Anti-EpCAM antibodies
A technology of antibody and antigen, applied in the field of binding protein
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0415] Example 1: Novel Antibody
[0416] Considering the need for further tumor-specific antibodies that can be used in cancer therapy, a human antibody was identified that specifically recognizes colon cancer cell lines such as HT29. This antibody can specifically bind EpCAM. A single-chain form of this antibody was cloned into the pHOG21 plasmid containing c-myc and a 6×His-tagged epitope ( Figure 8 ). TG1 bacteria were transformed and scFv was induced by IPTG to express. Binding of purified scFv was confirmed by flow cytometry using an Easycyte flow cytometer.
[0417] sequence
[0418] The nucleotide sequences of the heavy and light chains of the cloned antibodies were sequenced. This antibody was named 3-17I(scFv). The nucleotide and amino acid sequences of the light and heavy chains of 3-17I (scFv) are in figure 1 and shown in Table 1. The CDR regions of the 3-17I light and heavy chains are shown in Table 1.
[0419] This antibody was also produced in its ...
example 2
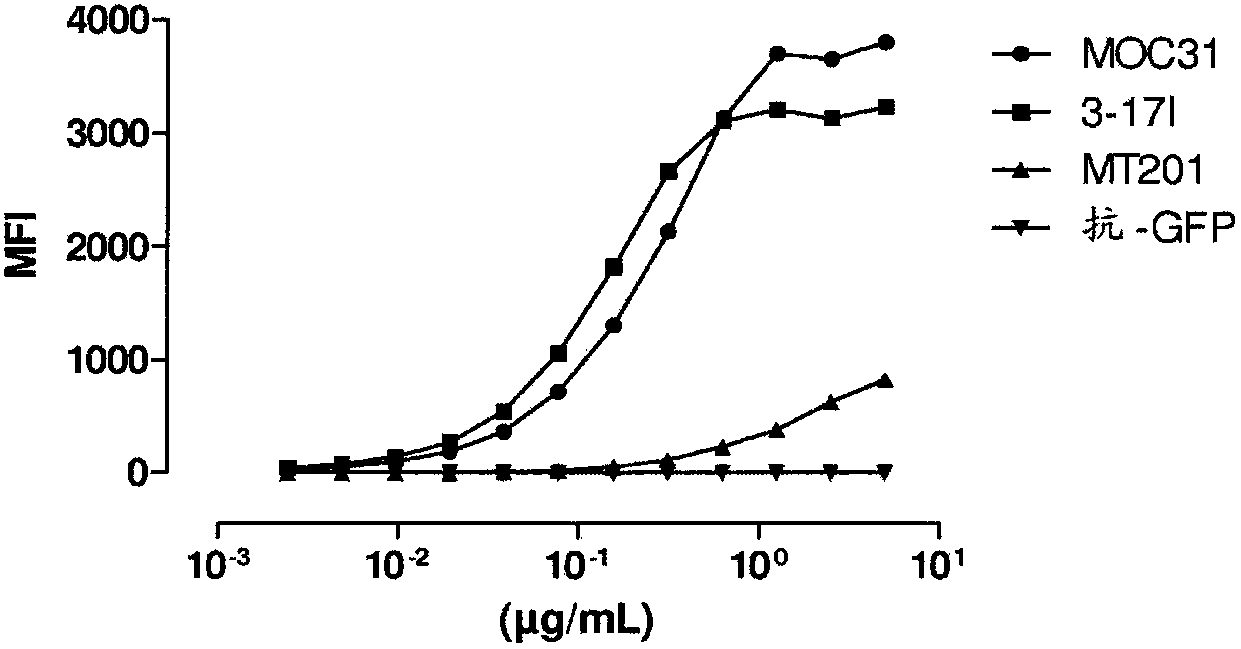
[0432] Example 2: Binding of 3-17I IgG to KatoIII cells
[0433] Flow cytometry was used to analyze the binding of 3-17I IgG to EpCAM positive cells. Anti-EpCAM chimeras (murine variable regions / human constant regions) and fully human antibodies, MOC31 and MT201, respectively, were used as positive controls.
[0434] The amino acid sequences of the complete heavy and light chains of the MT201 IgG and MOC31 IgG antibodies used are shown below. Constant regions are in bold italics.
[0435] MT201 IgG heavy chain (amino acid sequence)
[0436] EVQLLESGGGVVQPGRSLRLSCAASGFTFSSYGMHWVRQAPGKGLEWVAVISYDGSNK
[0437] YYADSVKGRFTISRDNSKNTLYLQMNSLRAEDTAVYYCAKDMGWGSGWRPYYYYGMD
[0438] VWGQGTTVTVSS
[0439]
[0440] MT201 IgG light chain (amino acid sequence)
[0441] ELQMTQSPSSLSASVGDRVTITCRTSQSISSYLNWYQQKPGQPPKLLIYWASTRESGVPDR
[0442] FSGSGSGTDFTLTISSLQPEDSATYYCQQSYDIPYTFGQGTKLEIK
[0443]
[0444] These sequences were deduced from the amino acid sequence of MT201, w...
example 3
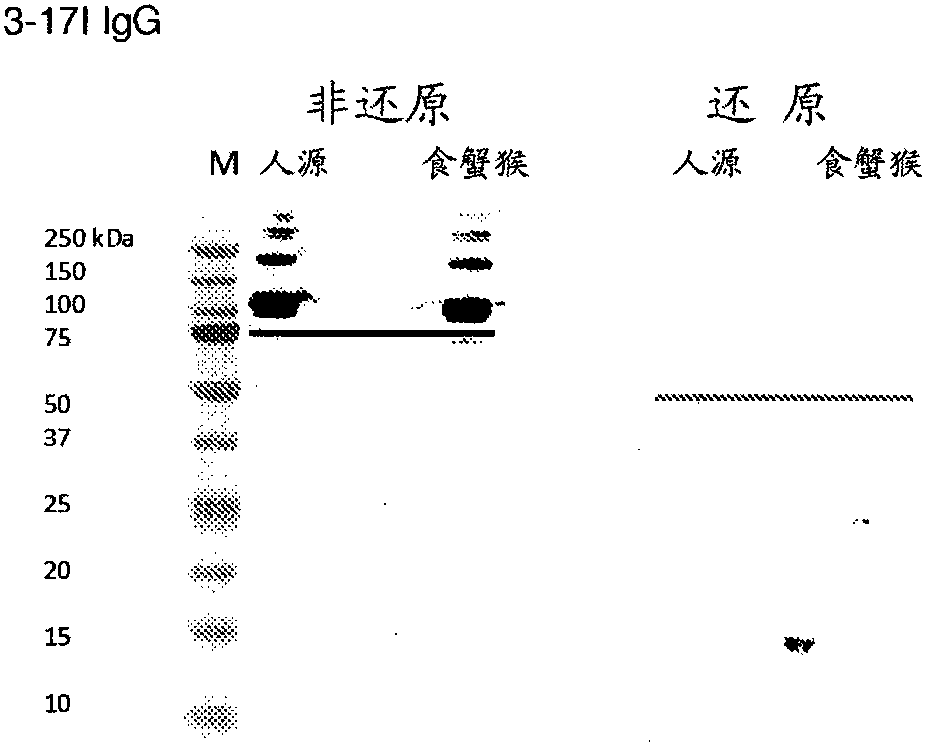
[0455] Example 3: Binding properties of 3-17I IgG
[0456] To determine the ability of 3-17I to bind EpCAM, Western blot analysis, ELISA and BIAcore assays were used.
[0457] Western blot analysis
[0458]To analyze the binding specificity and cross-reactivity of antibodies 3-17I, MT201 and MOC31 to human and cynomolgus EpCAM, sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS -PAGE) and Western blot analysis. All antibodies were in the IgG format and were produced by transiently transfected HEK-293 cells. Antibodies were then purified in Protein A Sepharose (GE Healthcare Uppsala, Sweden) followed by fractionation on two coupled molecular sieve columns, Superdex 200 and Superdex 75. The resulting IgG product exhibited a monomeric purity of >95%. Recombinant human and cynomolgus EpCAM antigens were also produced in HEK-293 cells and purified in one step on protein A sepharose columns. The purity of the tested antigen preparation is higher than 90%. Both Ep...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com