Preparation method of heavy metal solid waste curing agent
A technology for solid waste and solid waste, which is applied in the field of preparation of a solidifying agent for heavy metal solid waste, can solve the problems of poor solidification effect of heavy metals, inability of solid waste to be recycled, and harmless reduction in quantity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] The preparation method of heavy metal solid waste solidifying agent comprises the steps:
[0029] 1) Test block production, curing agent composition and weight percentage
[0030] Dead-burned magnesium oxide powder accounts for 30%; potassium dihydrogen phosphate accounts for 25%; borax accounts for 3%; fly ash accounts for 8%; heavy metal solid waste accounts for 19%, of which heavy metal accounts for 0.5% of the total curing agent After mixing with water, make a test block of 707mm×707mm×707mm;
[0031] The test block is used for testing after curing for 7 days at a temperature of 20°C and a relative humidity above 90%;
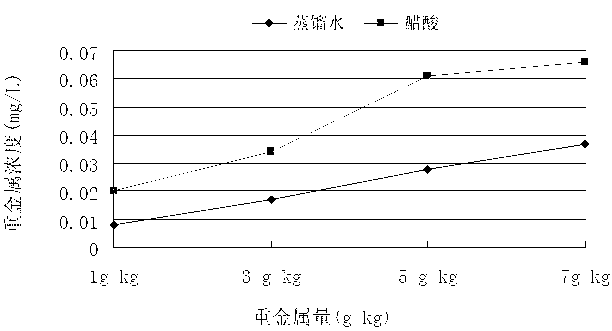
[0032] 2) Take the cured and crushed test piece and grind it finely, pass it through a 0.6 mm sieve for later use, mix 50 g of the finely ground powder with 1 000 mL of extraction solution, and stir for 18 hours with a dissolution tester; during the leaching process , take 2 different leaching conditions for horizontal comparison; these 2 leaching ...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Embodiment 2, the method comprises the steps:
[0045] 1) Test block production, curing agent composition and weight percentage
[0046]Dead-burned magnesium oxide powder accounted for 45%; potassium dihydrogen phosphate accounted for 30%; borax accounted for 5%; fly ash accounted for 10%; After mixing with water, make a test block of 707mm×707mm×707mm;
[0047] The test block is used for testing after curing for 8 days at a temperature of 20°C ± 3°C, a relative humidity of more than 90%;
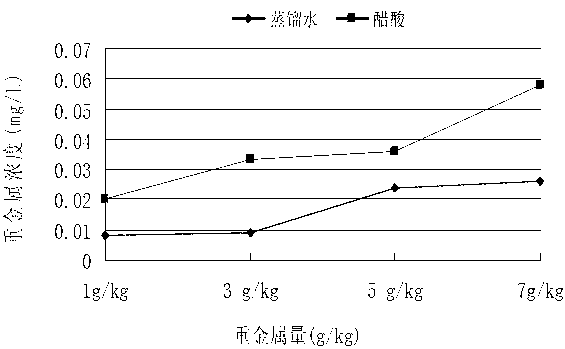
[0048] 2) Take the cured and crushed test piece and grind it finely, pass it through a 0.6 mm sieve for later use, mix 50 g of the finely ground powder with 1 000 mL of extraction solution, and stir for 18 hours with a dissolution tester; during the leaching process , take 2 different leaching conditions for horizontal comparison; these 2 leaching conditions are: Condition 1, according to TCLP standard preparation of extraction agent: 5.7 mL of glacial acetic acid in 500 mL of dist...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Embodiment 3, the method comprises the steps:
[0061] 1) Test block production, curing agent composition and weight percentage
[0062] Dead-burned magnesia powder accounted for 35%; potassium dihydrogen phosphate accounted for 28%; borax accounted for 4%; fly ash accounted for 9%; After mixing with water, make a test block of 707mm×707mm×707mm;
[0063] The test block is used for testing after being cured for 28 days at a temperature of 17°C and a relative humidity above 90%;
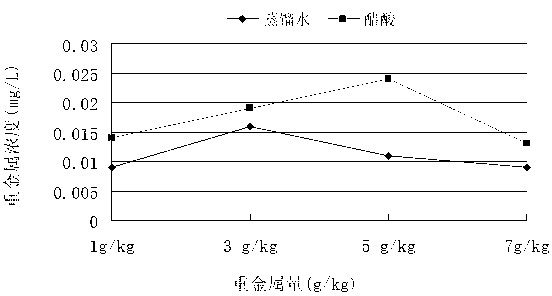
[0064] 2) Take the cured and crushed test piece and grind it finely, pass it through a 0.6 mm sieve for later use, mix 50 g of the finely ground powder with 1 000 mL of extraction solution, and stir for 18 hours with a dissolution tester; during the leaching process , take 2 different leaching conditions for horizontal comparison; these 2 leaching conditions are: Condition 1, according to TCLP standard preparation of extraction agent: 5.7 mL of glacial acetic acid in 500 mL of distilled water...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com