Full optics differential monitoring device based on Pockels effect
A monitoring device and optical technology, applied in the direction of voltage/current isolation, can solve the problems of beam interference and low deflection angle accuracy, and achieve the effect of low electromagnetic interference and high accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
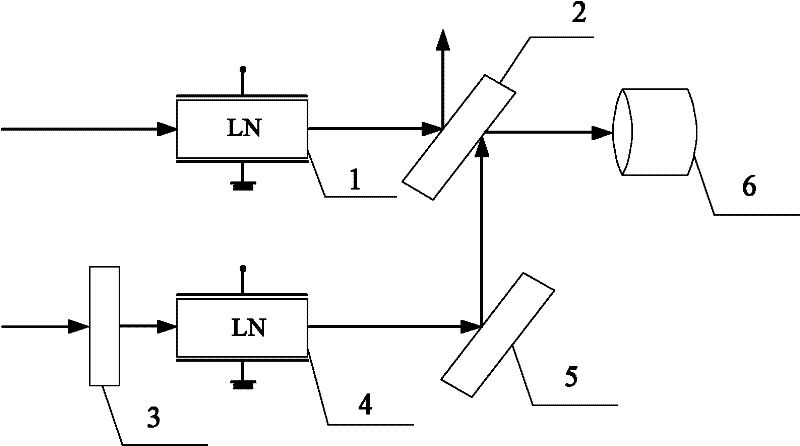
[0009] Specific implementation mode 1. Combination figure 1 Illustrate this specific embodiment, the all-optical differential monitoring device based on Pockels effect, it comprises photodetector 6, and it comprises No. 1 electro-optic crystal 1, No. 1 half mirror 2, half-wave plate 3, two No. electro-optic crystal 4 and No. one total mirror 5, the first incident light beam is transmitted through the first electro-optic crystal 2 to obtain the first polarized light beam, and the first polarized light beam is incident on the No. one half-transparent half-mirror 3, and passes through a No. half mirror 3 is divided into reflected light beam and transmitted light beam, and described reflected light beam emerges along the direction perpendicular to the optical axis of the first polarized light beam;
[0010] The second incident light beam is incident on the second electro-optic crystal 4 after being transmitted by the half-wave plate 3, and the second polarized light beam is obtain...
specific Embodiment approach 2
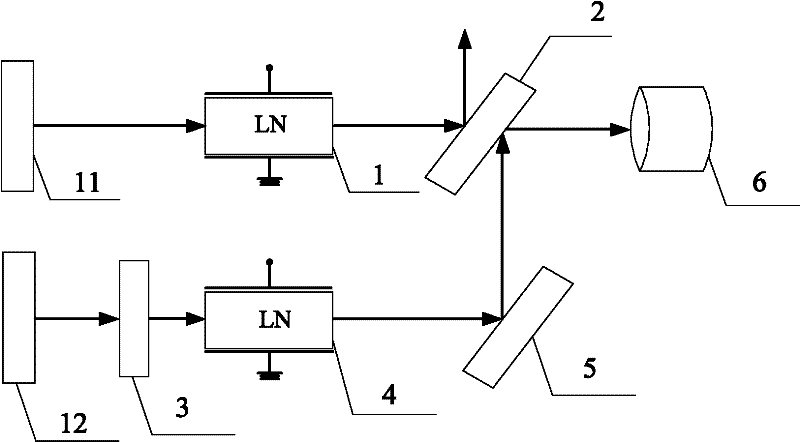
[0012] Embodiment 2. The difference between this embodiment and the all-optical differential monitoring device based on the Pockels effect described in Embodiment 1 is that it also includes No. 1 light source 11 and No. 2 light source 12. The first incident The light beam is emitted by No. 1 light source 11 , and the second incident light beam is emitted by No. 2 light source 12 .
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0013] Embodiment 3. The difference between this embodiment and the all-optical differential monitoring device based on the Pockels effect described in Embodiment 2 is that both the No. 1 light source 11 and the No. 2 light source 12 are semiconductors with a wavelength band of 850 nm. laser.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com