Method for calculating probability of dangerous failure on demand (PFD) and probability of dangerous failure per hour (PFH) in two out of four channel logic structure system
A technology of channel logic and calculation method, which is applied in the field of evaluation of non-common cause safety failure probability based on PFD and PFH based on two-out-of-four logic architecture, which can solve problems such as errors, failure to provide four-channel safety calculation formulas, and time-consuming
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
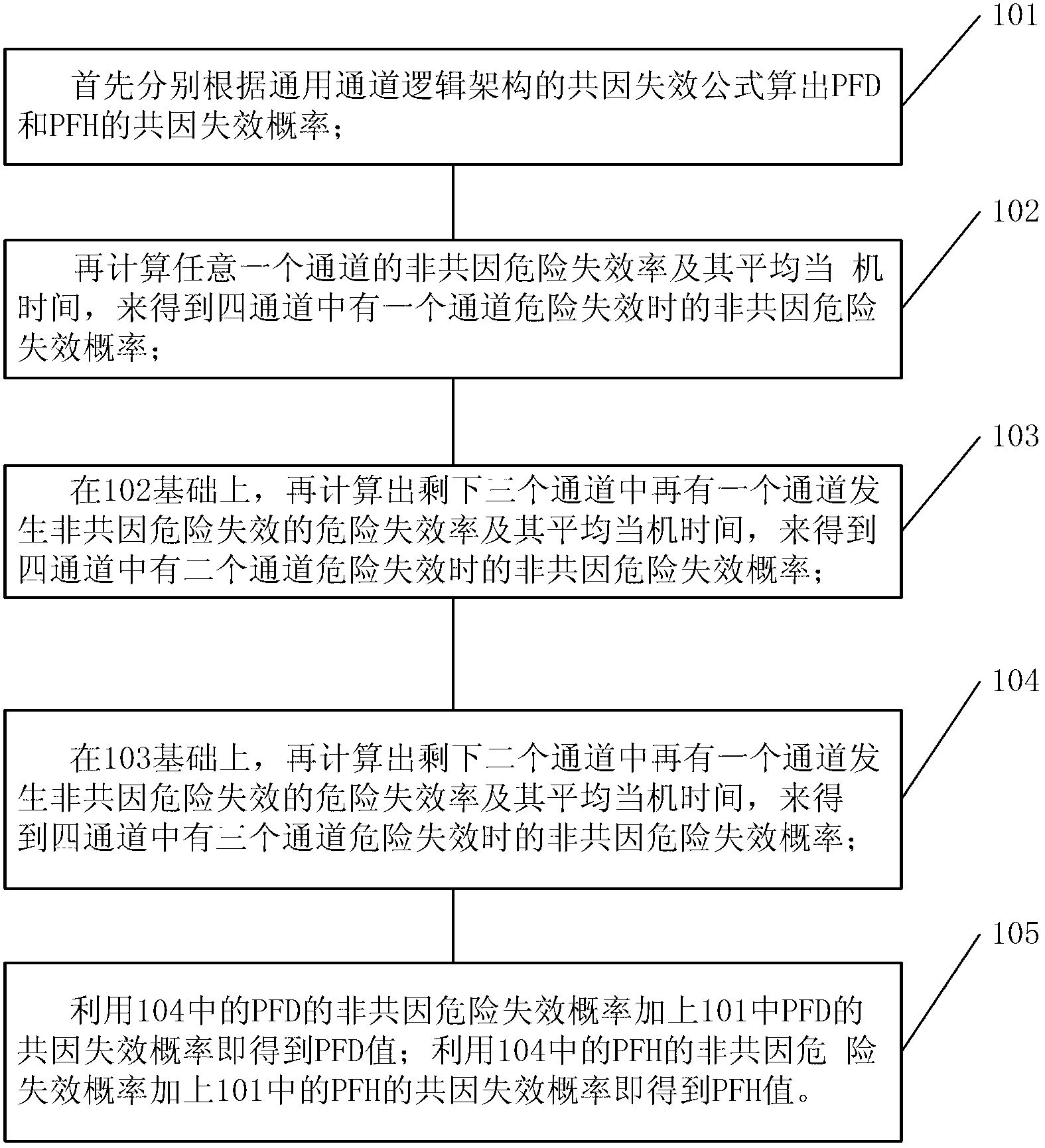
[0052] Because the basic idea of IEC61508 is to first analyze the dangerous failure rate and average downtime of the current system, and then use the above data to calculate the dangerous failure probability of the current system. Therefore, this scheme uses the basic formula given by IEC61508 to derive the scheme of the present invention.
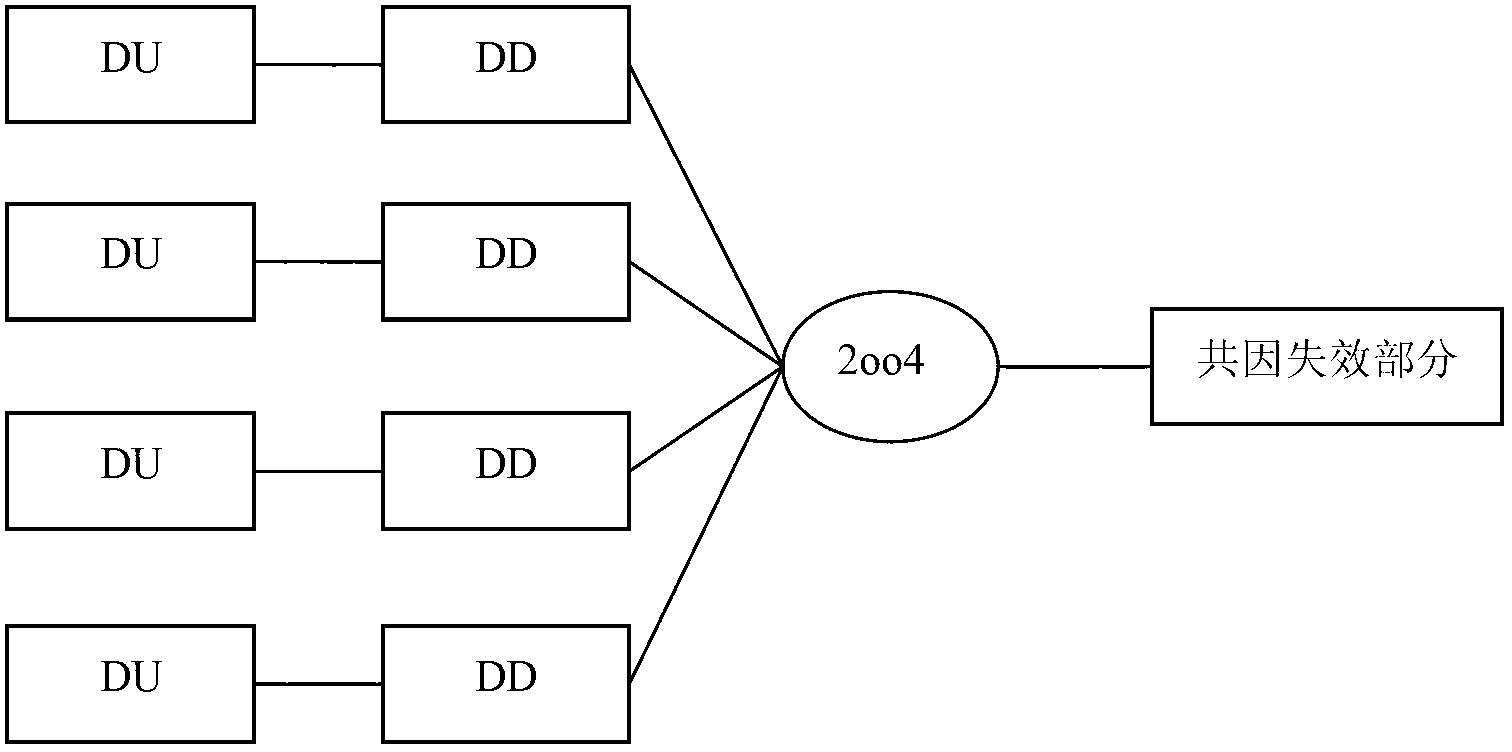
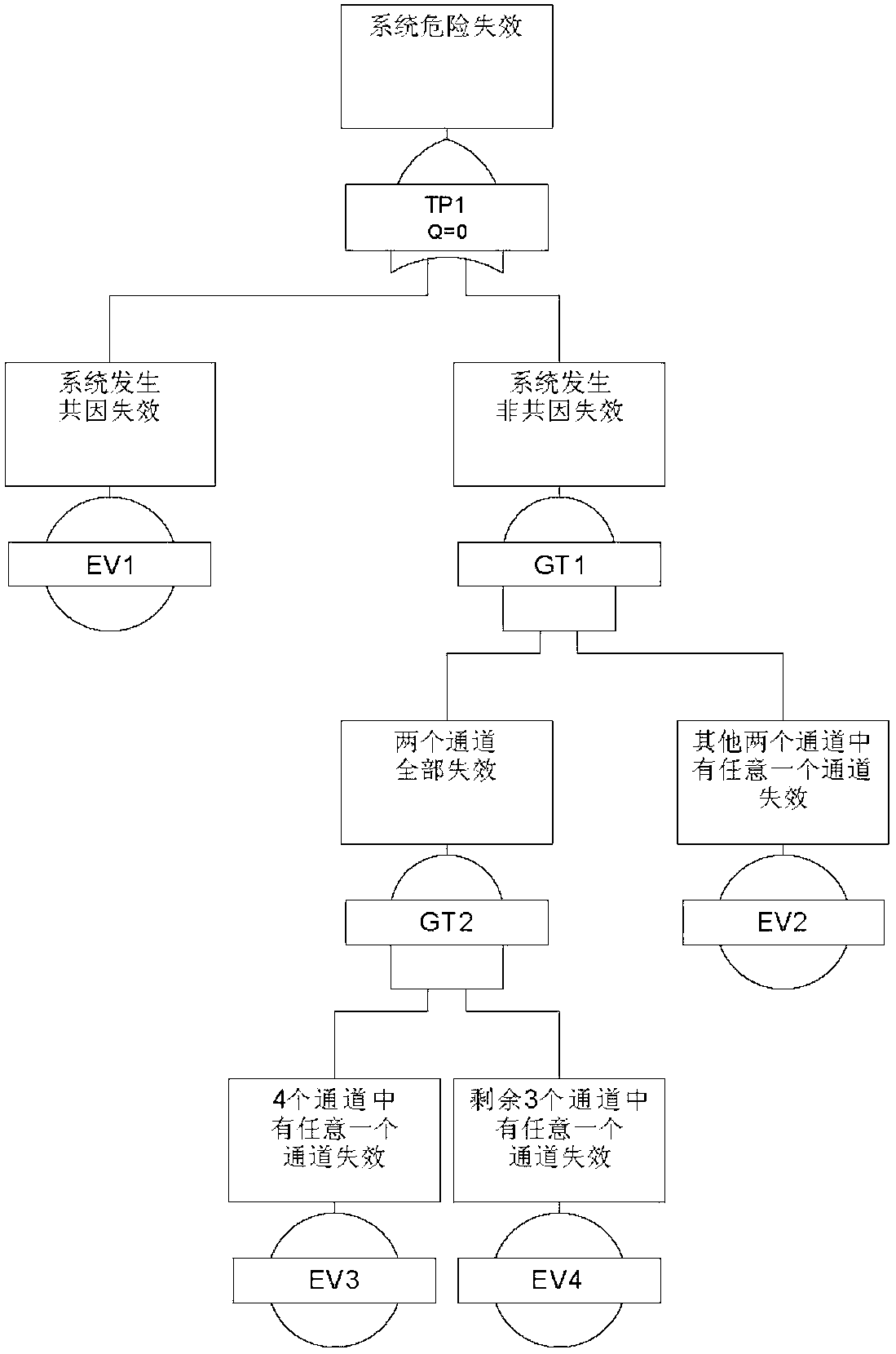
[0053] Such as figure 1 As shown, in order to better explain the derivation process of the formula of the present invention, the system of the four-out-two architecture is represented in the form of a reliability block diagram, where the faults of each of the four channels include DD (diagnosable dangerous fault) and DU (Dangerous faults cannot be diagnosed). 2oo4 means that the relationship between the four channels is two out of four, that is, if two of the four channels are normal, the system is normal. The common cause failure part means that four channels will fail due to a common cause. figure 2 It is an explanation of the dangerou...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com