Wind power blade damage monitoring and positioning system based on wireless acoustic emission sensor network
An acoustic emission sensor, wind power blade technology, applied in network topology, wireless communication, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of poor scalability, high installation and maintenance costs, and achieve the effects of simple configuration, convenient installation and maintenance, and convenient use.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
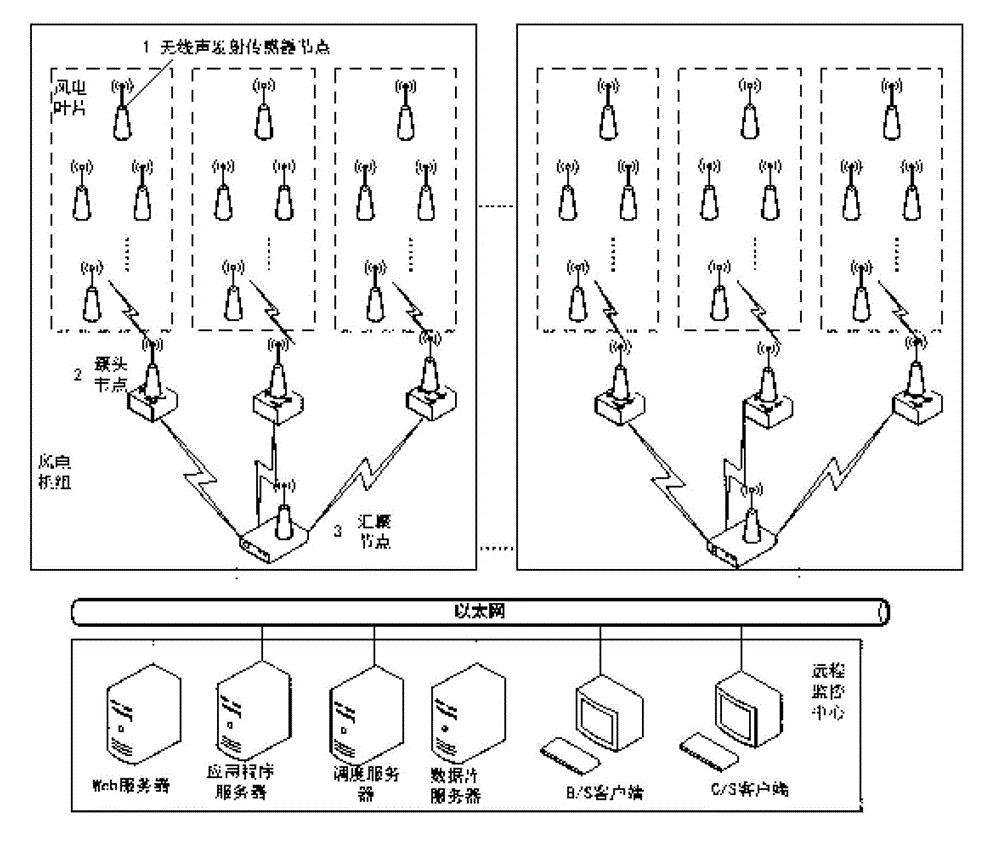
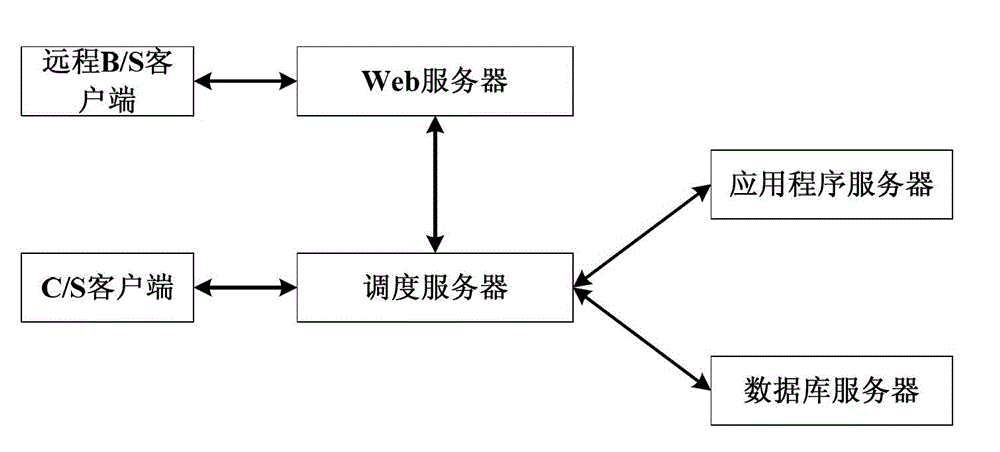
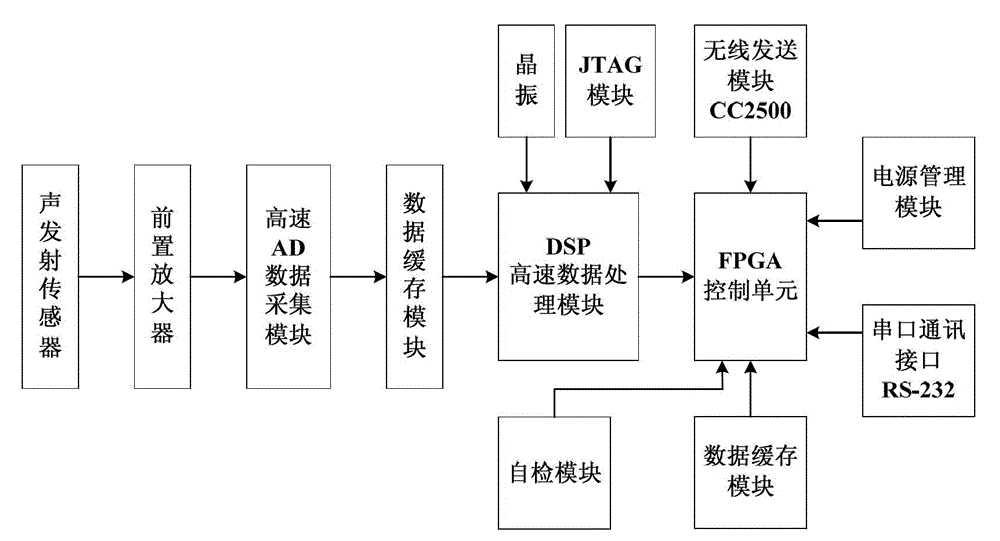
[0036] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of a wind turbine blade damage monitoring and positioning system based on a wireless acoustic emission sensor network. The user selects the position of the blade to be monitored according to the monitoring requirements, which mainly consists of three parts: the root, the shell, and the keel (that is, the reinforcement rib or the reinforcement frame). Where the stress concentration changes greatly, the corresponding wireless acoustic emission sensor nodes are deployed in these key positions. Since each blade is tens of meters long, the serious attenuation of the acoustic emission signal by the blade material and the sensing range of the acoustic emission sensor should be considered when deploying the wireless acoustic emission sensor node. The wireless acoustic emission sensor nodes are responsible for collecting crack data. The wireless acoustic emission sensor nodes deployed on each blade form a cluster, and each cluster is assigned ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com