Handheld thermal infrared imager
An infrared thermal imager, handheld technology, applied in the field of infrared thermal imager, can solve the problems of complex structure, unclear imaging, image mismatch, etc., and achieve the effects of high dynamic range, clear imaging, and simple structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
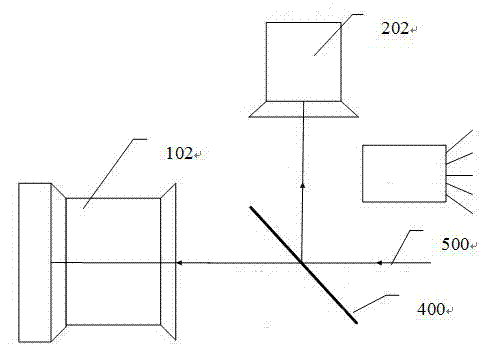
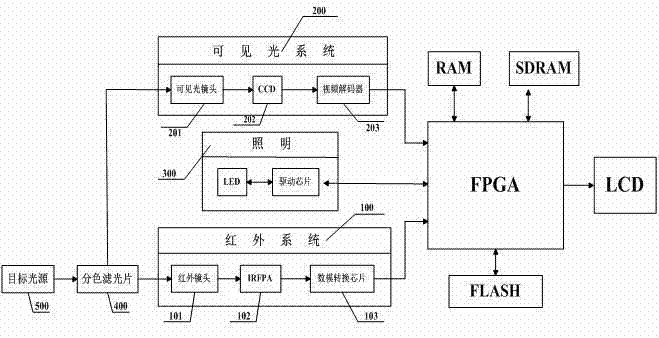
[0035] The coaxial optical path structure of the present invention requires that the light source emitted by the target must be received by the visible light photosensitive surface of the CCD and by the uncooled infrared focal plane at the same time, which requires a specific bandpass filter that separates visible light from far infrared light . As one of the preferred options: a dichroic filter with high transmittance of 8-14um infrared and high reflection of 0.4-0.7um of visible light is used. The dichroic filter uses germanium as a commonly used coating substrate, YbF 3 As a low-refractive-index film material, ZnS is used as a high-refractive-index film material. Using the design principle of long-wavelength interference cut-off filter, regular λ / 4 multilayer dielectric films are superimposed to obtain high visible light reflectivity; at the same time, the design of the film system, so that the far-infrared transmittance can also meet the requirements. After the target lig...
Embodiment 2
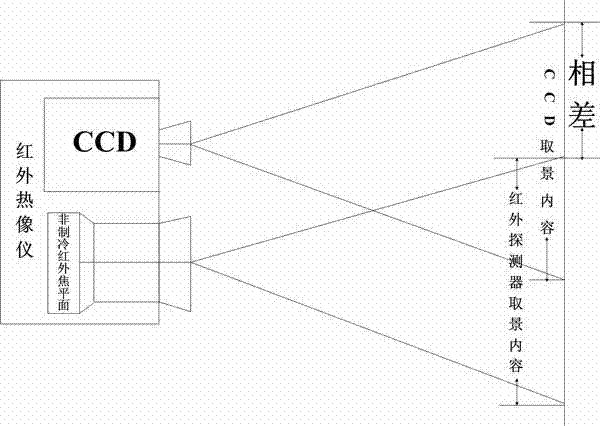
[0037] Since the minimum resolution of the human eye is about 0.5mrad. So the spatial resolution of the infrared system is greater than 0.5mrad. As one of the preferred options: the spatial resolution of the infrared system of the present invention is 1 mrad, and the uncooled infrared detector 102 adopts a 384×288 focal plane array (the size of the pixel is 35×35um, the field of view angle is 24°×18° ); the infrared lens 101 adopts a motorized focusing infrared lens with a focal length of 35mm.
Embodiment 3
[0039] In the present invention, the spatial resolution of the visible light system (200) should be proportional to the spatial resolution of the infrared system detection target of 1 mrad. The resolution is correspondingly 1mrad; when the ratio of visible light pixels to infrared image pixels is 1:4, the spatial resolution of the visible light system reaches 0.5mrad. As one of the preferred options: the visible light CCD 202 in the visible light system 200 adopts a 1 / 3-inch high-definition Sony CCD camera module (photosensitive area 4.8×3.6mm, effective pixel PAL: 752(H)×582(V)). The visible light lens 201 adopts a common photosensitive lens with a field angle of 60° and a focal length of 6mm, or a common photosensitive lens with a field angle of 30° and a focal length of 12mm.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com