Nuisanceless organic fertilizer prepared from edible fungus slag, preparation method thereof and application thereof
A technology of organic fertilizer and edible fungus, applied in the direction of application, fertilizer form, fertilizer mixture, etc., can solve the problems of the surrounding living environment, large investment in turning and throwing equipment, and large consumption of soil nutrients, etc., so as to facilitate large-scale application and increase production The effect is obvious, and the effect of improving the utilization rate and effectiveness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
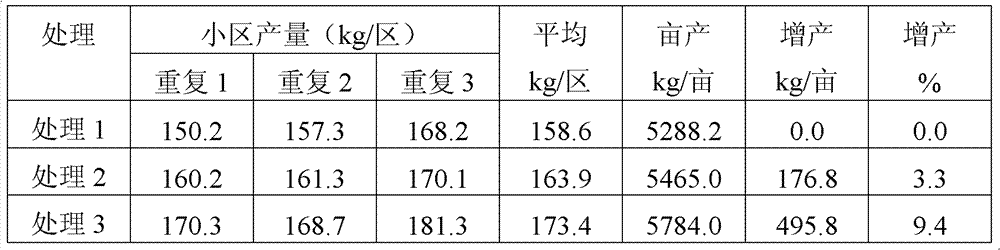
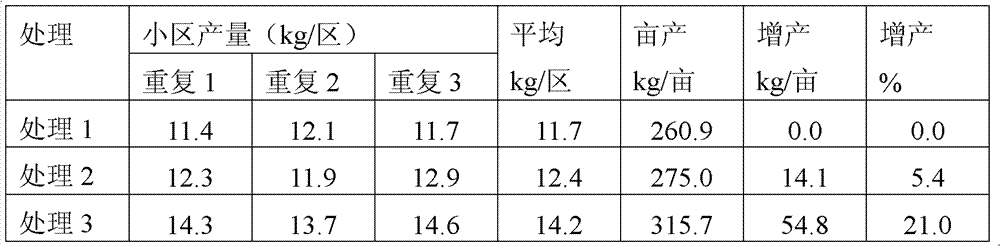
[0045] Example 1: Edible fungus slag is the waste material of Agaricus bisporus culture medium, with an organic matter content of 60wt% and a water content of 50wt%.
[0046] Edible fungus slag organic fertilizer, the raw material components are as follows, all in parts by weight:
[0047] 60 parts of edible mushroom residue, 8 parts of weathered coal, 5 parts of urea, 9 parts of monoammonium phosphate, 4 parts of potassium chloride, and 3 parts of trace element fertilizer (containing iron, zinc, molybdenum, boron). 4 parts of chemical degradation agent, 7 parts of curing agent;
[0048] Wherein the chemical degradation agent is a combination of potassium hydroxide and cobalt dichloride in a mass ratio of 1:0.2, and the curing agent is a combination of magnesium oxide (400 mesh) and triglycidyl isocyanurate in a mass ratio of 1:0.3;
[0049] The mass ratio of iron, zinc, molybdenum and boron in the trace element fertilizer is 1:0.5:03:0.3.
[0050] The preparation method is ...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Embodiment 2: Edible fungus slag is the waste material of the culture medium of Flammulina velutipes, and the organic matter content in the slag is 61wt%, and the water content is 50wt%.
[0053] The preparation method is the same as in Example 1, except that the raw material components by weight are as follows:
[0054] 50 parts of edible mushroom residue, 15 parts of weathered coal, 6 parts of urea, 12 parts of monoammonium phosphate, 6 parts of potassium chloride, 2 parts of trace element fertilizer (containing iron, zinc, molybdenum, boron). 3 parts of chemical degradation agent, 6 parts of curing agent;
[0055] Wherein, the chemical degradation agent is potassium hydroxide and cobalt dichloride mass ratio 1: 0.1, and the curing agent is the combination of magnesium oxide (400 mesh) and triglycidyl isocyanurate mass ratio 1: 0.2; The mass ratio of zinc, molybdenum and boron is 1:0.5:0.4.:0.2.
Embodiment 3
[0057] The edible fungus slag is the waste of Pleurotus ostreatus culture medium, and the organic matter content in the scum is 58wt%, and the water content is 49wt%.
[0058] The preparation method is the same as in Example 1, except that the raw material components by weight are as follows:
[0059] 65 parts of edible fungus residue, 5 parts of weathered coal, 4 parts of urea, 5 parts of monoammonium phosphate, 4 parts of potassium chloride, 2 parts of trace element fertilizer (containing iron, zinc, molybdenum, boron), 5 parts of chemical degradation agent, curing 10 doses;
[0060] Wherein, the chemical degradation agent is potassium hydroxide, cobalt dichloride mass ratio 1: 0.3, the curing agent is the combination of magnesium oxide (400 mesh) and triglycidyl isocyanurate mass ratio 1: 0.4; iron in the trace element fertilizer , zinc, molybdenum, boron mass ratio is 1:0.4:0.2:0.5.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com