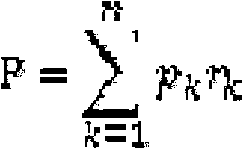Taxi riding car-sharing coating method
A technology of taxis and taximeters, applied in the field of pricing, can solve problems such as unfairness and difficulty in weighing the interests of all parties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] A taxi sharing method for pricing, comprising the steps of:
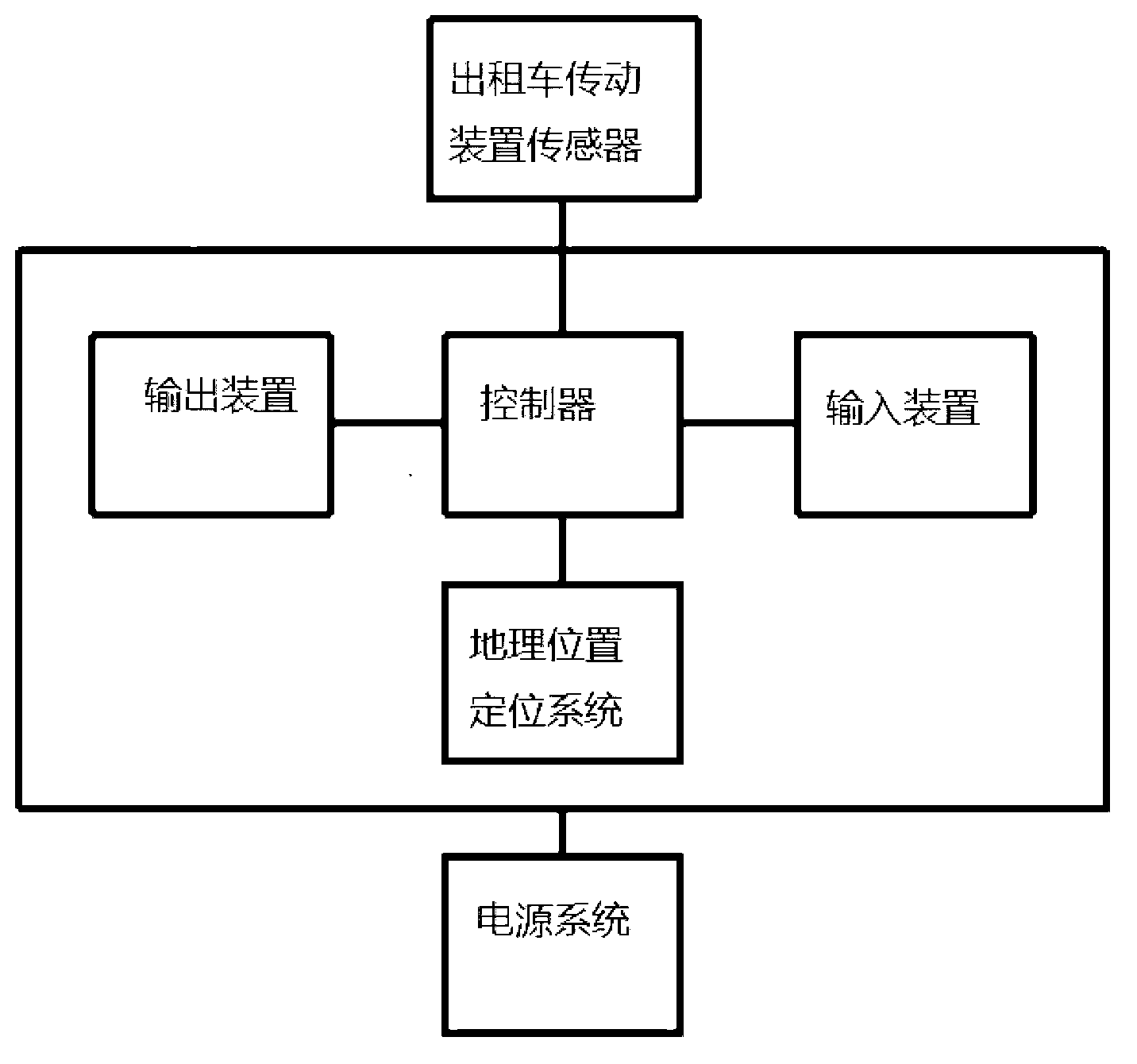
[0024] (1) Install a taximeter and a geographic location positioning system on the taxi. The taximeter consists of an input device, an output device, a controller and a power supply system, and is connected to the taxi transmission sensor. The output device includes a display screen and a printer. The controller is a conventional microcomputer, capable of managing the components connected to it, including the functions of a conventional microcomputer, with central processing unit, memory, external memory, clock and other components;
[0025] (2) When passengers get on the bus, they input the passing place, destination, number of passengers and other information through the input device, send it to the controller, display it on the display screen, and record the passenger’s boarding time, so as to obtain the passenger’s boarding time. order;
[0026] (3) When other passengers get on the bus, input through the...
Embodiment 2
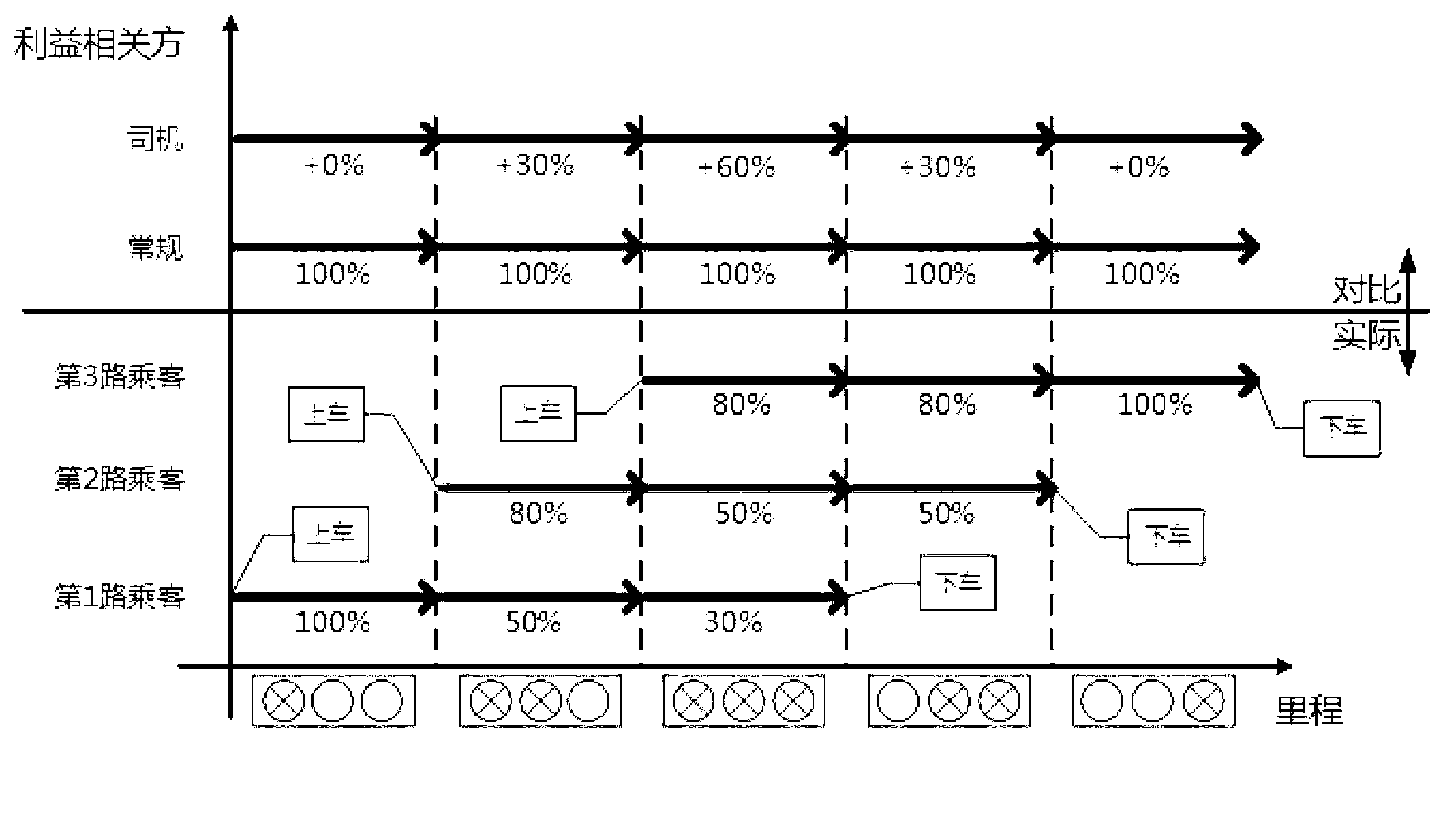
[0032] For example, suppose there are 3 routes of passengers, 2 passengers in the first route, 1 passenger in the second route and 1 passenger in the third route. Passengers on the three routes have different departure and destination points and board the bus sequentially. On the way, the passenger on the third route requested a special route for a priced segment. According to the joint points, the respective journeys are divided into 7 pricing segments (see Table 1 and Table 2 for details)
[0033] Table 1 Taxi sharing methods
[0034]
[0035] Table 2 Pricing description of "shared ride" sub-pricing segment
[0036]
[0037] According to Table 2, determine the standard fee p according to the mileage of the pricing section and the actual road conditions k (that is, the standard fare for completing the k-th segment of the journey in the case of a single ride), r k According to factors such as the number of passengers, boarding sequence, and whether the current passen...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Such as figure 2 As shown, for the first passenger, r in the first pricing segment k =1, r of the second pricing segment k =0.5, the third pricing segment r k =0.3; the second passenger, r in the first pricing segment k =0.8, the r of the second pricing segment k =0.5, the r of the third pricing segment k =0.5; the third passenger, r in the first pricing segment k =0.8, r in the second pricing segment k =0.8, r in the third pricing segment k =1.
[0040] The driver realizes profit in the case of pulling more passengers, and the passenger also saves costs when carpooling is allowed. If pulling one passenger, the driver is charged the original fee, and the passenger needs to pay all the charges; in the case of pulling two passengers, The driver's total charge will increase by 30%, the first passenger's payment will be reduced by 50%, and the second passenger's payment will be reduced by 20%. In the case of three passengers, the driver's total charge will increase...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com