Microbial Engineering For The Production Of Chemical And Pharmaceutical Products From The Isoprenoid Pathway
A terpenoid, pathway technology for application in the field of microbial engineering for the production of chemical and pharmaceutical products from isoprenoid pathways that can address dependencies, productivity and scalability limitations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
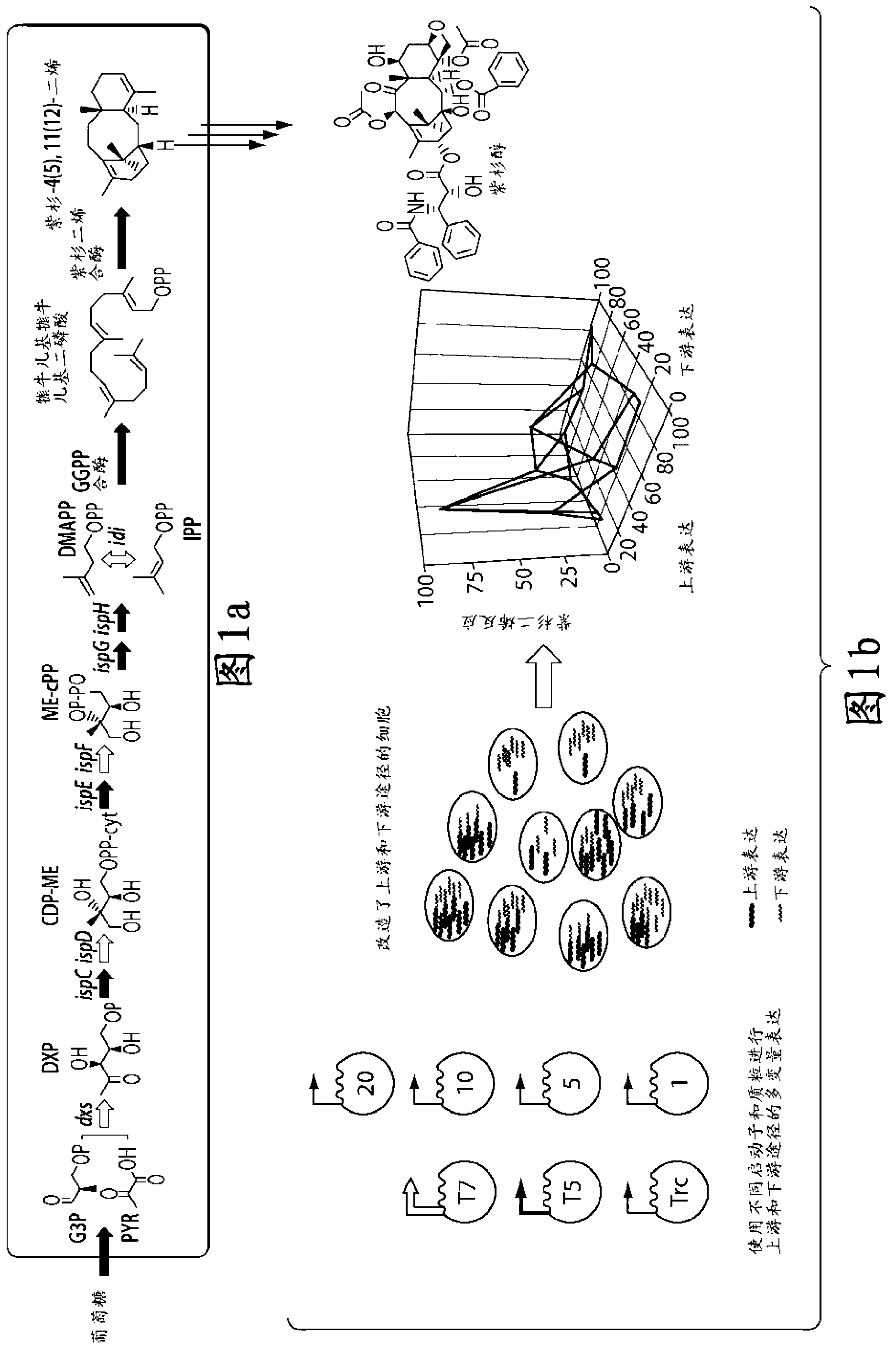
[0121] Example 1: Taxadiene accumulation shows a strong nonlinear dependence on the relative strength of the upstream MEP and downstream taxadiene synthesis pathways.
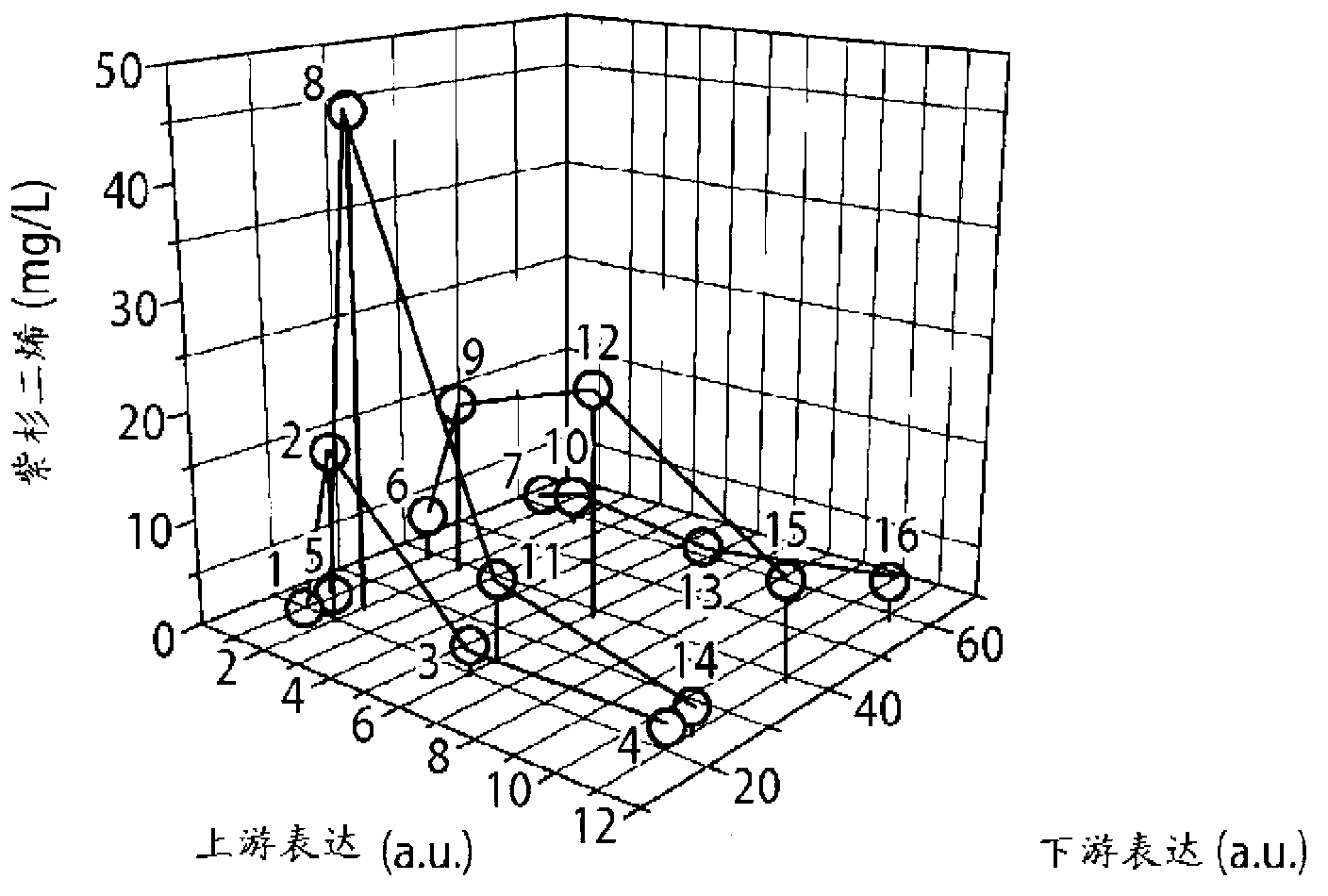
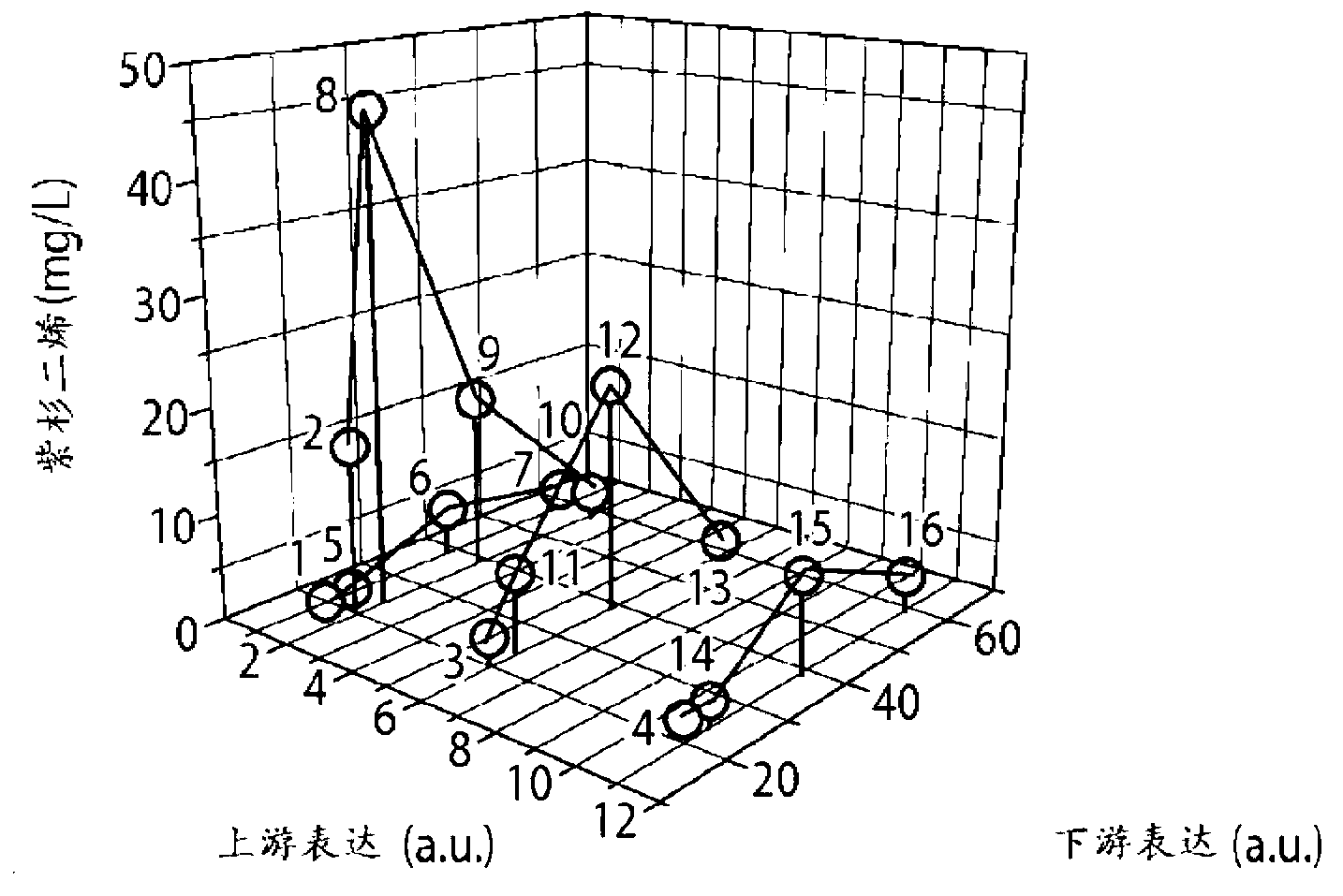
[0122] Figure 1b Multiple approaches to combining promoter and gene copy number to modulate relative flux (or intensity) through upstream and downstream pathways of taxadiene synthesis are depicted. A total of 16 strains were constructed to solve the bottleneck of the MEP pathway and to achieve an optimal balance between it and the downstream taxadiene pathway. Figure 2a , b summarizes the taxadiene accumulation results for each of these strains, where Figure 2a highlights the dependence of taxadiene accumulation on the upstream pathway when the downstream pathway is constant, whereas Figure 2b is the dependence of the upstream pathway on the downstream pathway when the strength of the upstream pathway is constant (expression of the upstream and downstream pathways is calculated from the reported promoter...
Embodiment 2
[0124] Example 2: Chromosomal integration and fine-tuning of upstream and downstream pathways to further enhance taxadiene production.
[0125] In order to provide sufficient downstream pathway strength while minimizing the metabolic burden brought by the plasmid37, two new sets of strains (strains 25-28 and 29-32) were designed, in which the downstream pathway was placed in a strong under the control of the promoter (T7), while maintaining a relatively low copy number of 5 and 10, respectively. As can be seen( Figure 2c ), maintaining taxadiene maxima at high downstream pathway strengths (strains 21-24), while obtaining monotonic responses at low downstream pathway strengths (strains 17-20, Figure 2c ). This observation prompted us to construct two additional sets of 4 strains that maintained the same level of downstream pathway strength as before but expressed very low levels of the upstream pathway (strains 25-28 and 29-32, Figure 2d ). Furthermore, the operons of th...
Embodiment 3
[0127] Example 3: Metabolites negatively correlated with taxadiene production and identification of metabolites.
[0128] Metabolome analysis of previously engineered strains identified metabolic byproducts that correlated strongly with pathway expression levels and taxadiene production (Figure 3 and Figure 8). Although the chemical identity of this metabolite is unknown, we speculate that it is an isoprene by-product that causes pathway shunting and has negatively correlated as a direct variable with taxadiene production in engineered bacteria (Fig. 3 and Fig. 8). A key attribute of our best strains is a delicate balance of reduced accumulation of this metabolite leading to higher taxadiene production. This balance can be regulated by different levels from chromosomes or different plasmid copy numbers, using different promoters, resulting in significantly different accumulation of taxadiene.
[0129] Subsequently, by GC-MS,1 H and 13 C nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spect...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| absorbance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com