Pseudo-three-dimensional wireless sensor network routing method based on geographical position
A wireless sensor, geographic location technology, used in wireless sensor networks, communication fields
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
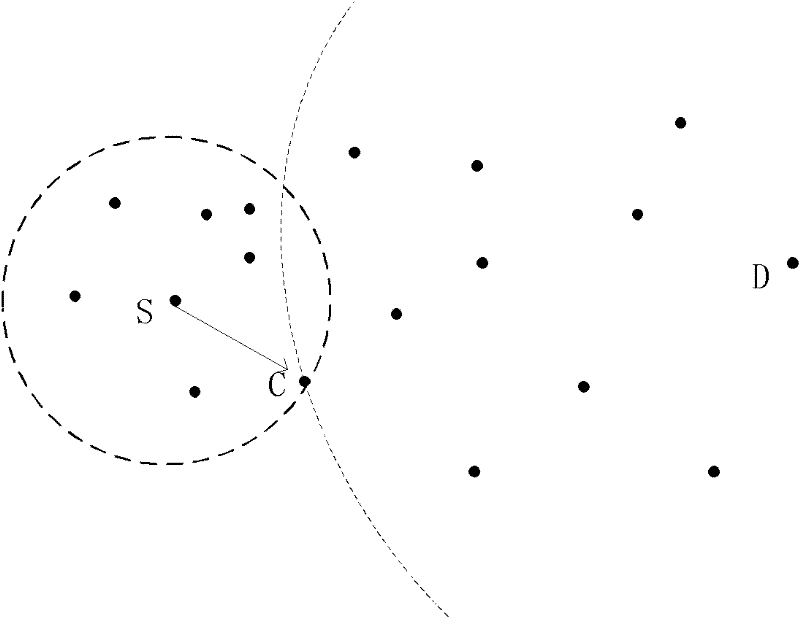
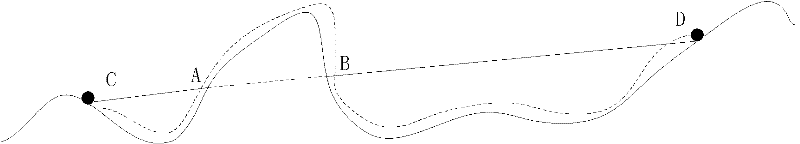
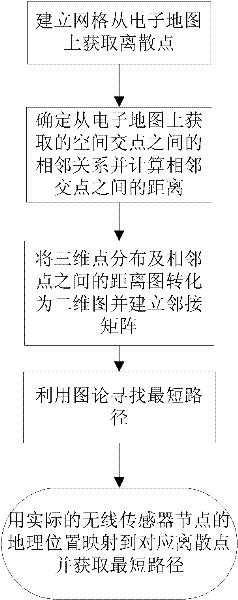
[0028] The pseudo three-dimensional wireless sensor network routing method based on geographic location of the present invention selects some discrete points on the surface of the electronic map by means of spatial point selection, and these discrete points can reflect the surface fluctuation trend of the electronic map as a whole. By calculating the Euclidean distance between adjacent discrete points and mapping them to the projected points on the two-dimensional plane through the adjacent relationship, and using the shortest path calculation method in graph theory (such as the Dijkstra algorithm), a certain point on the surface of the electronic map can be calculated. The shortest path between the projection point of one discrete point and the projection point of another discrete point. Because this path is generated from the projection point...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com