Automatic fiber laying variable-angle path planning method for non-developable curved surface part
A curved surface part and fiber laying technology, which is applied in the field of fiber laying trajectory planning for non-developable curved surface parts, can solve the problems affecting the shape accuracy of composite material components, the impact of various performances, and the complexity of the fiber laying process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0101] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 , Figure 4 , Figure 5 , Figure 8 ~ Figure 10 , Figure 15 and Figure 16 Explain, the non-developable curved surface parts automatic fiber laying variable angle trajectory planning method of this embodiment, the method is implemented by the following steps:
[0102] Step 1: Obtain data information of non-developable surface parts;
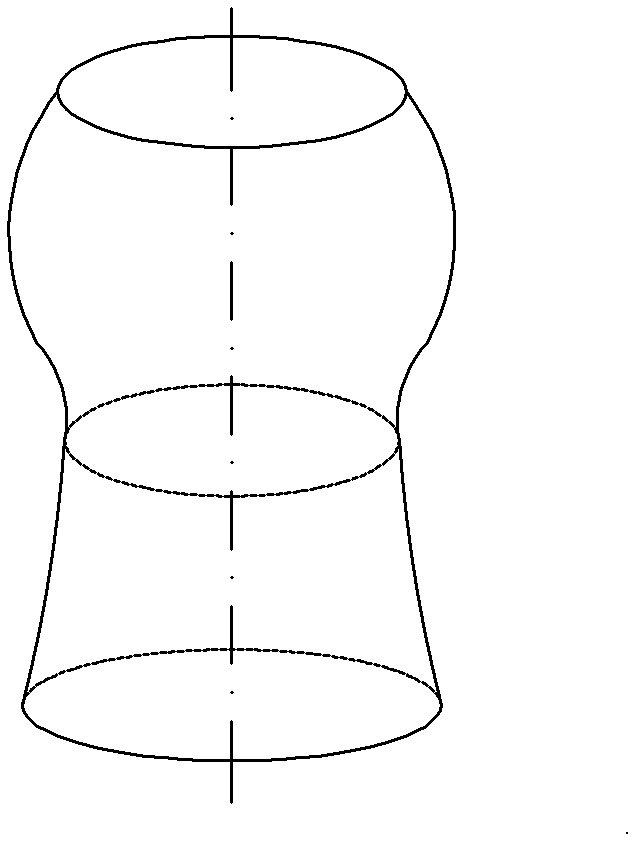
[0103] The non-extensible curved surface part is a non-extensible rotary cylindrical part (such as a device casing), the axis of the non-extensible rotary cylindrical part is a straight line, and the cross-sections perpendicular to the axis are all circular sections, and the non-extensible rotary cylindrical part is a circular section. The generatrices of rotary cylinder parts are spline curves;
[0104] Divide the axis into m-1 parts (equal division principle: the spacing should be greater than the motion accuracy of the laying equipment, and at the same time be less than the accur...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0135] Specific implementation mode two: combination figure 2 , Figure 6 , Figure 11 , Figure 12 , Figure 15 and Figure 16 Explain, the non-developable curved surface parts automatic fiber laying variable angle trajectory planning method of this embodiment, the method is implemented by the following steps:
[0136] Step 1: Obtain data information of non-developable surface parts;
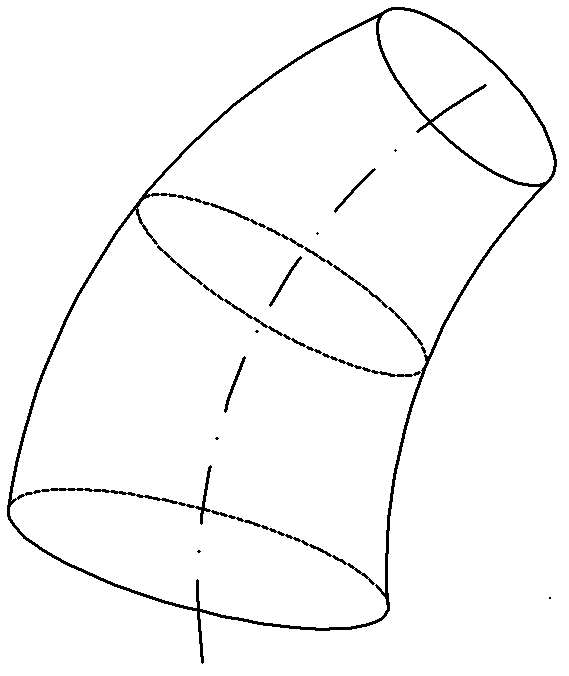
[0137] The non-developable curved surface part is a non-developable curved surface variable-section conical shell part, the axis of the non-developable curved surface variable-section conical shell part is a curve, and the sections perpendicular to the axis are all circular sections, and the circular section The size of the perimeter changes continuously, and the circular section with the smallest perimeter appears on one end of the non-developable surface variable-section conical shell part;
[0138] Divide the axis into m-1 parts (equal division principle: the spacing should be greater...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0160] Specific implementation mode three: combination image 3 , Figure 7 and Figure 13 to Figure 16 Explain, the non-developable curved surface parts automatic fiber laying variable angle trajectory planning method of this embodiment, the method is implemented by the following steps:
[0161] Step 1: Obtain data information of non-developable surface parts;
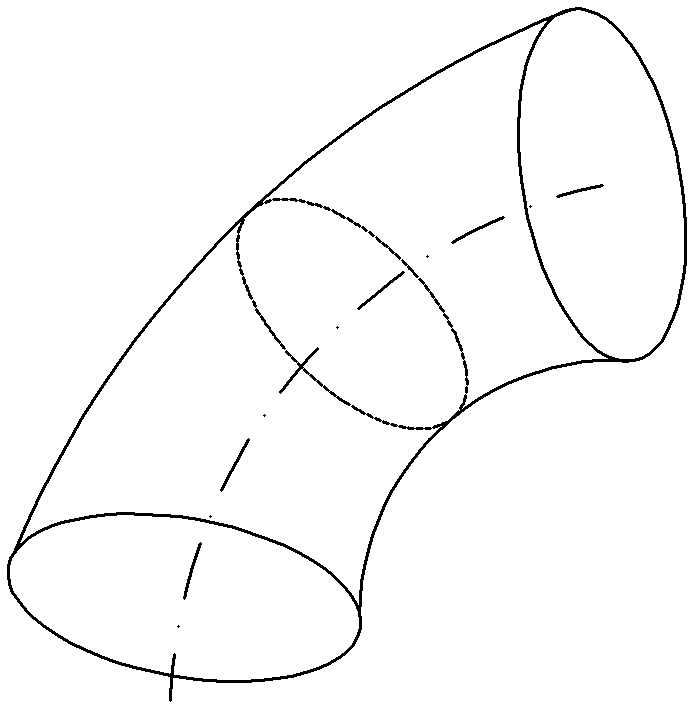
[0162] The non-developable curved surface part is a non-developable curved surface variable-section joint type part, the axis of the non-developable curved surface variable-section joint type part is a curve, and the sections perpendicular to the axis are all circular sections, and the circumference of the circular section is The size of is continuously changing, and the circular section with the smallest circumference appears in the middle of the non-developable surface variable section joint parts;
[0163] Divide the axis into m-1 parts (equal division principle: the spacing should be greater than the motion acc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com