Tangential permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor structure
A permanent magnet synchronous motor and rotor structure technology, applied in the direction of magnetic circuit shape/style/structure, magnetic circuit rotating parts, etc., can solve problems such as occupying the effective length of the rotor, breaking positioning and tension bolts, and unsuitable motors, etc., to achieve Avoid magnetic flux leakage, not easy to break, long service life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025] With reference to accompanying drawing, further illustrate the present invention:
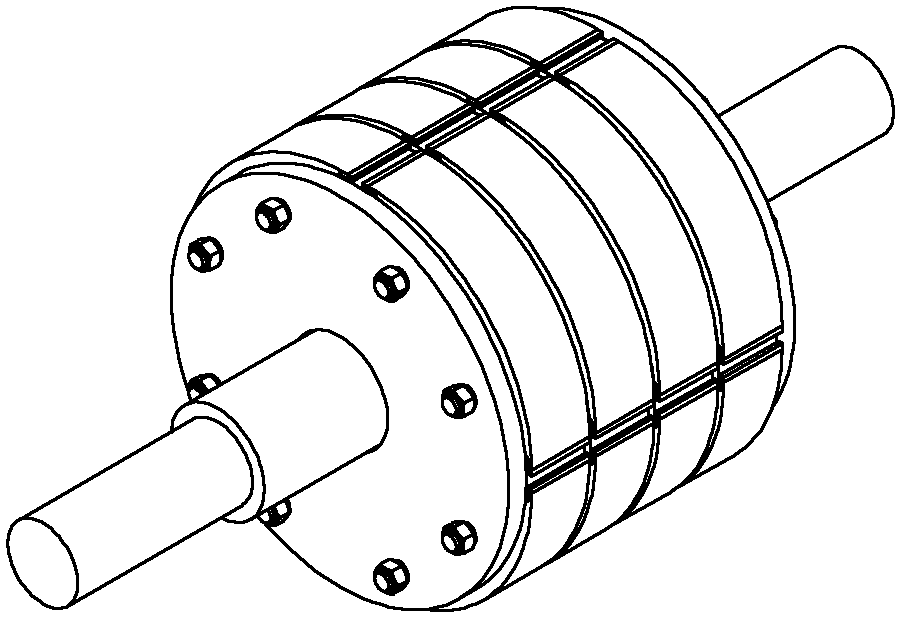
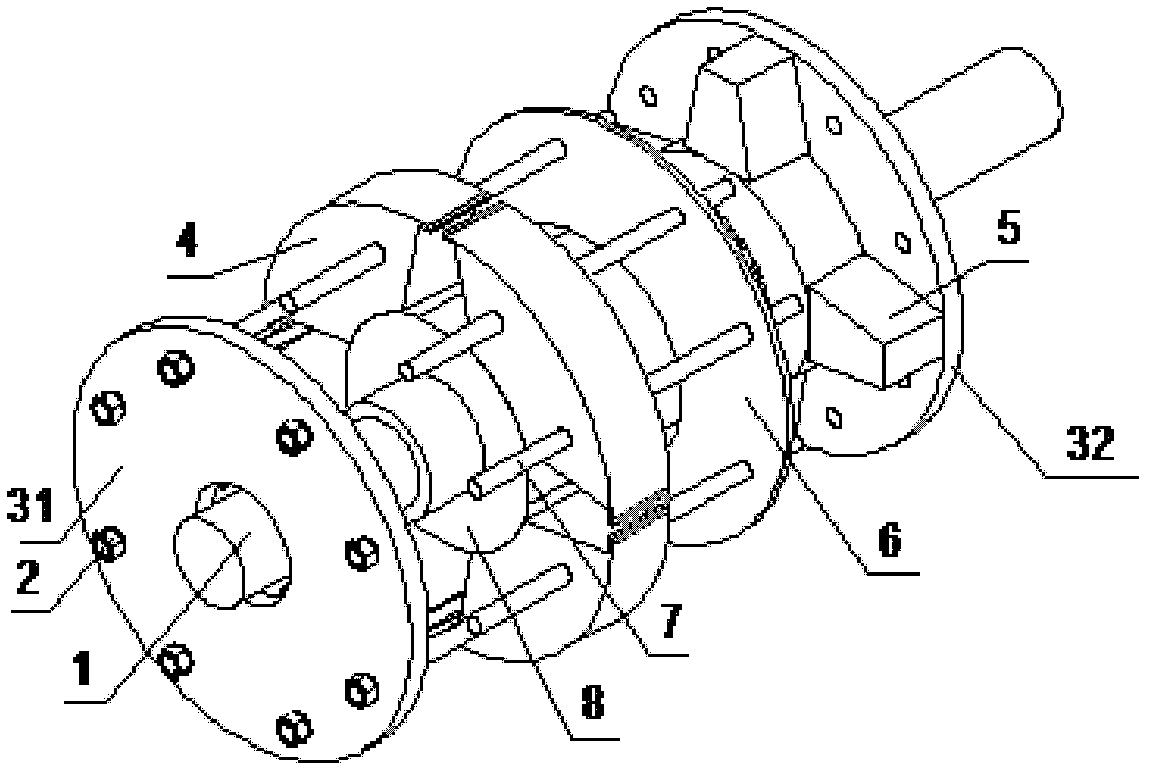
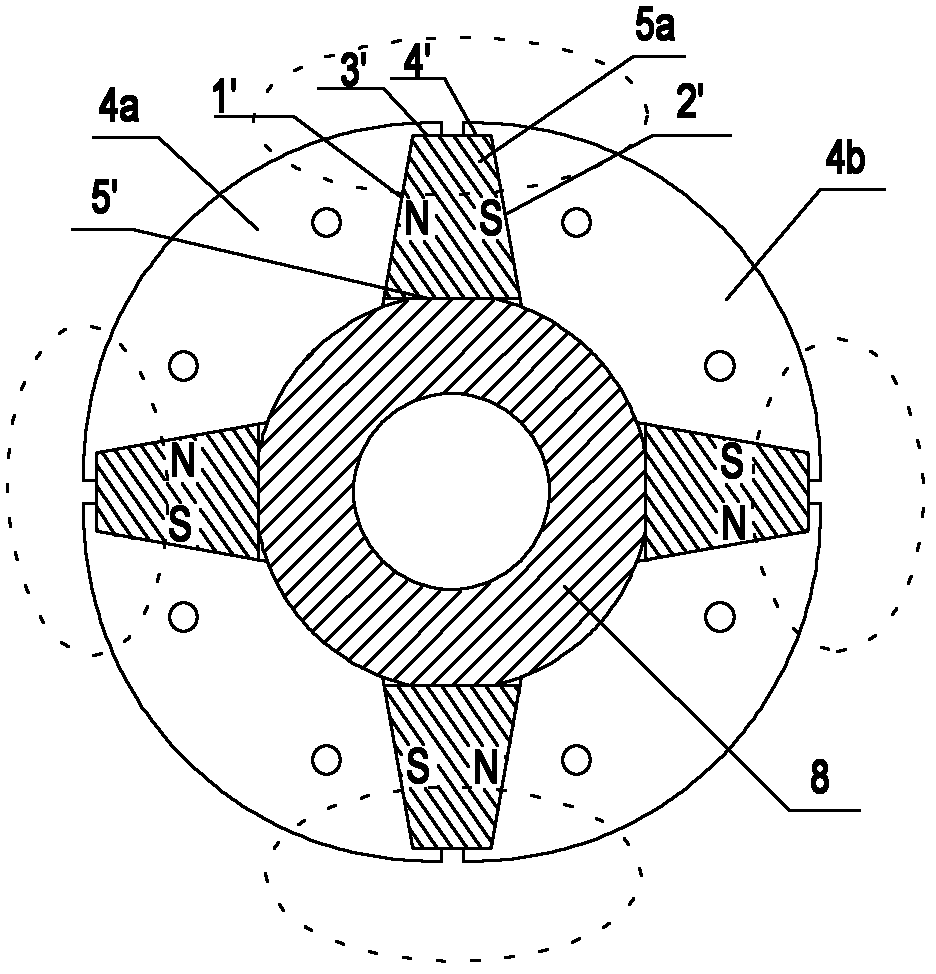
[0026] like figure 1 , figure 2 As shown, the rotor structure of a tangential permanent magnet synchronous motor includes a rotating shaft 1, a magnetic isolation bushing 8 fixedly connected to the rotating shaft 1, permanent magnets 5 and rotor pole shoes 4 evenly distributed along the periphery of the magnetic isolation bushing 8, and respectively The left end plate 31 and the right end plate 32 located at both ends of the magnetic isolation sleeve 8; the permanent magnets 5 and the rotor pole shoes 4 are distributed along the circumference of the magnetic isolation sleeve 8, and the permanent magnets 5 are close to the rotor pole shoes 4. The magnetic isolation sleeve 8 is made of non-magnetic material to prevent magnetic flux leakage inside the rotor.
[0027] Between the two end plates 31 and 32, there are a plurality of rotor separators 6 made of non-magnetic materials. The roto...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com