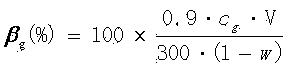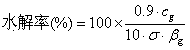Pretreatment method for high-efficiency enzyme hydrolysis of wood waste fiber
A waste fiber and pretreatment technology, applied in the direction of fermentation, etc., can solve the problems of polluting the environment, destroying the ecology, and the waste fiber cannot be fully and effectively recycled, and achieve the goals of reducing volume consumption, saving water consumption, and high enzymatic hydrolysis effect Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] 1) Preprocessing
[0027] Weigh 30 g of wood waste fiber with an absolute dry weight and place it in an autoclave, add 3.893 g of ferric chloride, and add an appropriate amount of water to adjust the solid-liquid ratio to 1:8 (unit: g / mL), stir and mix After uniformity, start to heat up, and keep warm for 20 min after reaching the highest temperature of 180 °C. Immediately after the pretreatment, steam is released, unloaded and cooled for solid-liquid separation, and the pretreated fibers are washed with water until neutral for biological enzyme hydrolysis.
[0028] 2) Cellulase hydrolysis rate of pretreated raw materials
[0029] Weigh 1 g of pretreated fibers with a dry weight in a 100 mL Erlenmeyer flask, add acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer solution (pH = 4.8), and mix in a constant temperature shaker at a temperature of 50 °C and a speed of 150 rpm 15 min to wet and disperse the fibers. Add 20 FPU of cellulase and 25 CBU of β-glucosidase and add water so that t...
Embodiment 2
[0031] 1) Preprocessing
[0032] Weigh 30 g of wood waste fiber with an absolute dry weight and place it in an autoclave, add 3.893 g of ferric chloride, and add an appropriate amount of water to adjust the solid-liquid ratio to 1:8 (unit: g / mL), stir and mix After uniformity, start to heat up, and keep warm for 0 min after reaching the highest temperature of 200 °C. Immediately after the pretreatment, steam is released, unloaded and cooled for solid-liquid separation, and the pretreated fibers are washed with water until neutral for biological enzyme hydrolysis.
[0033]2) Cellulase hydrolysis rate of pretreated raw materials
[0034] Weigh 1 g of pretreated fibers with a dry weight in a 100 mL Erlenmeyer flask, add acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer solution (pH = 4.8), and mix in a constant temperature shaker at a temperature of 50 °C and a speed of 150 rpm 15 min to wet and disperse the fibers. Add 20 FPU of cellulase and 25 CBU of β-glucosidase and add water so that the...
Embodiment 3
[0036] 1) Preprocessing
[0037] Weigh 30 g of wood waste fiber with an absolute dry weight and place it in an autoclave, add 3.893 g of ferric chloride, and add an appropriate amount of water to adjust the solid-liquid ratio to 1:8 (unit: g / mL), stir and mix After uniformity, start to heat up, and keep warm for 240 min after reaching the highest temperature of 180 °C. Immediately after the pretreatment, steam is released, unloaded and cooled for solid-liquid separation, and the pretreated fibers are washed with water until neutral for biological enzyme hydrolysis.
[0038] 2) Cellulase hydrolysis rate of pretreated raw materials
[0039] Weigh 1 g of pretreated fibers with a dry weight in a 100 mL Erlenmeyer flask, add acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer solution (pH = 4.8), and mix in a constant temperature shaker at a temperature of 50 °C and a speed of 150 rpm 15 min to wet and disperse the fibers. Add 20 FPU of cellulase and 25 CBU of β-glucosidase and add water so that ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com