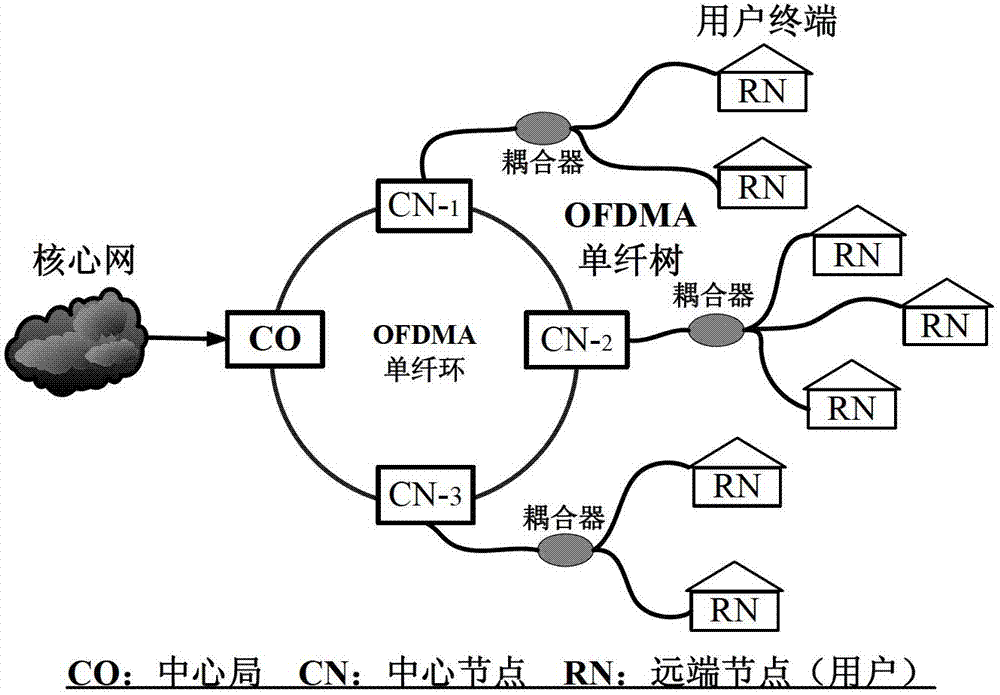
Reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer on basis of OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Modulation)
A technology of optical add-drop multiplexer and polarization beam splitter, which is applied in the field of optical communication, can solve the problems of residual interference signal, interference of adjacent frequency bands of add-drop multiplexer, and decrease of frequency band utilization ratio between adjacent frequency bands, and achieves Guaranteeing orthogonality, reducing requirements, and improving the effect of frequency band utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
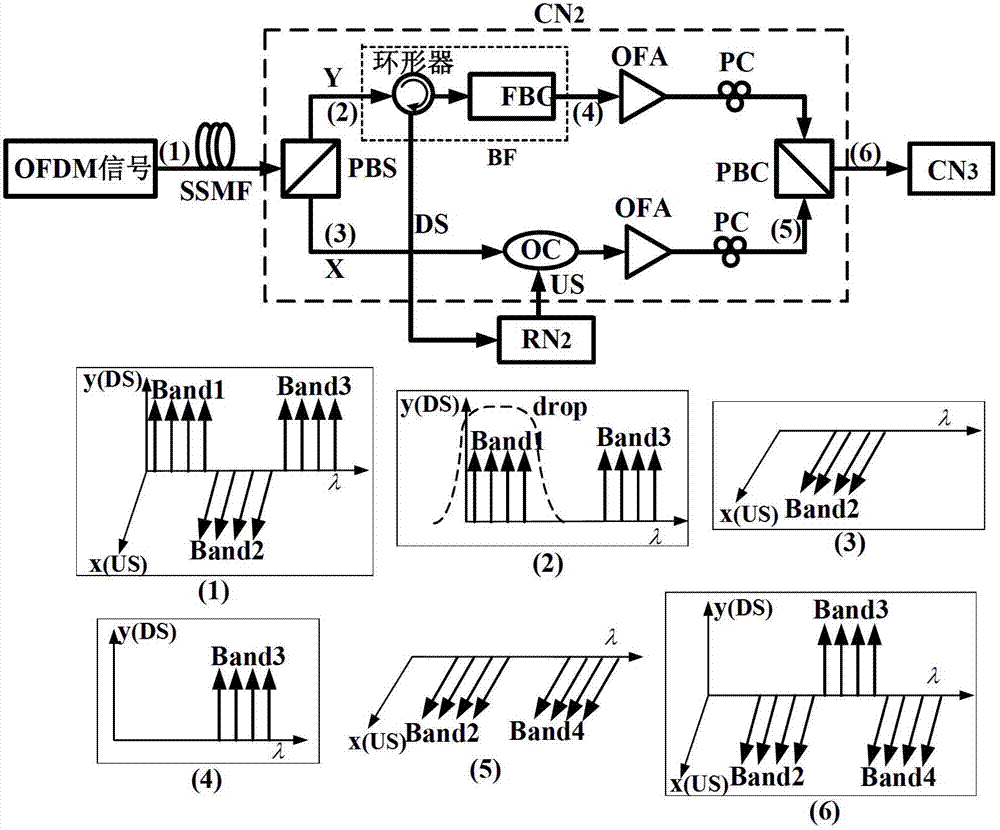
[0052] figure 2 It is a structural diagram and a schematic spectrum diagram of a specific embodiment of the OFDMA-based reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer of the present invention.
[0053] Such as figure 2 As shown, in this embodiment, a fixed allocation method is adopted. In the case of fixed allocation, the central node CN of the reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer (ROADM) is figure 1 The second central node CN2 in , all central nodes have the same structure, here we take the second central node CN2 as an example. The so-called fixed allocation means that each remote node RN only needs a certain fixed service. For example, the remote node RN1 only needs the data of the frequency band Band1, and the remote node RN2 only needs the data of the frequency band Band2, and each remote node The services required by RN are different. In this case, each central node CN does not need to carry all the signals, and the frequency band required by the remote node RN...
Embodiment 2
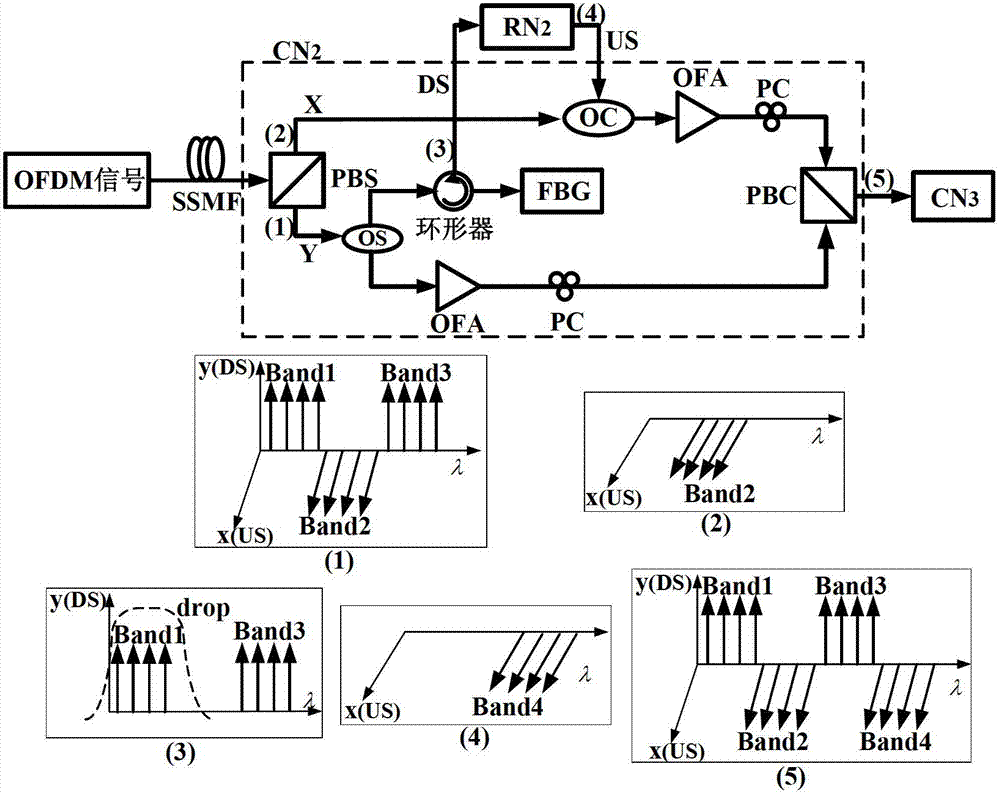
[0059] image 3 It is a structural diagram and a schematic spectrum diagram of another embodiment of the OFDMA-based reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer of the present invention.
[0060] Such as image 3 As shown, in this embodiment, a dynamic allocation method is adopted. The central node CN that implements the reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer (ROADM) under dynamic allocation is the second central node CN2, and all central nodes have the same structure, and the second central node CN2 is still used as an example here. The so-called dynamic allocation means that each remote node RN may need any kind of service, a certain kind of service is not fixedly corresponding to a certain remote node RN, and the service allocation is carried out dynamically according to the demand. The main difference between it and fixed allocation is that each central node CN needs to carry signals of all frequency bands.
[0061] In this embodiment, the configuration of the mult...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com