Resource seizing method for long term evolution (LTE) system during service congestion
A technology for long-term evolution and business congestion, applied in network traffic/resource management, wireless communication, access restriction, etc., to avoid time-consuming and improve satisfaction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
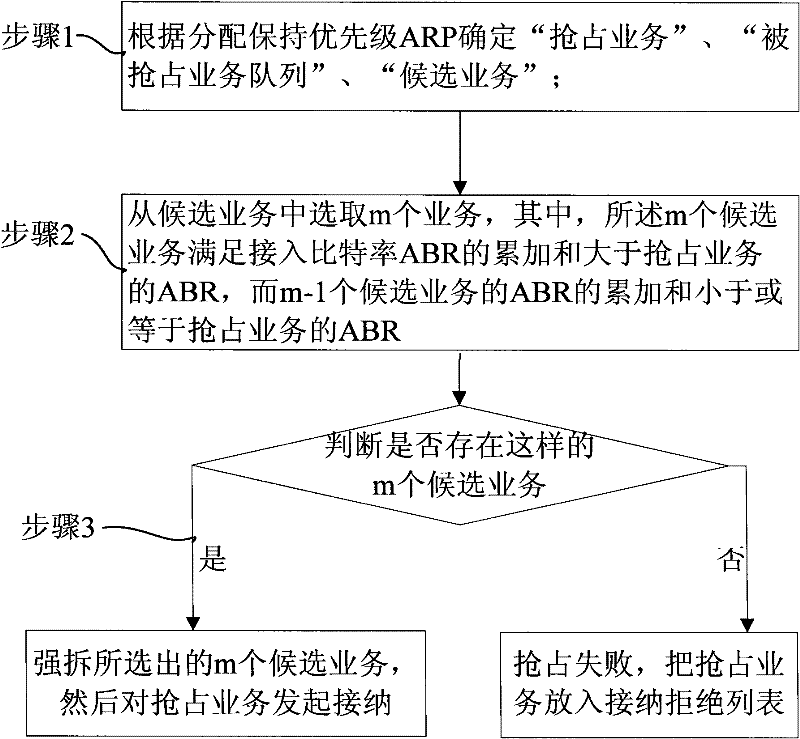
[0059] Assume that a service with preemption capability of downlink admission and rejection is assigned a priority ARP of 3, and the downlink guaranteed bit rate GBR is 256kbps, that is, the downlink access bit rate ABR is 256kbps.
[0060] It is assumed that the service bearers with the preempted attribute have been accessed:
[0061] A service with ARP of 5 and downlink GBR of 128kbps, hereinafter referred to as ARP5GBR128;
[0062] A service with ARP of 6 and downlink GBR of 64kbps, hereinafter referred to as ARP6GBR64;
[0063] A service with ARP of 7 and downlink GBR of 32kbps, hereinafter referred to as ARP7GBR32;
[0064] A service with ARP of 8 and downlink GBR of 32kbps, hereinafter referred to as ARP8GBR32;
[0065] A service with an ARP of 9 and a downlink GBR of 128kbps, hereinafter referred to as ARP9GBR128;
[0066] An NGBR service with ARP of 7 and downlink PBR of 64kbps, hereinafter referred to as ARP7NGBR64;
[0067] An NGBR service with ARP of 8 and downl...
Embodiment 2
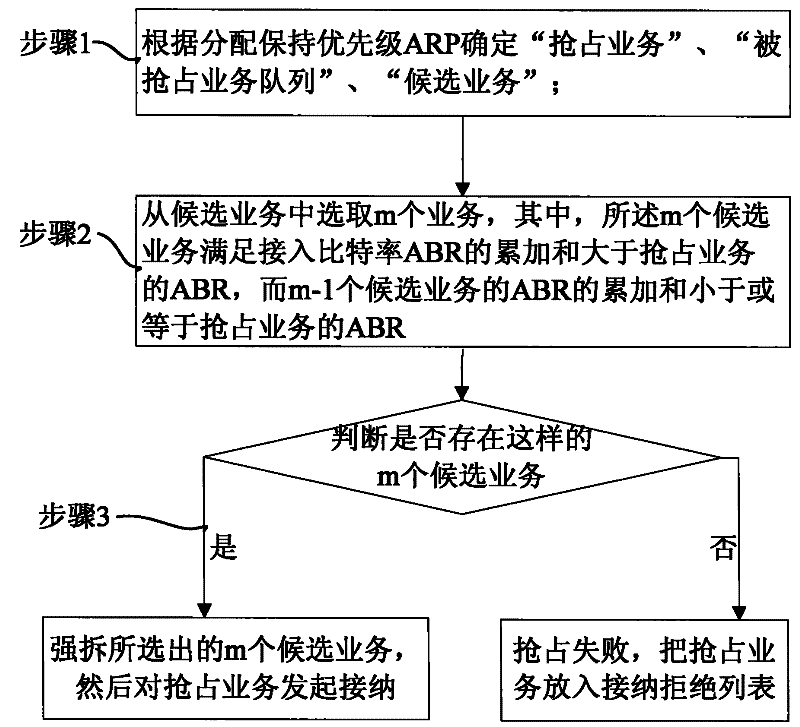
[0076] Assuming that a service with preemption capability accepts and rejects the downlink service, its allocation and maintenance priority ARP is 8, and the downlink GBR is 512kbps, that is, the downlink ABR is 512kbps.
[0077] It is assumed that the service bearers with the preempted attribute have been accessed:
[0078] A service with ARP of 6 and downlink GBR of 64kbps, hereinafter referred to as ARP6GBR64;
[0079] A service with ARP of 7 and downlink GBR of 32kbps, hereinafter referred to as ARP7GBR32;
[0080] An NGBR service with an ARP of 9 and a downlink PBR of 64kbps, hereinafter referred to as ARP9NGBR64;
[0081] A service with ARP of 10 and downlink GBR of 128kbps, hereinafter referred to as ARP10GBR128;
[0082] An NGBR service with an ARP of 11 and a downlink PBR of 32kbps, hereinafter referred to as ARP11NGBR32;
[0083] An NGBR service with an ARP of 12 and a downlink PBR of 16 kbps, hereinafter referred to as ARP12NGBR16.
[0084] Step 201: Sort the ac...
Embodiment 3
[0090] Assuming that a service with preemption capability is accepted and rejected by the upstream, its allocation and maintenance priority ARP is 3, and the upstream guaranteed bit rate GBR is 256kbps, that is, the upstream access bit rate ABR is 256kbps.
[0091] It is assumed that the service bearers with the preempted attribute have been accessed:
[0092] A service with an ARP of 5 and an uplink GBR of 128kbps, hereinafter referred to as ARP5GBR128;
[0093] A service with an ARP of 6 and an uplink GBR of 64kbps, hereinafter referred to as ARP6GBR64;
[0094] A service with an ARP of 7 and an uplink GBR of 32kbps, hereinafter referred to as ARP7GBR32;
[0095] A service with an ARP of 8 and an uplink GBR of 32kbps, hereinafter referred to as ARP8GBR32;
[0096] A service with an ARP of 9 and an uplink GBR of 16kbps, hereinafter referred to as ARP9GBR16;
[0097] An NGBR service with an ARP of 7 and an upstream PBR of 64kbps, hereinafter referred to as ARP7NGBR64;
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com