Optical scanning device based on MEMS (Micro-electromechanical Systems) micromirror
An optical scanning and micro-mirror technology, applied in optics, optical components, mirrors, etc., can solve the problems of small scanning range and complex optical path structure, and achieve the effect of simple structure, extended scanning range and wide scanning range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
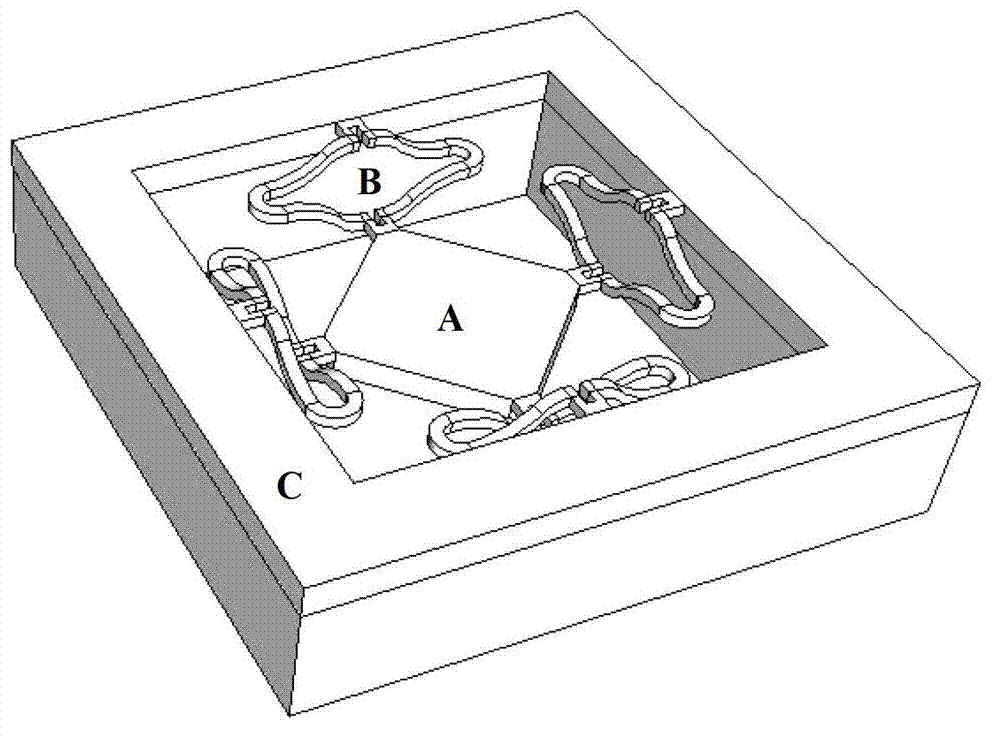
[0032] The optical scanning device in this embodiment, such as Figure 5 As shown, it includes: an optical collimator 1 , a mirror 2 , a MEMS micromirror 3 , a sleeve 4 , and an exit window 5 . In order to prevent the optical path from being blocked and realize circular scanning, the MEMS micromirror in this embodiment is an electromagnetically driven two-dimensional MEMS micromirror that does not need wire connection. In order to make the structure more compact, such as Figure 7 As shown, the middle part of the mirror 2 is hollow, and the shape and size of the hollow part are adapted to the external shape and size of the optical collimator. The mirror 2 is sleeved outside the optical collimator 1 through the hollow part. The whole mirror surface of the reflector 2 is a semi-conical shape with a tapered mouth pointing to the MEMS micromirror 3 . The optical collimator 1 , mirror 2 and MEMS micromirror 3 are all sealed in the casing 4 to protect each optical device, wherein ...
Embodiment 2
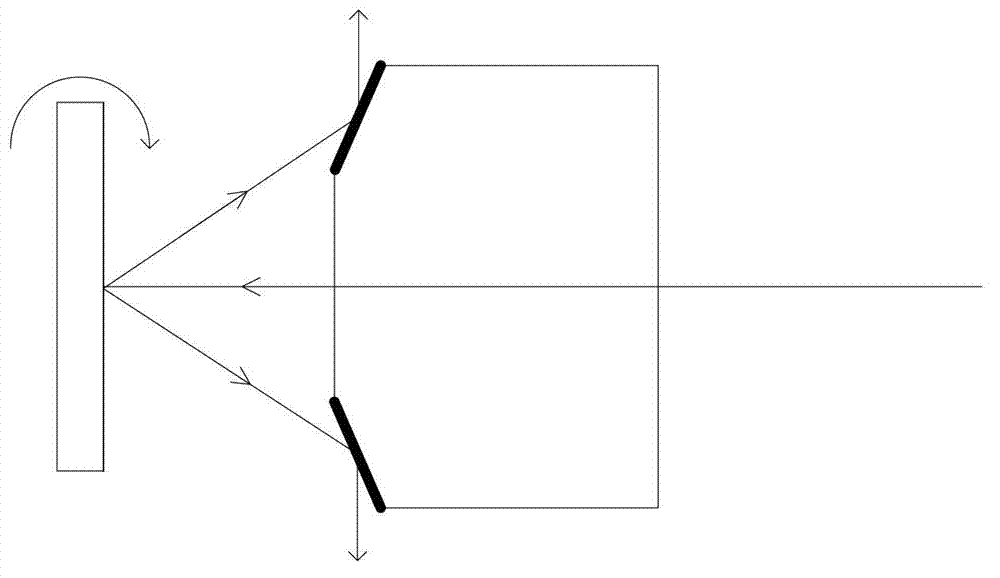
[0035] The optical scanning device in this implementation also includes: optical collimator 1, mirror 2, MEMS micromirror 3, sleeve tube 4, exit window 5, its structure is as follows Image 6 shown. In the present embodiment, the mirror surface of reflector 2 is a semi-conical shape with a tapered mouth pointing to the light source as a whole; correspondingly, according to the reflection direction of reflector 2, the head of sleeve tube 4 is a transparent exit window 5 as a whole; MEMS micromirror 3 is fixed on the side wall of the casing 4 through the pillar 6, in order not to block the light, the pillar 6 is made of transparent material. The rest of this example is the same as Example 1.
[0036] The incident light emitted by the light source from the left is collimated by the optical collimator 1 and passes through the reflector 2, then hits the mirror surface of the MEMS micromirror 3, and the mirror surface of the MEMS micromirror 3 reflects the light to the outer circle...
Embodiment 3
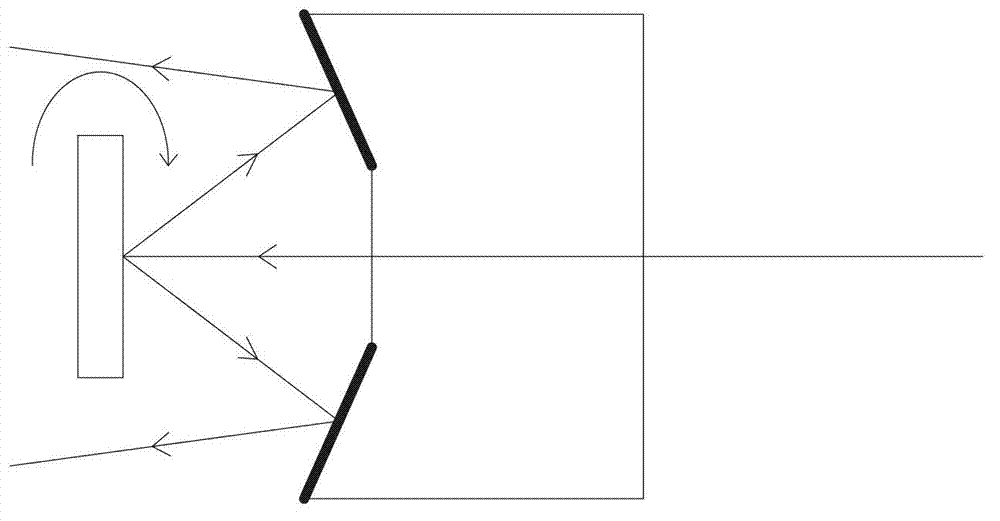
[0038] The optical scanning device in the present embodiment also includes: optical collimator 1, mirror 2, MEMS micromirror 3, sleeve pipe 4, exit window 5, and its structure is as follows Figure 7 shown. In the present embodiment, the mirror surface of reflector 2 is made of two coaxial semi-conical shapes, as shown in the figure, the semi-conical cone opening of the outer ring points to the MEMS micromirror 3, and the semi-conical cone opening of the inner ring points to the light source , according to the description of Embodiments 1 and 2, it can be seen that the reflective mirror surface of the outer ring will reflect light to the side, and the reflective mirror surface of the inner ring will reflect light forward; correspondingly, the exit window 5 in this embodiment is as shown in the figure , consisting of the head of the casing 4 and a ring connected to the head of the casing 4, which is equivalent to the combination of the exit windows in Embodiment 1 and Embodimen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com