A minimally invasive drilling positioning tool for spinal canal expansion
A tool and spinal canal technology, applied in the field of minimally invasive drilling positioning tools for spinal canal expansion, to achieve the effects of preventing shaking, being easy to hold by hand, and simple in structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
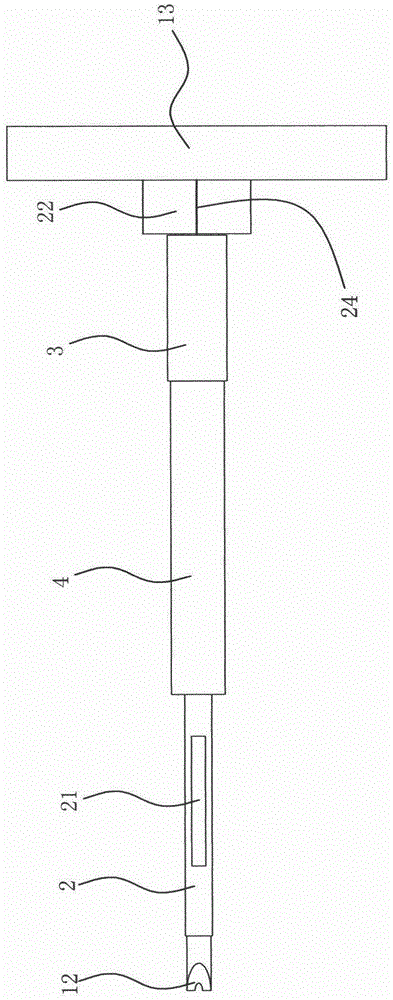
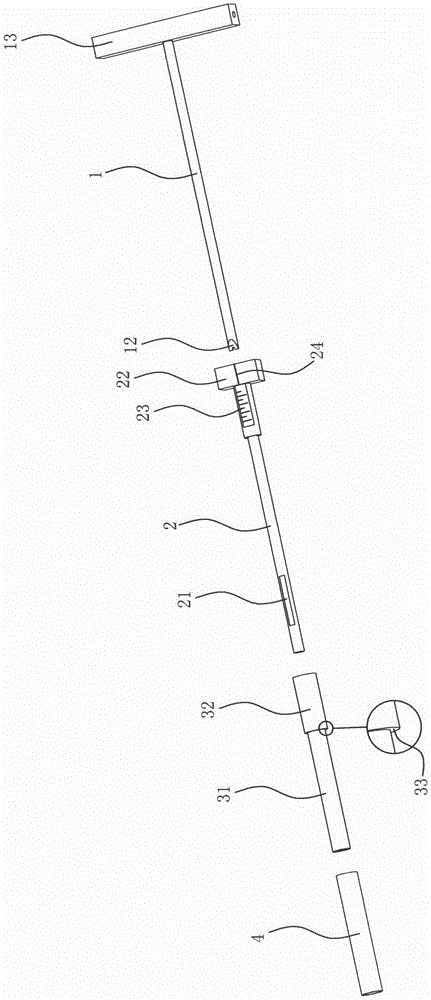
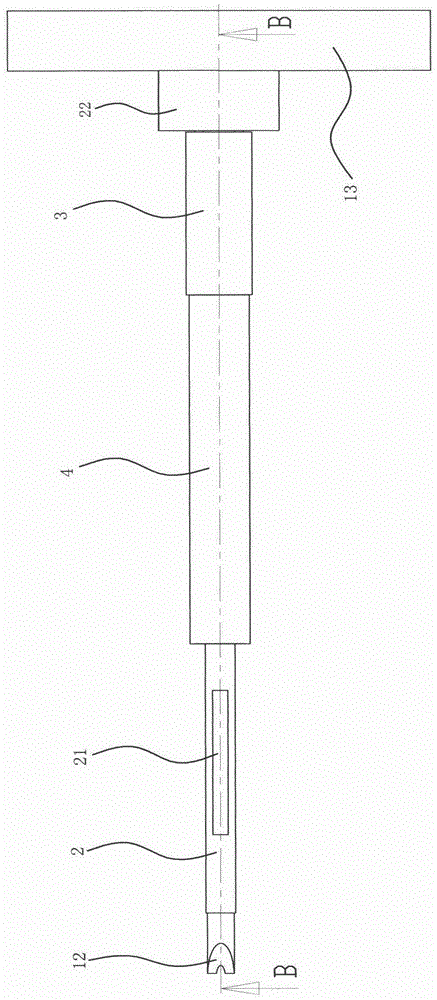
[0028] Embodiment one: if Figure 1 to Figure 4 As shown, a minimally invasive drilling positioning tool for spinal canal expansion includes a drill rod 1, a sleeve rod 2 slidingly socketed with the drill rod 1, a positioning screw sleeve 3 threadedly socketed with the sleeve rod 2, and The positioning screw sleeve 3 is matched with the fixed sleeve 4, and the drill rod 1 is provided with a through hole 11 in the axial direction. The through hole 11 is used to allow the positioning guide pin to pass through the Insert the through hole, then take out the drill pipe, and then insert the tool to be replaced through the through hole. During the replacement process, the positioning guide pin and the through hole play a positioning role, so that when the tool is replaced, the working position is always positioned constant.
[0029] The drill bit 12 of the drill rod 1 extends out of the sleeve rod 2, the length of the sleeve rod 2 is greater than the length of the positioning screw ...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Embodiment 2: On the basis of the above embodiments, the length of the fixing sleeve 4 is the same as that of the positioning screw sleeve 3, which ensures that once the fixing sleeve 4 contacts the surface of the bone, the positioning screw sleeve 3 and the sleeve rod 2 will be fixed The sleeve stops and will not continue to extend into the borehole. In addition, in order to prevent the rotating positioning screw from touching the surface of the bone when the tool is working, the length of the fixing sleeve 4 is greater than the length of the socket section 31 . The fixed sleeve 4 forms a certain distance between the socket section 31 of the positioning screw sleeve 3 and the surface of the bone.
Embodiment 3
[0034] Embodiment 3: The improvement with the above embodiment is that, as Figure 6 As shown, the fixed sleeve 4 is movably sleeved on the sleeve rod 2 and leans against the positioning screw sleeve 3 , and the positioning screw sleeve 3 is threadedly connected with the sleeve rod 2 . The difference between this solution and the above-mentioned solution is that the fixed sleeve 4 is directly placed on the sleeve rod 2 , and the rear end of the fixed sleeve 4 abuts against the positioning screw sleeve 3 . When carrying out the drilling operation, when the front end of the fixed sleeve 4 leaned against the surface of the bone, the rear end promptly leaned against the positioning screw sleeve 3, thereby preventing the positioning screw sleeve 3 and the sleeve rod 2 and the drilling rod 1 from drilling further. In comparison, this scheme has a simpler structure. The socket relationship between the fixed sleeve 4 and the positioning screw sleeve 3 is cancelled.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com