Calibration of a base coordinate system for an industrial robot
A technology of industrial robots and robots, applied in the directions of instruments, manipulators, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of inaccuracy, difficulty in adjustment, and inaccessibility, and achieve the effect of fast, easy-to-use, and easy-to-use calibration methods.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
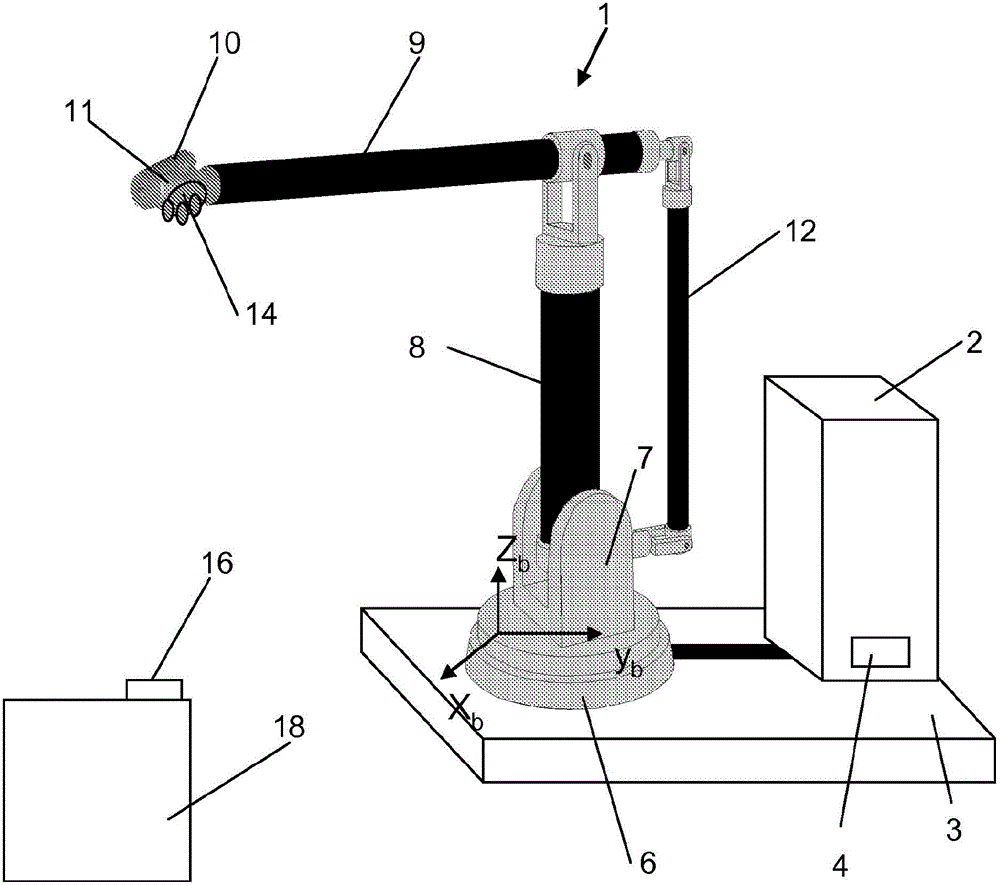
[0037] figure 1 An example of a portable robot is given in which a lightweight robot 1 including a robot controller 2 is mounted on a movable platform 3 . The portable robot is positioned in a robot cell that defines the robot's work area. The robot controller 2 is also mounted on the platform, but there are cases when each robot cell can have its own controller, then only the robot will be on the platform. The robot 1 is connected to the controller 2 through a cable, and when docking, the robot, tool and controller are electrically connected to the unit using contacts 4 . The robot comprises a fixed base part 6 bearing a stand 7 rotatable about a first axis. This bracket 7 supports a lower arm 8 which is rotatable about a second axis. The lower arm 8 supports an upper arm 9 rotatable about a third axis. The upper arm 9 supports a wrist 10 rotatable about fourth, fifth and sixth axes. The wrist 10 supports a wrist interface 11 , hereinafter referred to as a wrist flange, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com