Planar articulated robot arm mechanism
A robot arm, planar multi-joint technology, applied in the direction of manipulators, claw arms, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of rigidity reduction, etc., and achieve the effect of improving reliability, good structural rigidity, and high reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
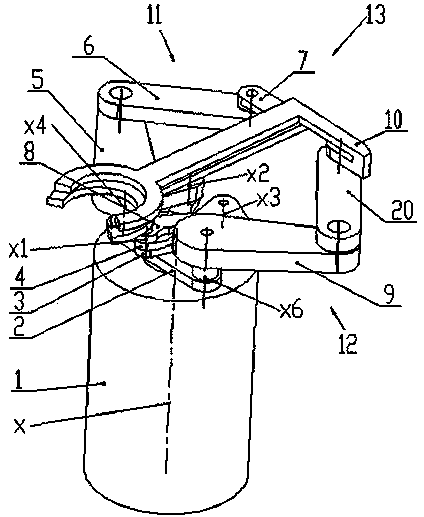
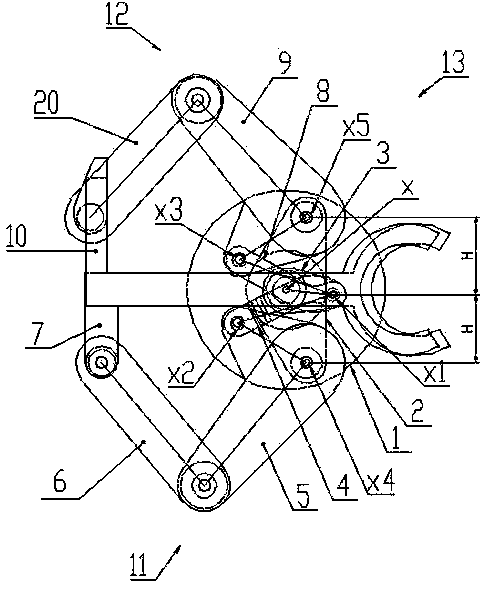
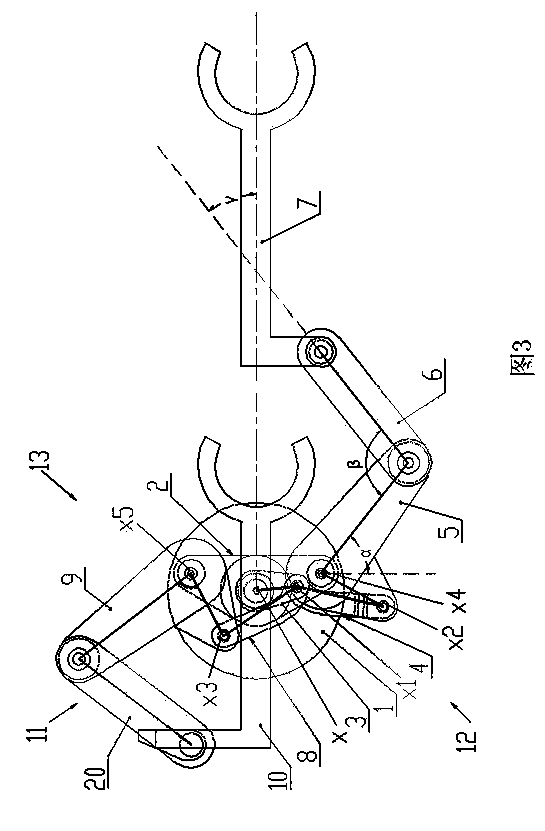
[0023] Embodiment 1: as Figure 1-Figure 4 As shown, this example includes a drive unit 1, a base platform 2 and a double telescopic arm assembly 13. The drive unit 1 has two rotating shafts nested in each other—the inner shaft 27 of the rotating shaft and the outer shaft 26 of the rotating shaft. The base platform 2 of the rotation axis is connected to the lifting mechanism of the drive unit 1, and the double telescopic arm assembly 13 is symmetrically installed on the base platform 2 with respect to the rotation axis x of the drive unit 1 through the fourth and fifth rotary joints x4 and x5 On the outer shaft 26 of the rotating shaft, the inner shaft 27 of the rotating shaft is affixed to the common drive link 3 of the double telescopic arm assembly 13, and the lifting shaft 24, the outer shaft 26 of the rotating shaft and the inner shaft 27 of the rotating shaft of the lifting mechanism pass through respectively The independent motors are connected to the controller of the ...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Embodiment 2: as Figure 5 As shown, the overall structure of this example is the same as that of Embodiment 1, the difference is: the third motor 16 of the inner shaft 27 of the rotating shaft described in this example is installed on the outer shaft 26 of the rotating shaft, and the two pulleys of the synchronous belt drive mechanism They are respectively connected to the outer shaft 26 of the rotating shaft and the third motor 16 . In this way, the outer shaft 26 of the rotating shaft and the inner shaft 27 of the rotating shaft are no longer driven independently. Do any movement, when the inner shaft 27 of the rotating shaft moves, the double SCARA arm assembly does telescopic movement.
Embodiment 3
[0034] Embodiment 3: as Figure 6 As shown, the difference between this example and Embodiment 1 is that the drive unit 1 of this example has a rotating shaft—the inner shaft 27 of the rotating shaft, and the base platform 2 with the inner shaft 27 of the rotating shaft is connected to the lifting mechanism of the driving unit 1 Above, the double telescopic arm assembly 13 is mounted on the base platform 2 symmetrically with respect to the rotation axis x of the drive unit 1 through the fourth and fifth rotary joints X4 and X5 respectively, namely: the first and second telescopic arm assemblies 13 The first pulley 17 in the boom 5, 9 is fixed on the base platform 2, and the inner shaft 27 of the rotating shaft is respectively hinged to the first and second booms 5, 9 of the double telescopic arm assembly 13 through the common drive link 3 , the lifting shaft 24 and the inner shaft 27 of the rotating shaft of the lifting mechanism are connected to the controller 28 of the drive...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com