Power transmission device
A technology of power transmission device and driving force, which is applied to transmission devices, electrical components, belts/chains/gears, etc., can solve the problems of reduced electromagnetic wave shielding performance and leakage, and achieve the effect of suppressing leakage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
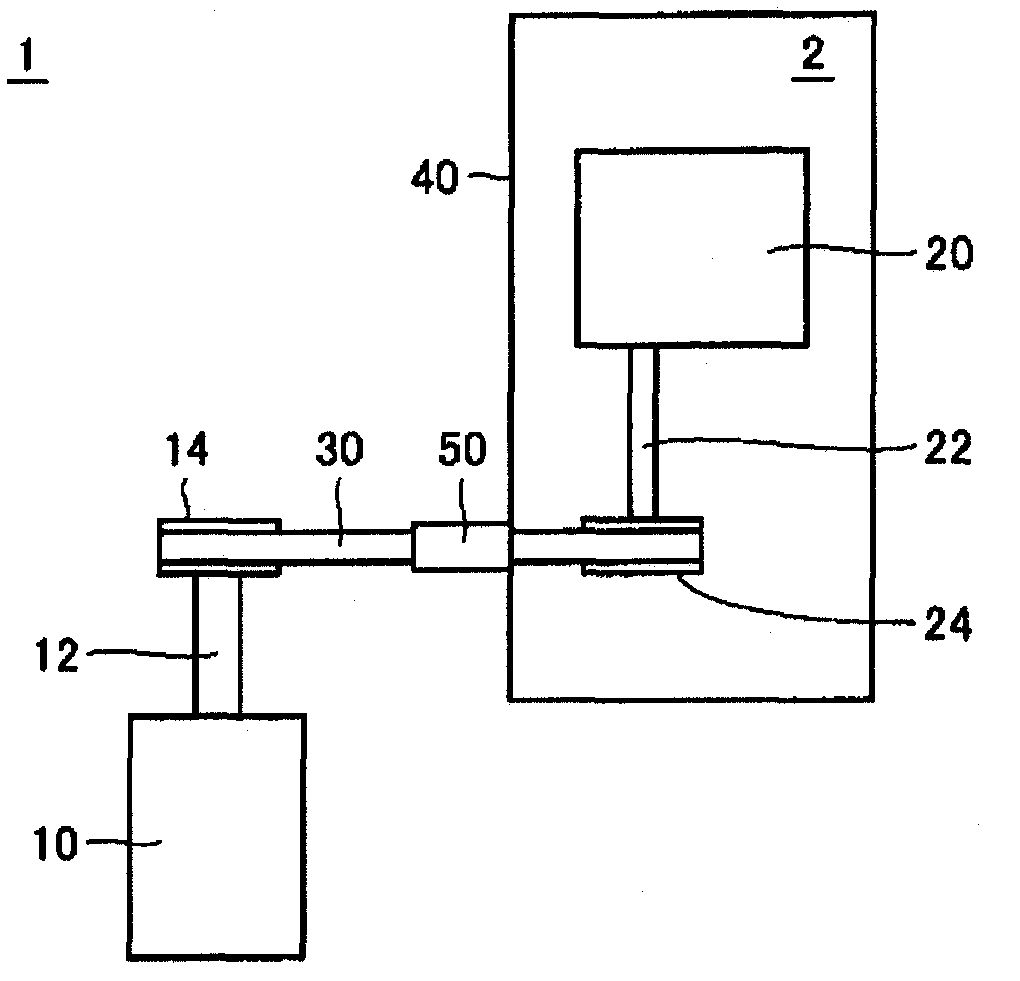
[0046] figure 1 It is a schematic plan view showing the structure of the power transmission device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. Such as figure 1 As shown, the power transmission device is a device for transmitting rotational driving force between the first space 1 and the second space 2 surrounded by the electromagnetic wave shielding wall 40 . The second space 2 is an area surrounded by the electromagnetic wave shielding walls 40 . The electromagnetic wave shielding wall 40 is formed by combining plate members of electric conductors, and can prevent propagation of electromagnetic waves between the first space 1 and the second space 2 . The electromagnetic wave shielding wall 40 constitutes the outer wall of the second space 2 serving as an electromagnetic wave shielding room. The second space 2 is a space adjacent to the first space 1 which is a space outside the electromagnetic wave shielding wall 40 , and is separated from the first space 1 by the ...
Embodiment approach 2
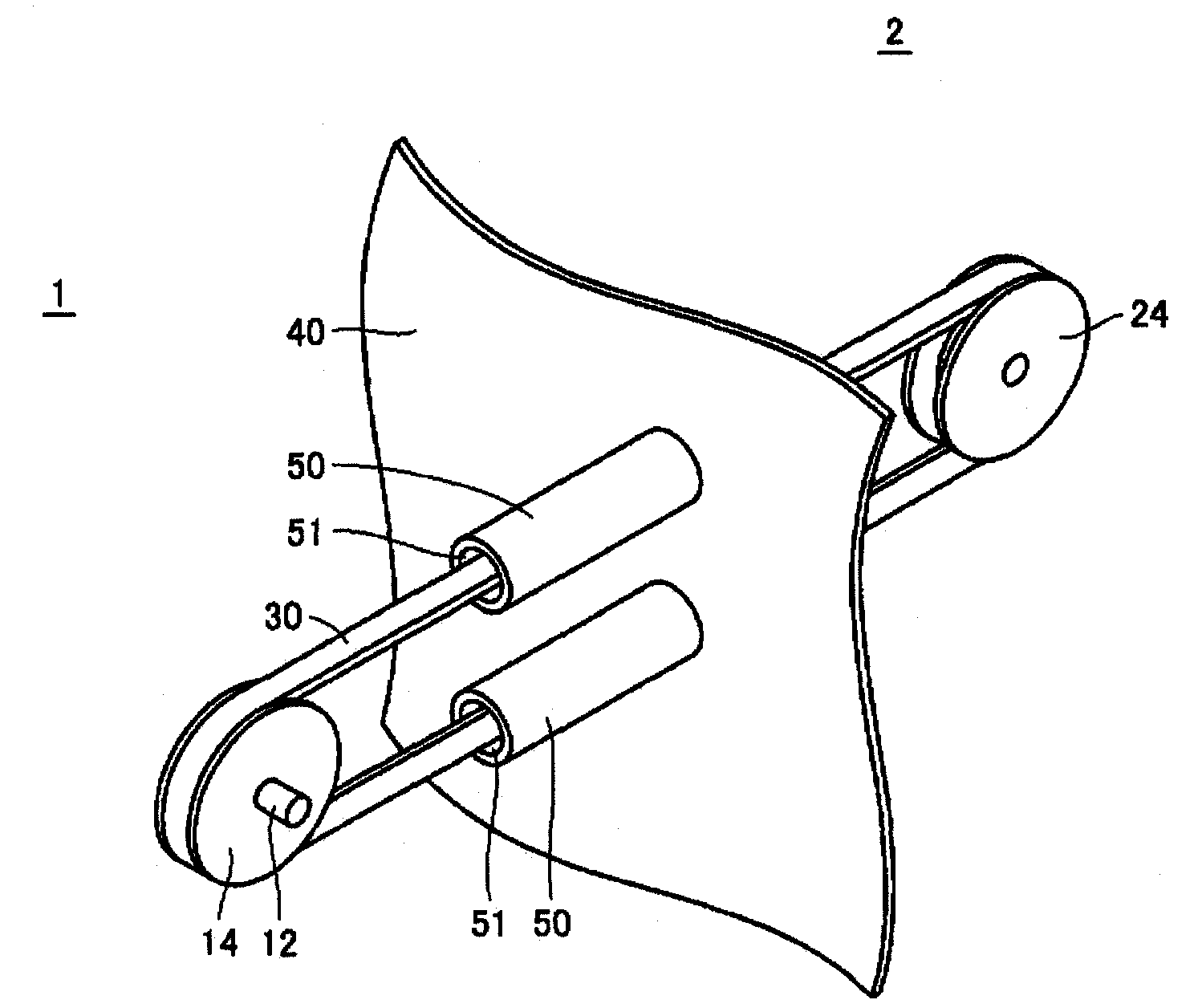
[0060] Figure 6 It is a perspective view showing a partial configuration of the power transmission device according to the second embodiment. exist Figure 6 2 shows a structure in which the belt 36 wound around the first pulley 16 and the second pulley 26 passes through the inside of the cylindrical member 56 and penetrates the electromagnetic wave shielding wall 40 according to the second embodiment.
[0061] The belt 36 according to Embodiment 2 is a toothed belt (cogged pulley) in which teeth are provided on one surface side and the other surface side is formed flat over the entire length of the belt shape. The first pulley 16 and the second pulley 26 on which the belt 36 is wound are toothed in a shape corresponding to the tooth shape of the toothed belt (Japanese: 歯付けベルト) in the circumferential direction of the outer peripheral surface. Pulley (gear pulley). Typically, the belt 36 can be used as a timing belt, and the first pulley 16 and the second pulley 26 can be u...
Embodiment approach 3
[0069] Figure 8 It is a perspective view showing a partial configuration of the power transmission device according to the third embodiment. exist Figure 8 In the diagram, the second pulley 28 of Embodiment 3, the belts 38 (38a, 38b) wound around the second pulley 28, and the cylindrical members 58a, 58b penetrated by the belt 38 are shown, and the first belt is omitted. Diagram of the wheel and electromagnetic wave shielding wall.
[0070] A plurality of (six in this case) pulley grooves 29 are formed in the second pulley 28 in the circumferential direction. exist Figure 8 The same number of pulley grooves 29 as the number of second pulleys 28 are also formed on the first pulley (not shown). A plurality of (four in this case) belts 38 are wound around the first pulley and the second pulley 28 to transmit a rotational driving force from the first pulley to the second pulley 28 . The belt 38 is a V-belt, and the first pulley and the second pulley 28 are V-pulleys. In t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com