Evaluation of image processing algorithms
An image processing and algorithm technology, applied in image data processing, 2D image generation, image enhancement, etc., can solve problems such as inappropriateness and error-prone
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
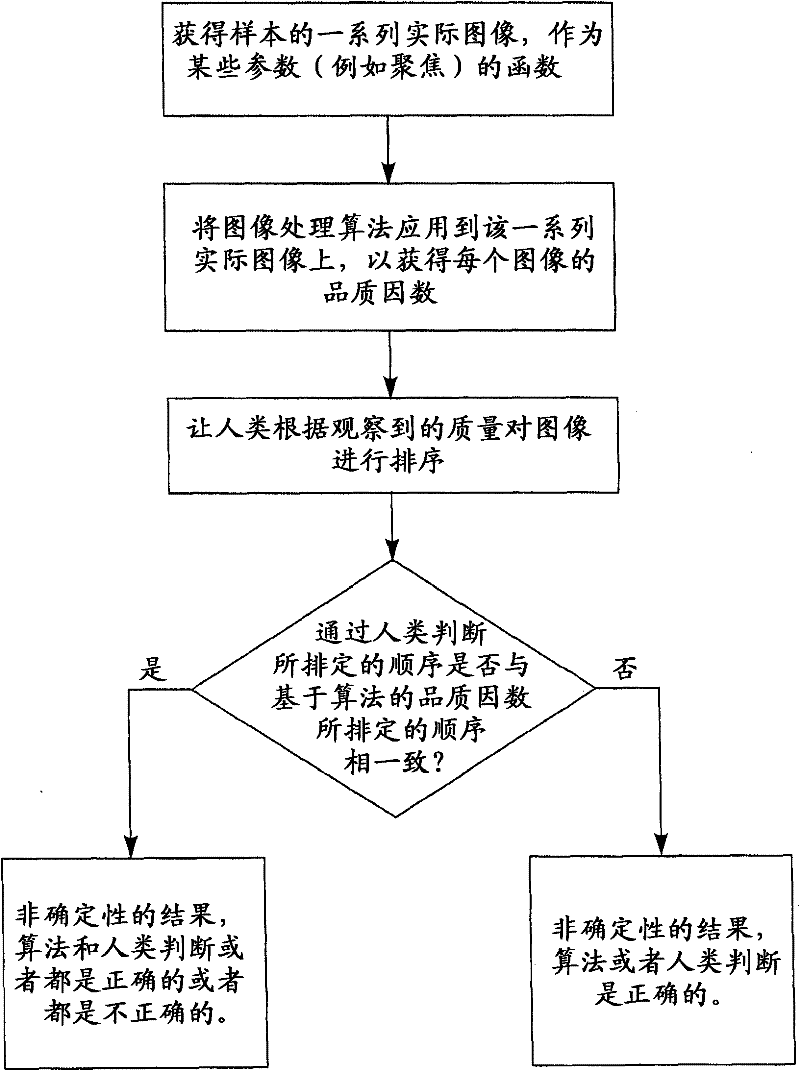
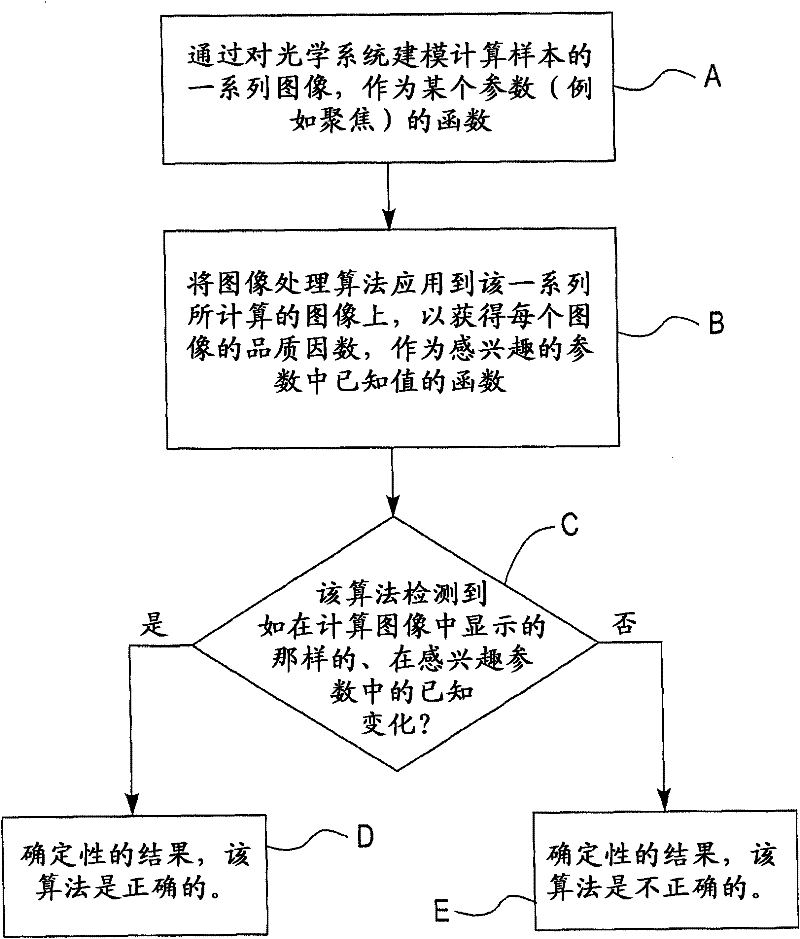
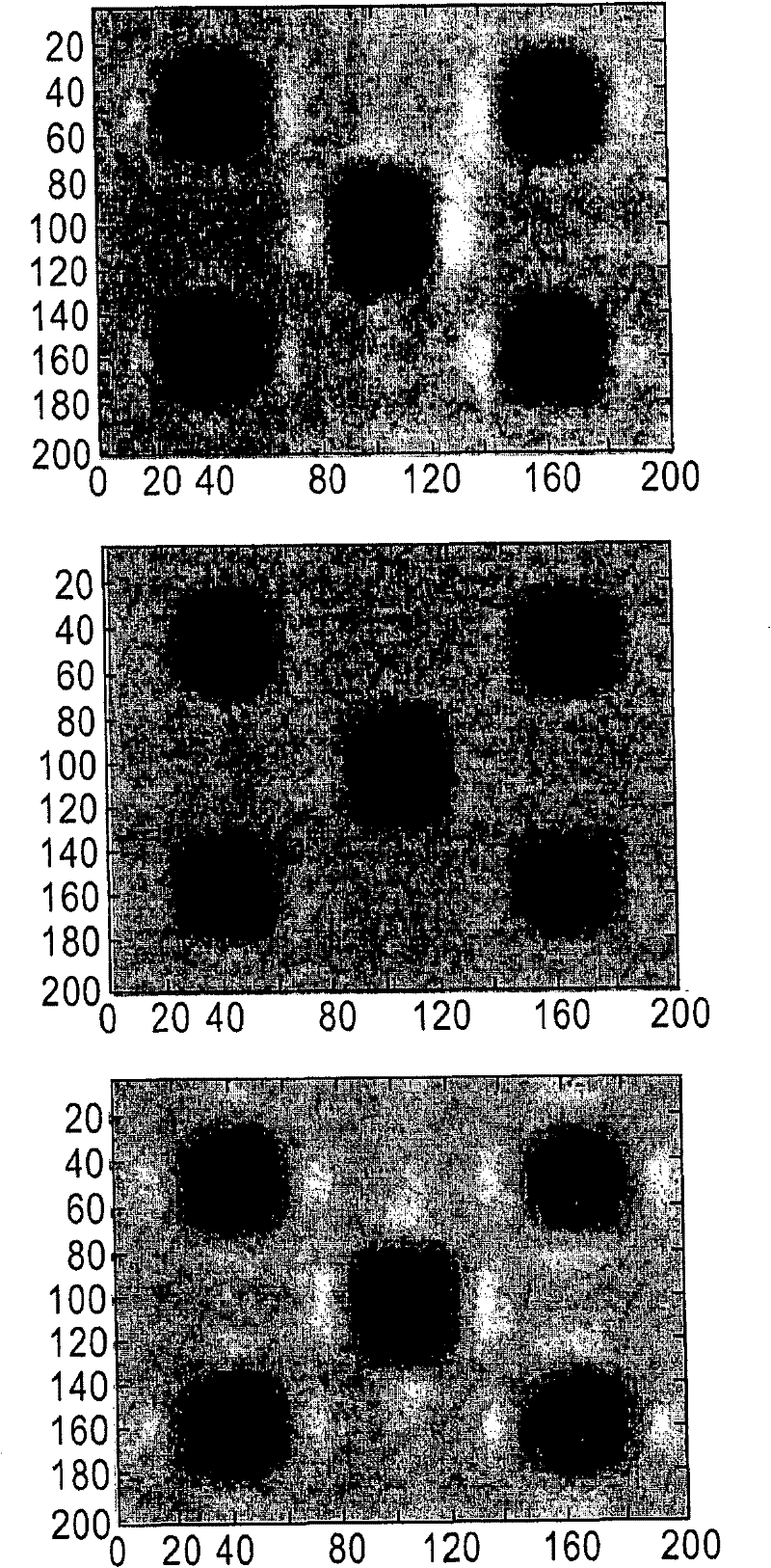
[0024] Image processing algorithms are routinely used to assess the quality of an image or series of images. Algorithms can be used to evaluate, without limitation, for example, the focus, uniformity of illumination, spatial distortion and / or noise of an image, or to detect defects or changes in the spatial extent of an image relative to a standard. The algorithm provides a figure of merit that attempts to select the "best" image from a series of images, or provides a quantitative measure of variation in a series of images. Typically, the performance of an algorithm can be tested using actual images of samples. The testing of the algorithm suffers since the number of real images in most (if not all) cases involves a large number of parameter variations and uncertainties in the parameter values of interest.
[0025] As mentioned above, these algorithms are usually evaluated by comparing the "best" images chosen by the algorithms with those chosen by humans. Unfortunately, h...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com