Method for estimating modulation frequency and starting frequency of linear frequency-modulated signal
A technology of linear frequency modulation signal and starting frequency, which is applied in the field of signal processing, and can solve problems such as limited engineering application, precision limitation, and slow operation speed.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
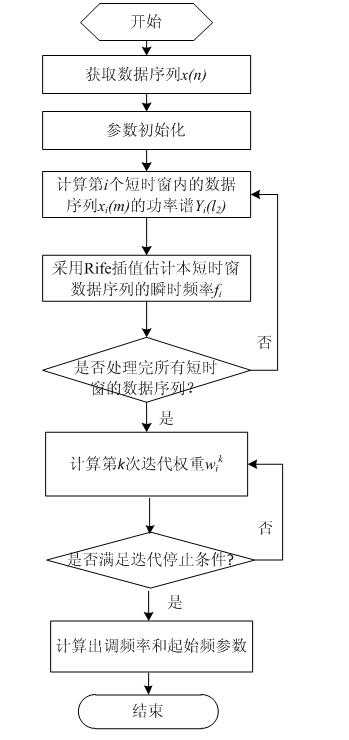
[0074] Example 1: Initialize the parameters first, set the short-time window length M=128, the short-time window moving step L=64, and the weight correction factor σ 1 =1, the maximum iteration threshold K=2000 and the precision control index ε=10 -6 , to calculate the total number of short-time windows The number of initialization window moves i=1, and the number of iterations k=1.
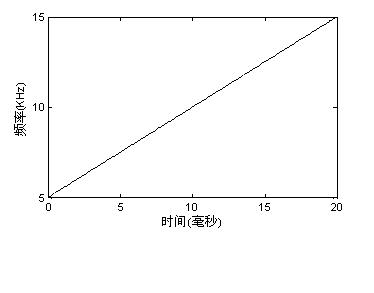
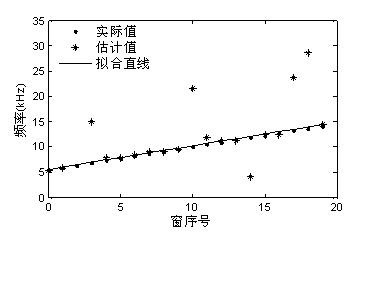
[0075] Then move the time window, use the Rife interpolation algorithm to estimate the instantaneous frequency estimated value of the data sequence in each short time window, and obtain the instantaneous frequency estimated value sequence f i ,i=1,2,...,20, as shown in Table 1
[0076] Table 1 The instantaneous frequency sequence estimated by Rife interpolation algorithm
[0077]
[0078] where f 3 , f 4 , f 11 , f 15 , f 18 , f 19 are outliers present in the instantaneous frequency estimate.
[0079] Finally, the iterative calculation is carried out by weighted least squares linear...
Embodiment 2
[0080] Example 2: Initialize the parameters first, set the short-time window length M=128, the short-time window moving step L=64, and the weight correction factor σ 1 =100, the maximum iteration threshold K=100 and the precision control index ε=10 -3 , to calculate the total number of short-time windows The number of initialization window moves i=1, and the number of iterations k=1.
[0081] Then move the time window, use the Rife interpolation algorithm to estimate the instantaneous frequency estimated value of the data sequence in each short time window, and obtain the instantaneous frequency estimated value sequence f i ,i=1,2,...,20;
[0082] Finally, the iterative calculation is carried out by weighted least squares linear fitting method, and the estimated value of the modulation frequency of the chirp signal is estimated The relative error is starting frequency estimate f ^ l = ...
Embodiment 3
[0083] Example 3: Initialize the parameters first, set the short-time window length M=256, the short-time window moving step L=128, and the weight correction factor σ 1 =1000000, the maximum number of iterations threshold K=100000 and the precision control index ε=10 -16 , to calculate the total number of short-time windows The number of initialization window moves i=1, and the number of iterations k=1.
[0084] Then move the time window, use the Rife interpolation algorithm to estimate the instantaneous frequency estimated value of the data sequence in each short time window, and obtain the instantaneous frequency estimated value sequence f i ,i=1,2,...,9;
[0085] Finally, the iterative calculation is carried out by weighted least squares linear fitting method, and the estimated value of the modulation frequency of the chirp signal is estimated The relative error is starting frequency estimate f ^ l ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com