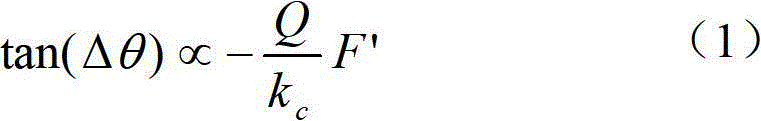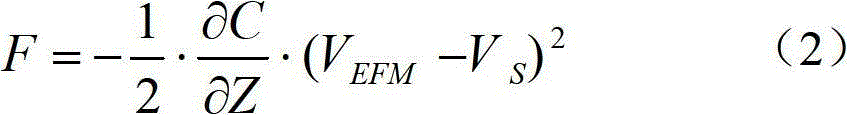Method for measuring surface potential by using electrostatic force microscope
A technology for measuring surfaces and microscopes, applied in measuring devices, scanning probe microscopy, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of limited measurement range of Kelvin microscope surface potential and achieve the effect of reducing drift
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
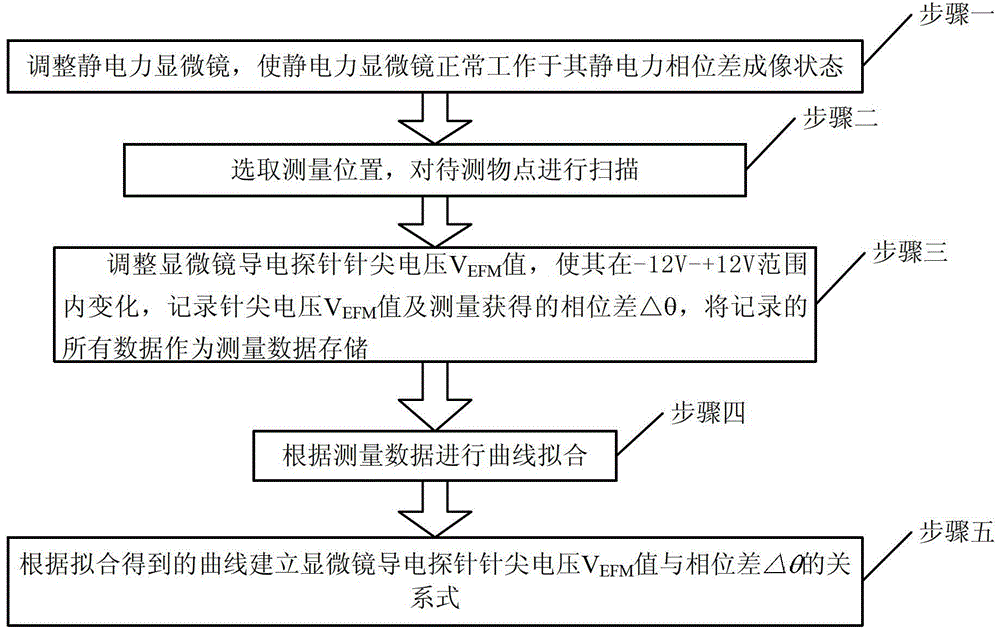
[0021] Specific implementation mode 1. Combination figure 1 This specific embodiment will be described. This specific implementation mode is:
[0022] Step 1: Adjust the electrostatic force microscope to make the electrostatic force microscope work normally in its electrostatic force phase contrast imaging state;
[0023] Step 2: Select the location point to be measured, and scan the location point to be measured;
[0024] Step 3: During the scanning process, adjust the microscope conductive probe tip voltage V EFM value, making it change in the range of -12V~+12V;
[0025] During each adjustment of the tip voltage V EFM value, record the tip voltage V EFM value and the phase difference Δθ obtained by measurement; the phase difference Δθ is the difference between the actual vibration phase of the microscope conductive probe and the free vibration phase; all the recorded data are stored as measurement data;
[0026] Step 4: Carry out curve fitting according to the measure...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0033] Embodiment 2. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that before scanning the position to be measured described in step 2, the height of the object is first detected by tapping mode, and the microscope conductive probe is adjusted according to the detection result. Keep the distance Z between the conductive probe and the measured position point.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0034] Embodiment 3. This embodiment is different from Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2 in that the distance Z is 10-200 nm.
[0035] Since the conductive probe of the microscope keeps a distance Z from the measured position and scans according to the surface fluctuation of the measured object, the conductive probe of the microscope does not touch the surface of the measured object during the second scanning process, and there is no contact between the conductive probe of the microscope and the measured object. The short-range repulsion of atoms between the surface of the object, and maintain a constant distance from the surface of the measured object, eliminating the influence of the surface topography of the measured object. The amplitude and phase difference Δθ of the conductive probe are changed due to the long-range electrostatic force.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com