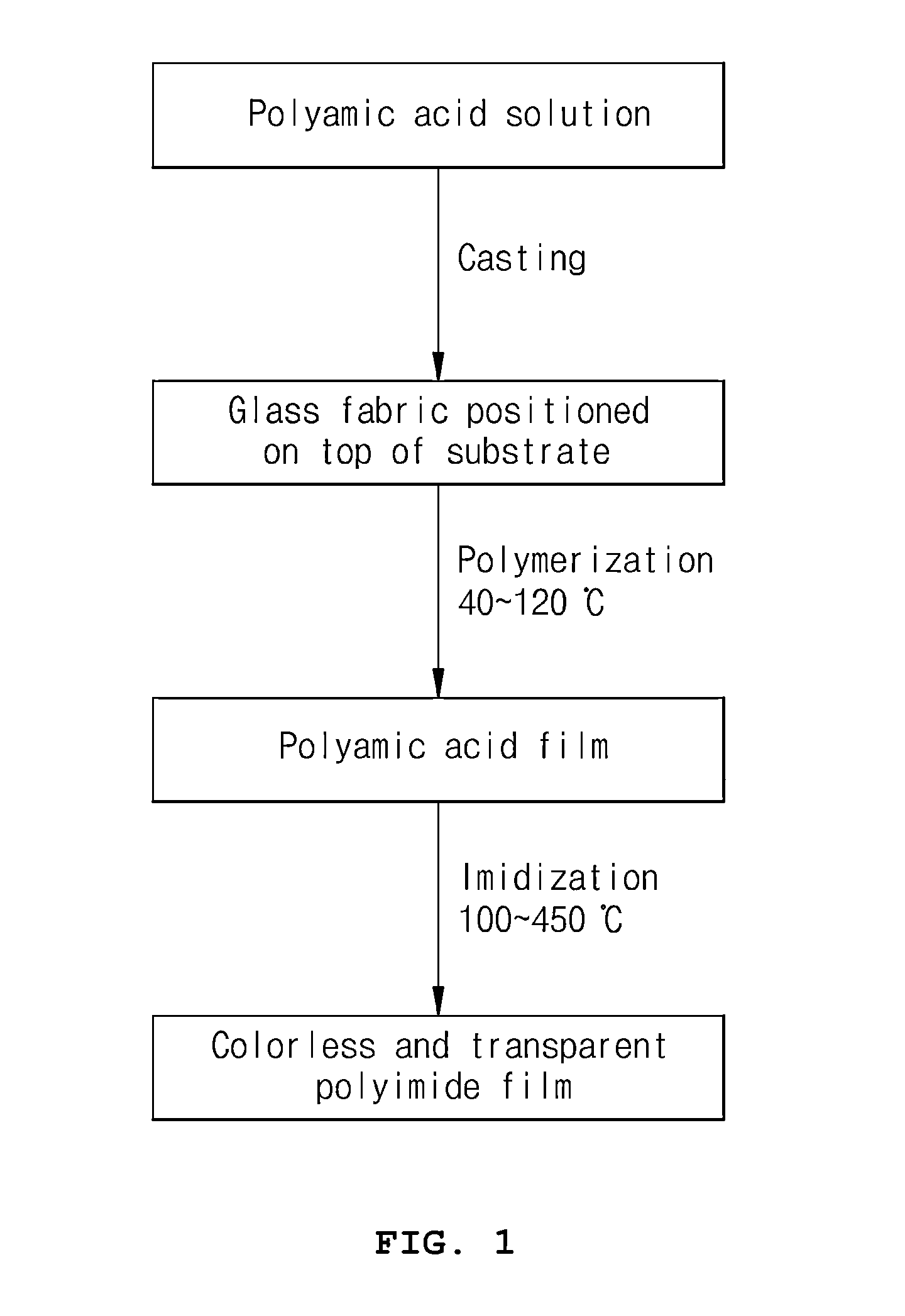
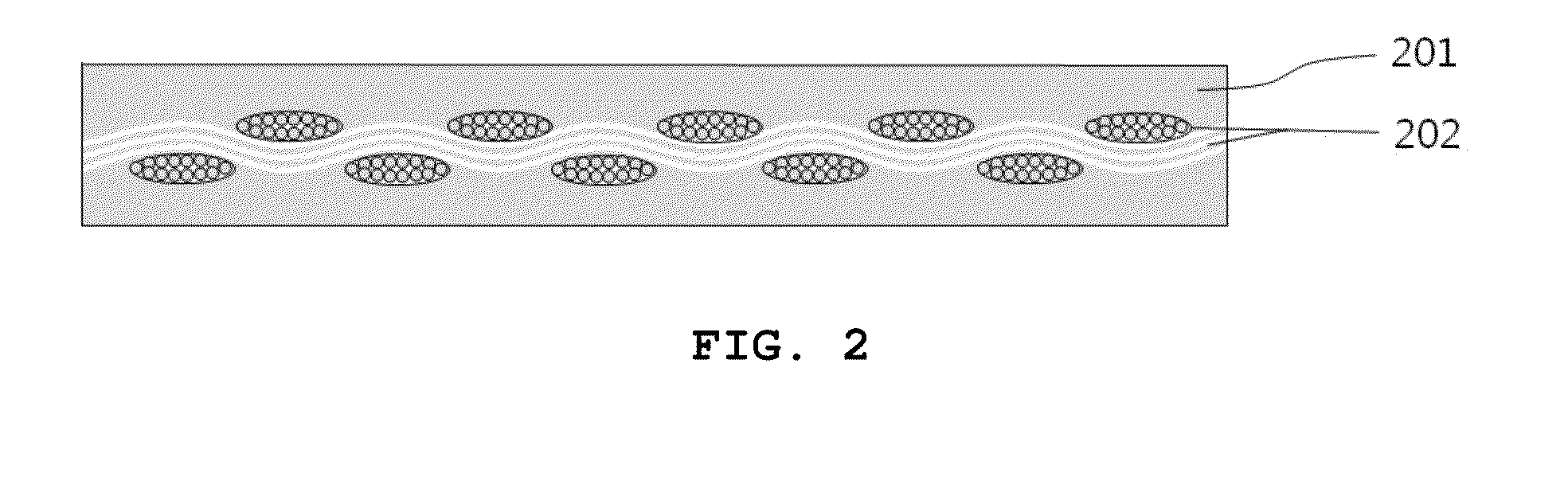
Method of manufacturing colorless transparent polyimide film having impregnated glass fabric and of flattening surface thereof
ActiveUS20160009882A1Prevent surface scatteringHigh optical transmittancePretreated surfacesGlass/slag layered productsDisplay deviceEngineering
Disclosed is a method of manufacturing a colorless transparent polyimide film having impregnated glass fabric, wherein the surface of the polyimide film substrate having impregnated glass fabric is flattened by two flattening steps using a roll-to-roll process, thereby solving problems with an increase in surface roughness of the polyimide substrate when manufacturing the polyimide film having impregnated glass fabric in order to enhance thermal and mechanical properties of a film for use in flexible display substrates and in cover windows for flat panel displays and mobile phones. As the surface roughness of the polyimide film having impregnated glass fabric is flattened to the level of ones of nm from the level ranging of tens of nm to ones of μm, a thin film transistor process can be performed on the polyimide film substrate and the polyimide film is increased in optical transmittance and transparency and can thus be utilized as flexible display substrates and cover windows for flat panel displays and mobile phones.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Method for opening window on polyimide base material of flexible printed circuit board and its etching fluid
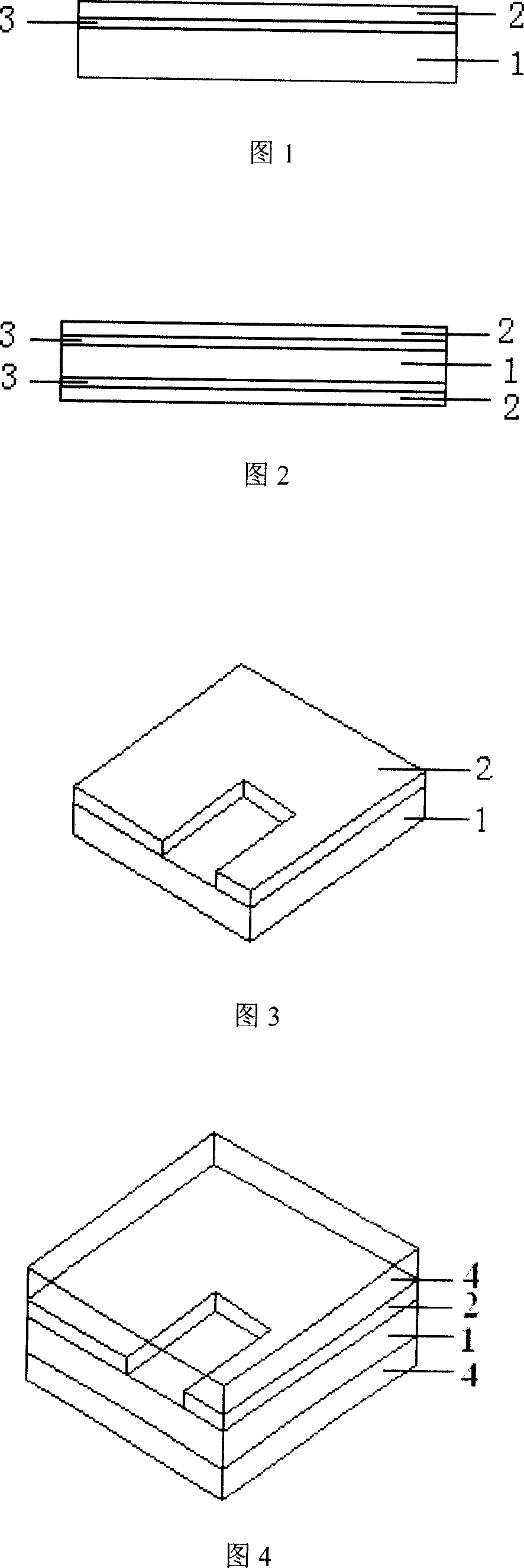
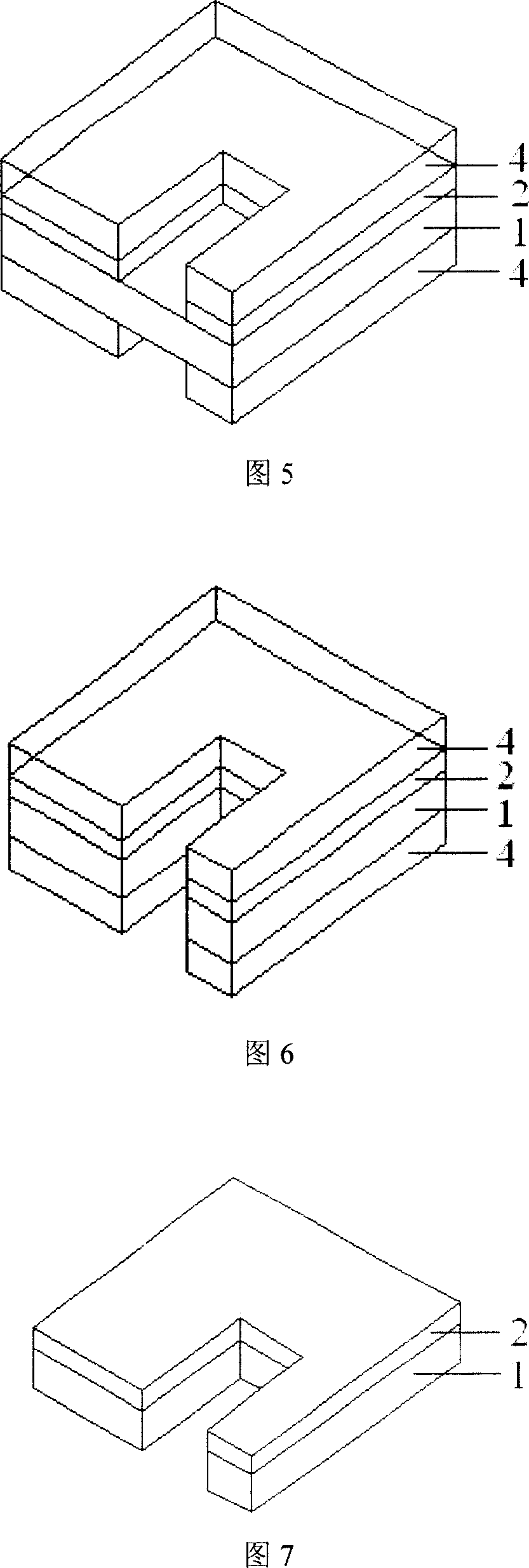
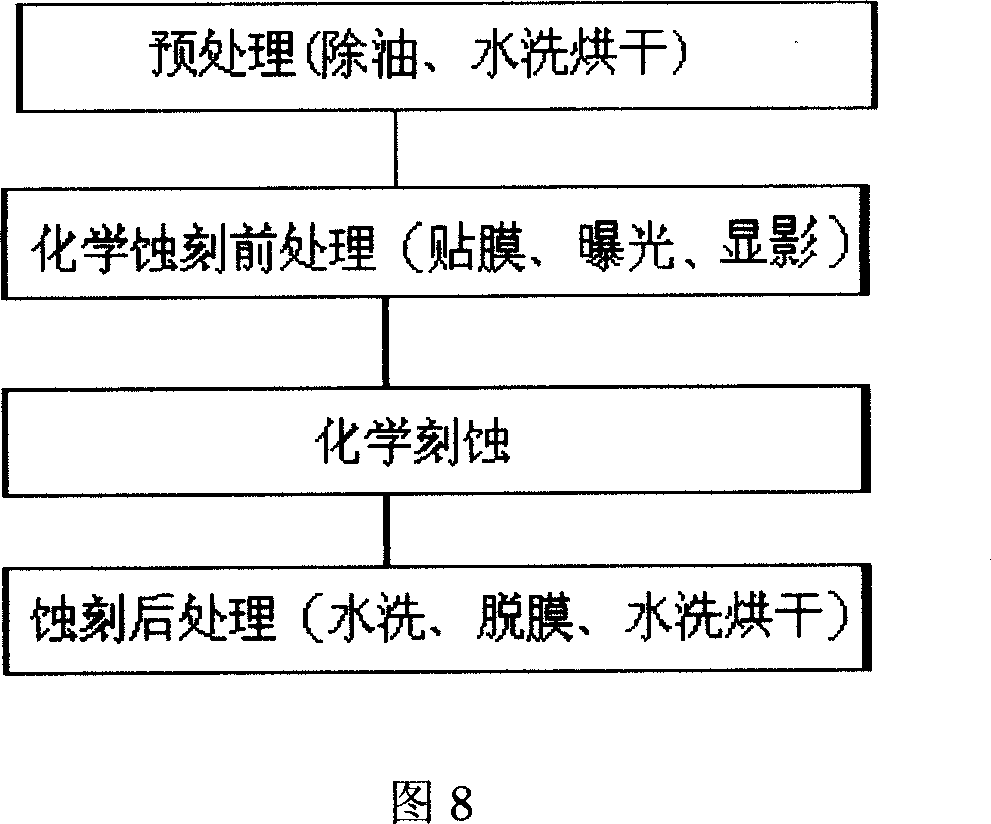
InactiveCN1953643ACheap methodSimple methodConductive material chemical/electrolytical removalConductive pattern polishing/cleaningEtchingEngineering
The invention relates to a method for opening window on the polyimide substrate of flexible printed circuit board. Wherein, it comprises that pretreatment (removing oil, washing and drying), chemical etching pretreatment (plastering film, exposure, and developing), chemical etching, and etching following treatment (washing, removing film, washing and drying). The etching liquid is the mixed solution of caustic potash and caustic soda, while it can be added with azimido-benzene (BTA) and derivate additive 1 or / and mercaptobenzothiazole (MBT) and derivate additive 2, and micro penetrant. The invention has low cost and high accuracy.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
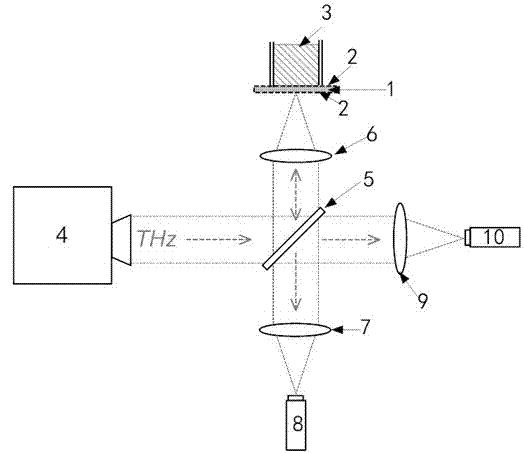
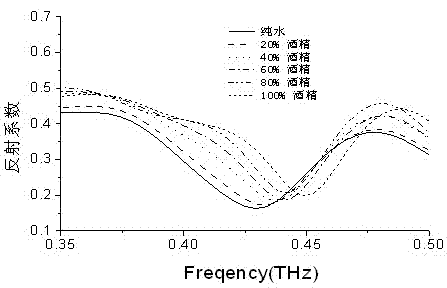
Alcohol concentration measuring device by using terahertz anisotropic medium resonance effect and method thereof
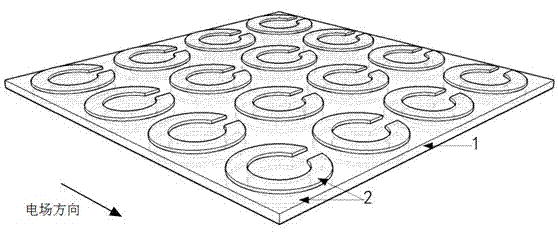
InactiveCN102830069AAccurately Measure Alcohol ContentMaterial analysis by optical meansFrequency spectrumParticle physics
The invention discloses an alcohol concentration measuring device by using terahertz anisotropic medium resonance effect and a method thereof. The terahertz anisotropic medium in the invention is formed by arranging two layers of metal resonance ring arrays on upper and lower surfaces of a polyimide substrate. An alcohol solution to be measured is disposed on the metal resonance ring array at one side of the anisotropic medium; terahertz waves sent by a backward wave oscillator vertically enter the metal resonance ring array at the other side; when the terahertz waves scan and change within a certain frequency range, a double-layer metal resonance ring array reflection coefficient curve is obtained by detection by two schottky diode detectors. The resonance effect of the metal resonance rings allows the resonance peaks on the reflection coefficient curve to move with the change of the alcohol concentration. The frequency spectrum resolution of the backward wave oscillator is less than 5 MHz, and the resonance peak movement in the reflection coefficient curve is more than 25 GHz when the solution to be measured changes from pure water to pure alcohol, so the precision of the measuring device for measuring alcohol concentration is up to more than 0.02%.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
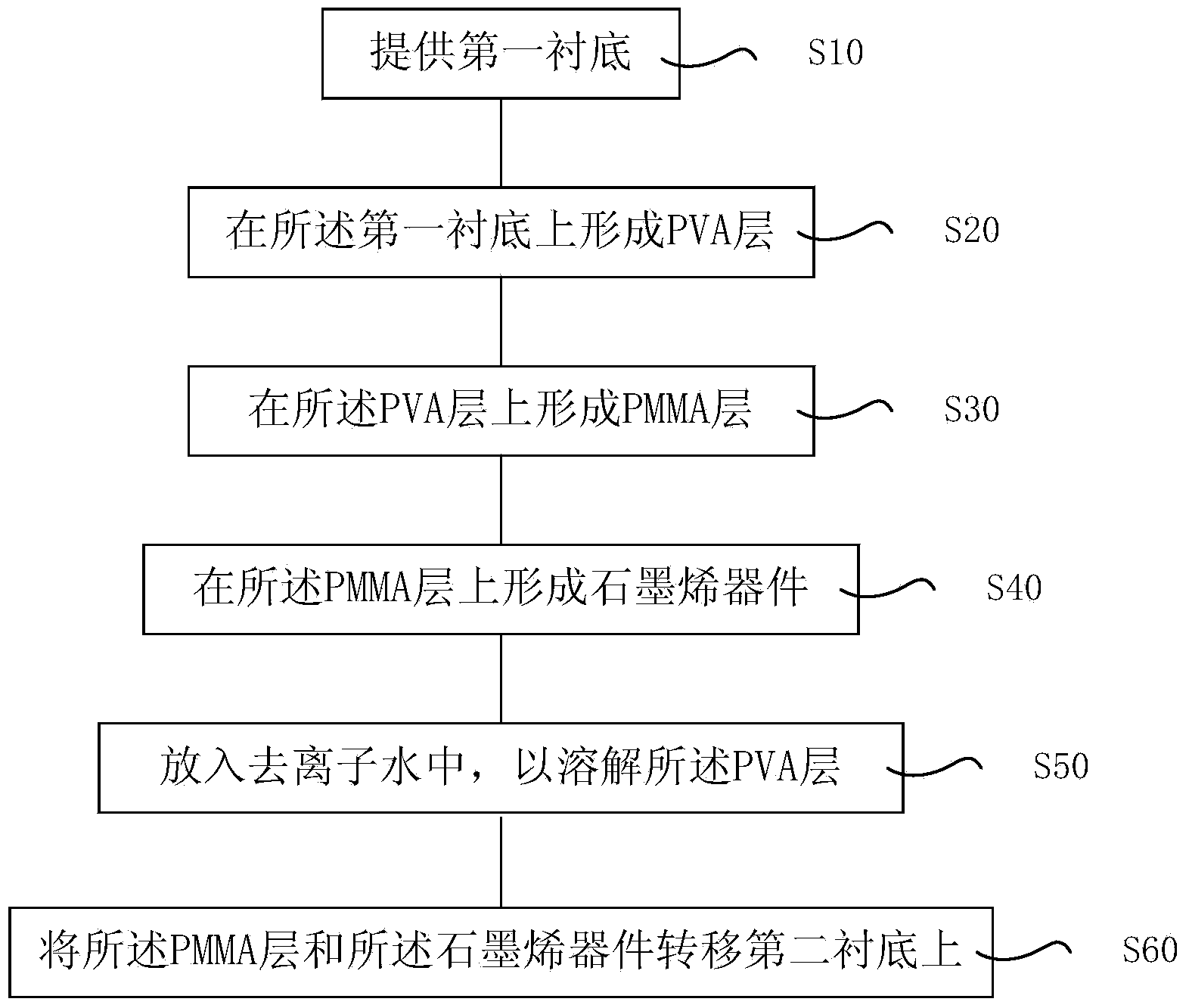
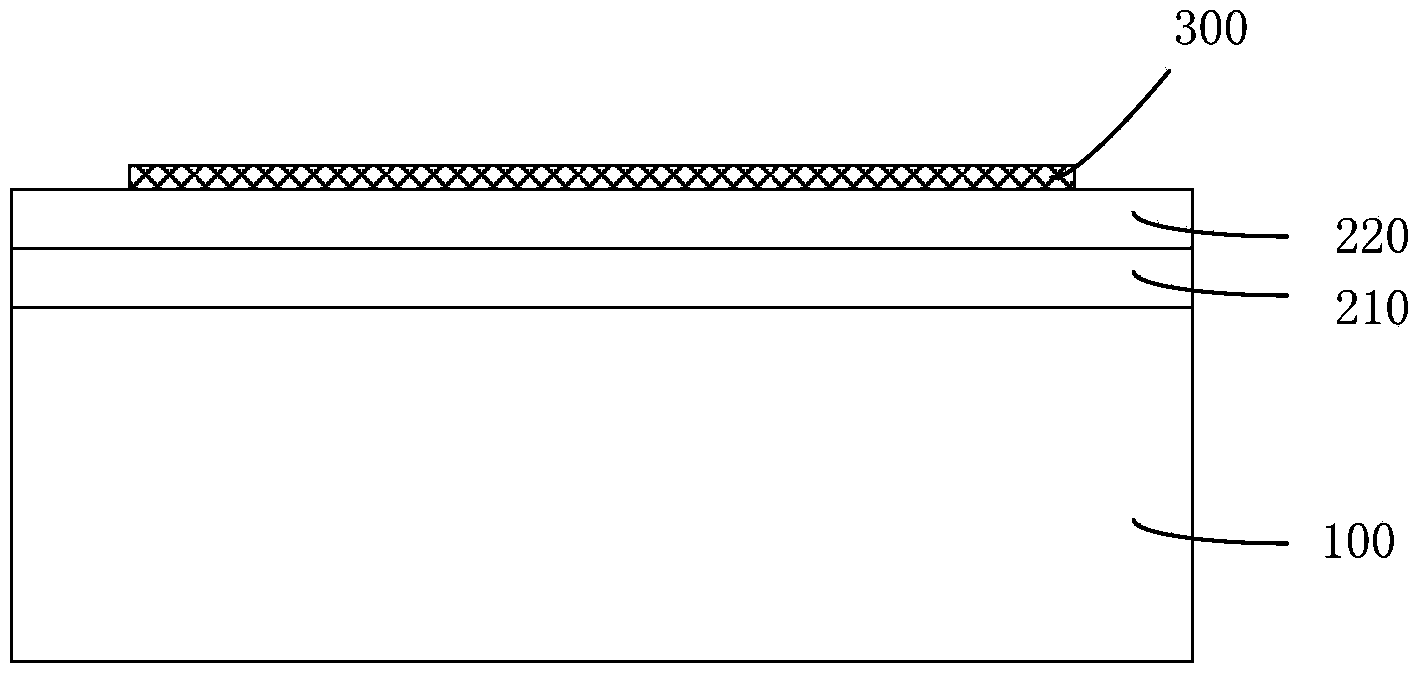
Manufacturing method of graphene device
ActiveCN103646855AFully formedEnsure complete formationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPolyimide substratePolyvinyl alcohol
The invention provides a manufacturing method of a graphene device. The manufacturing method of the graphene device at least comprises providing a first substrate; forming a PVA (polyvinyl alcohol) layer; forming a PMMA (polymethyl methacrylate) layer on the PVA layer; forming the graphene device on the PMMA layer; putting the first substrate, the PVA layer, the PMMA layer and the graphene device into deionized water to dissolve the PVA layer and to separate the PMMA layer and the graphene device from the first substrate; transferring the PMMA layer and the graphene device to a second substrate. According to the manufacturing method of the graphene device, PMMA serves as the support layer and meanwhile PVA serves as the sacrificial layer; by removing the PVA, the graphene device formed on the PMMA layer and the PMMA layer can be separated from the first substrate simultaneously and then adhered to the second substrate (a polyimide substrate in the embodiment), therefore, the graphene device can be formed on the second substrate. The manufacturing method of the graphene device can widen the application range of the graphene device.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Polyimide substrates having enhanced flatness, isotropy and thermal dimensional stability, and methods and compositions relating thereto
InactiveUS6949296B2Low raw material costExcellent film performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWood working apparatusPolyimide substrateElectron
The substrates of the present invention comprise a polyimide base polymer derived at least in part from non-rigid rod monomers together with optionally rigid rod monomers where the substrates are cured under low tension. The resulting polyimide materials have been found to provide advantageous properties (e.g. balanced molecular orientation, good dimensional stability, and flatness) particularly useful for electronics type applications.
Owner:DUPONT ELECTRONICS INC
Power supply printed circuit board and processing method thereof
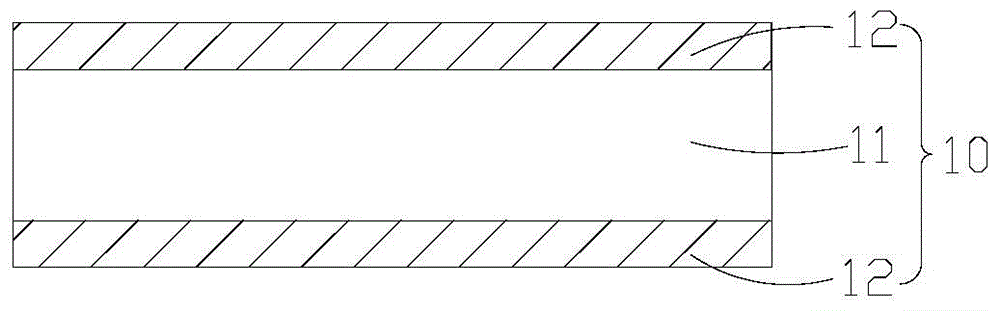
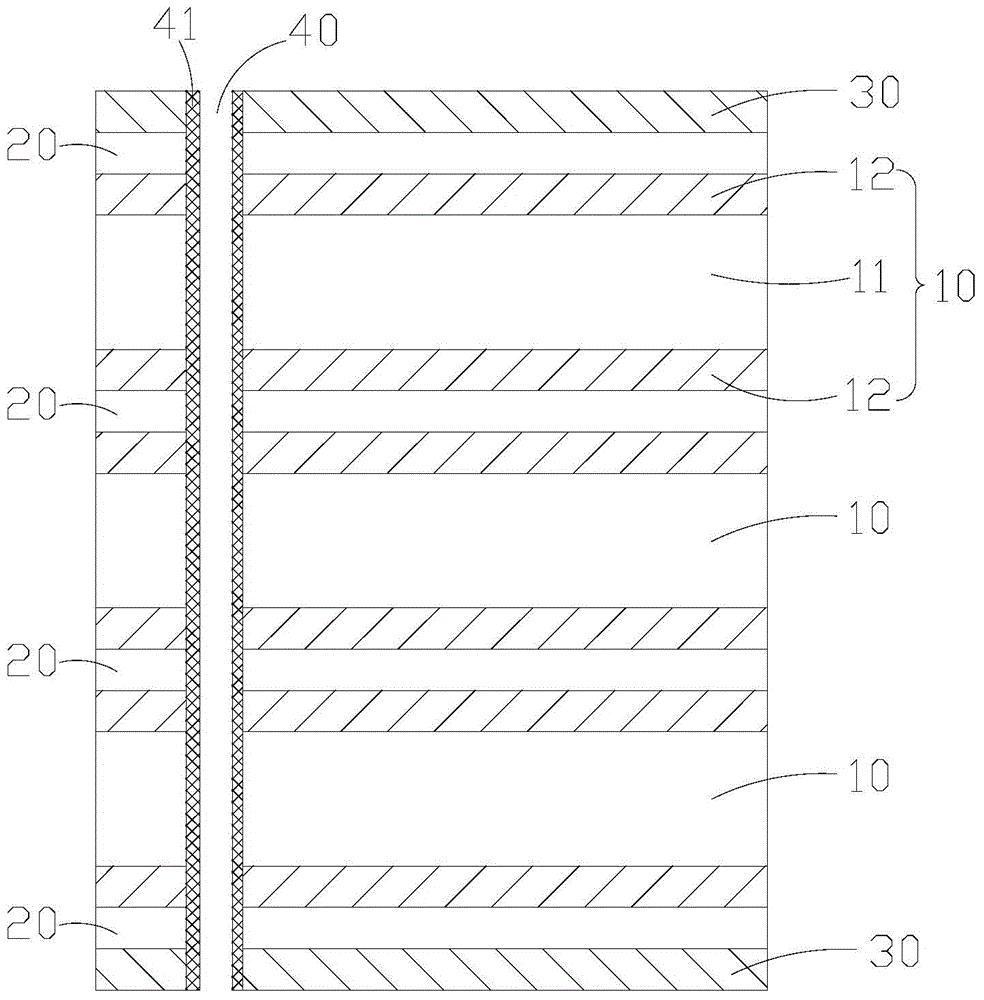
InactiveCN104812157AMeet the requirements of high voltage resistanceReduce thicknessPrinted circuit detailsPrinted circuit aspectsCopper foilPolyimide substrate
The invention is applied to the technical field of a printed circuit board, and provides a processing method of a power supply printed circuit board and a power supply printed circuit board formed by use of the processing method, for the purpose of solving the problems of poor voltage-withstanding capability of a conventional power supply printed circuit board and inconvenient assembling due to large board thickness in the prior art. The processing method of the power supply printed circuit board comprises the following steps: manufacturing an internal layer core plate, providing a soft plate copper-clad plate as the inside core plate, wherein the soft plate copper-clad plate comprises a polyimide substrate and copper coil layers arranged at the two opposite surfaces of the polyimide substrate; performing plasma coarsening processing on the surfaces of the copper foil layers; performing lamination and pressing to form a multilayer circuit board; performing boring processing on the multilayer circuit board and forming a conducting hole; performing plasma glue removing; and performing metallization processing on the conducting hole and forming an external line graph on an external copper layer. According to the processing method, the soft plate copper-clad plate is taken as the internal layer core plate, the voltage withstanding capability of the soft plate copper-clad plate is improved, and the thickness of the power supply printed circuit board is effectively reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN SUNTAK MULTILAYER PCB
Wearable flexible capacitive pressure sensor and preparation method thereof
PendingCN111551290ASimple methodEasy to operateSynthetic resin layered productsForce measurementCapacitive pressure sensorFlexible electronics
The invention relates to the technical field of flexible electronics, in particular to a wearable flexible capacitive pressure sensor and a preparation method thereof. The structure of the wearable flexible capacitive pressure sensor comprises an upper electrode, a dielectric layer, a bottom electrode and a wire; the upper electrode and the bottom electrode are composed of polyimide matrixes and electrodes, and the wires are attached to the polyimide substrate and connected with the electrodes, wherein the dielectric layer is formed by mixing a compressible polymer matrix and a conductive filler, and the polymer matrix has an internal microstructure; the graphene aerogel is a conductive filler and is applied to a dielectric layer of a flexible capacitive pressure sensor. Compared with theprior art, the capacitance pressure sensor structure based on the electronic skin technology improves the capacitance value of the pressure sensor, improves the sensitivity of the sensor, and is widely applied to electronic skin as wearable electronic equipment to monitor human body health.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of polyimide/ladder-like polysiloxane double-sided anisotropic composite thin film
The invention relates to a preparation method of a polyimide / ladder-like polysiloxane double-sided anisotropic composite thin film, which belongs to the field of polymer materials. The existing polyimide / organic siloxane composite thin film is prepared by introducing a poly-linear siloxane chain segment into a polyimide substrate through the copolymerization method or the doping method, and the prepared thin film has low mechanical property, low thermal resistance and great brittleness. The preparation method comprises the steps of using gamma-aminopropyltriethoxysilane and polyamic acid for carrying out reaction, utilizing hydrolytic condensation of the gamma-aminopropyltriethoxysilane for introducing ladder-like polysiloxane into the polyamic acid, and carrying out curing for preparing the polyimide / ladder-like polysiloxane double-sided anisotropic composite thin film. Compared with the prior art, the method can simultaneously maintain the mechanical property of the thin film while preparing the double-sided anisotropic composite thin film, and also solve the brittleness problem of the thin film and the obvious decline problem of the thermal performance. Simultaneously, the preparation method has the advantages of simple reaction steps, strong operationability, no toxicity, no pollution, easy industrialization and the like.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Application of zinc phthalocyanine complex as ink in micro-contact printing
InactiveCN102516841AReduce bloatReduce distortionInksOther printing apparatusMicrocontact printingPolyimide substrate
The invention discloses application of a zinc phthalocyanine complex as ink in micro-contact printing. The 2-propyl alcohol solution of 8(Octanohydroxamic)-zinc phthalocyanine serves as micro-contact printing ink; the pattern of a Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) seal is transferred to the surface of carboxylation polyethylene terephthalate, polyethylene naphthalate or polyimide substrate; and a delicate metal pattern is obtained on the substrate with a chemical plating method. The application of the zinc phthalocyanine complex as the ink in the micro-contact printing has the beneficial effect that the common phenomena of pattern inflation and pattern torsion in the micro-contact printing can be reduced by the phthalocyanine metal complex ink, and the phthalocyanine metal complex ink has a lowpreparation cost and great potential in the industrial application and is stable.
Owner:GUANGXI TEACHERS EDUCATION UNIV
Method for manufacturing colorless transparent glass-fabric reinforced polyimide film for flexible displays
ActiveUS20140238594A1Improve mechanical propertiesImprove thermal propertiesSynthetic resin layered productsLaminationPolyimide substrateOptical transparency
A method of manufacturing a colorless transparent polyimide film having reinforced glass fabric for flexible displays, suitable for use in increasing optical transmittance of a polyimide substrate having reinforced glass fabric for flexible displays. This method enables the glass fabric and the colorless transparent polyimide film to be matched in refractive index when the glass fabric is reinforced in the colorless transparent polyimide film to enhance thermal and mechanical properties of a substrate for flexible displays, thus satisfying high optical transparency and optical transmittance of 85% or more, required of a substrate for flexible displays, and thereby the colorless transparent polyimide film having reinforced glass fabric can be used as a substrate for flexible displays.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com