Electrochemical reactor and method for processing organic pollutant in water
A technology for organic pollutants and water treatment, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problem of unfavorable proximity of positive and negative electrodes, poor treatment effect, and difficult local maintenance, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of reducing plate corrosion, small electrode spacing, and energy consumption reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
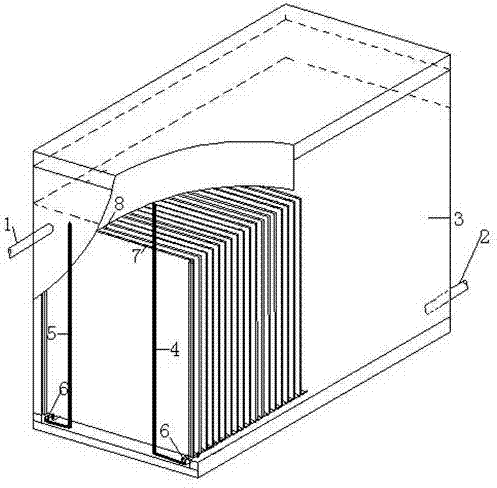
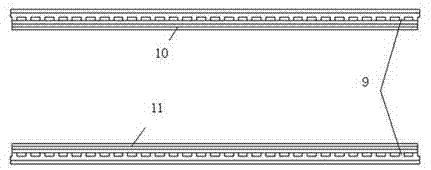
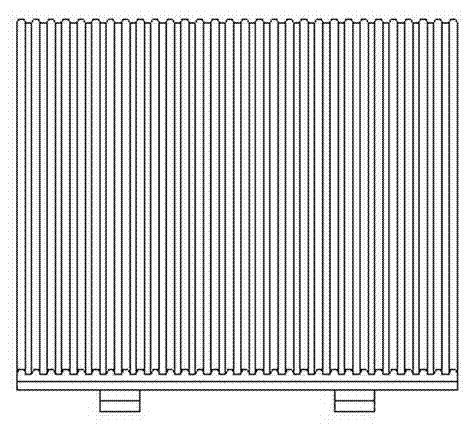
[0026] Embodiment one: see Figure 1 to Figure 4 As shown, an electrochemical reactor for treating organic pollutants in water includes a DC power supply, an electrolytic cell 3 and an electrode assembly arranged in the electrolytic cell 3, and the electrolytic cell 3 is provided with a water inlet 1 and a water outlet 2. The electrode assembly is mainly composed of an electrode frame, a cathode plate 7 and an anode plate 8. The electrode frame and the electrolytic cell 3 are of a split structure. The electrode frame includes insulating two side walls, a cathode conductive strip 10 and an anode conductive strip 11. The cathode conductive strip 10 and the anode conductive strip 11 are respectively fixed on the inner bottom of the two side walls, and the opposite inner sides of the two side walls are respectively provided with longitudinally arranged grooves 9, and the grooves 9 on the side plates are evenly distributed, and the adjacent grooves The distance between 9 is between...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Embodiment 2: The device of Embodiment 1 is used to process pharmaceutical wastewater test
[0029] The pharmaceutical wastewater is diluted 3 times and placed in an electrochemical reactor. The anode uses a titanium-based lead dioxide electrode, the cathode uses a titanium plate electrode, and the cathode and anode each use one piece. The electrode area is 12cm×15cm, and the distance between the cathode and the anode is 2cm. Control current density 12mA / cm 2 , T=20℃, degrade for 10h. See Table 1 for the results.
[0030] Table 1 Test results of treating pharmaceutical wastewater
[0031]
[0032] It can be seen from Table 1 that the chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal rate of wastewater after treatment is 60%, the removal rate of total phosphorus (TP) is close to 100%, and the removal rate of ammonia nitrogen (NH 3 -N) removal rate is about 91%, total nitrogen (TN) removal rate is 76.3%. The lower SUVA can indirectly reflect the better biochemical degradation p...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Embodiment 3: Treatment of chemical wastewater test
[0034] The device of Example 1 was used to treat certain chemical wastewater, and the results are shown in Table 2. The chemical wastewater is diluted 3 times and placed in an electrochemical reactor. The test conditions: the anode uses a titanium-based iridium-tantalum electrode, and the cathode uses a titanium plate electrode. The area of the cathode and anode is 12cm×15cm, 8 pieces are used for the anode and 9 pieces are used for the cathode, the distance between the cathode and the anode is 0.5cm, and I=20A. The test temperature is 10°C, and the degradation takes 3 hours.
[0035] Table 2 Test results of chemical wastewater treatment
[0036]
[0037] The result shows that the device of the invention can effectively treat chemical wastewater.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com