Time-Frequency Domain Modeling Method of Wind Farm Based on Empirical Mode Decomposition
A technology of empirical mode decomposition and modeling method, which is applied in the field of wind farm grid-connected impact analysis, and can solve problems such as difficulty in finding corresponding relationships, unfavorable analysis of wind farm grid-connected impacts, and inability to reproduce output power fluctuation characteristics. The effect of high reliability, clear observation and analysis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
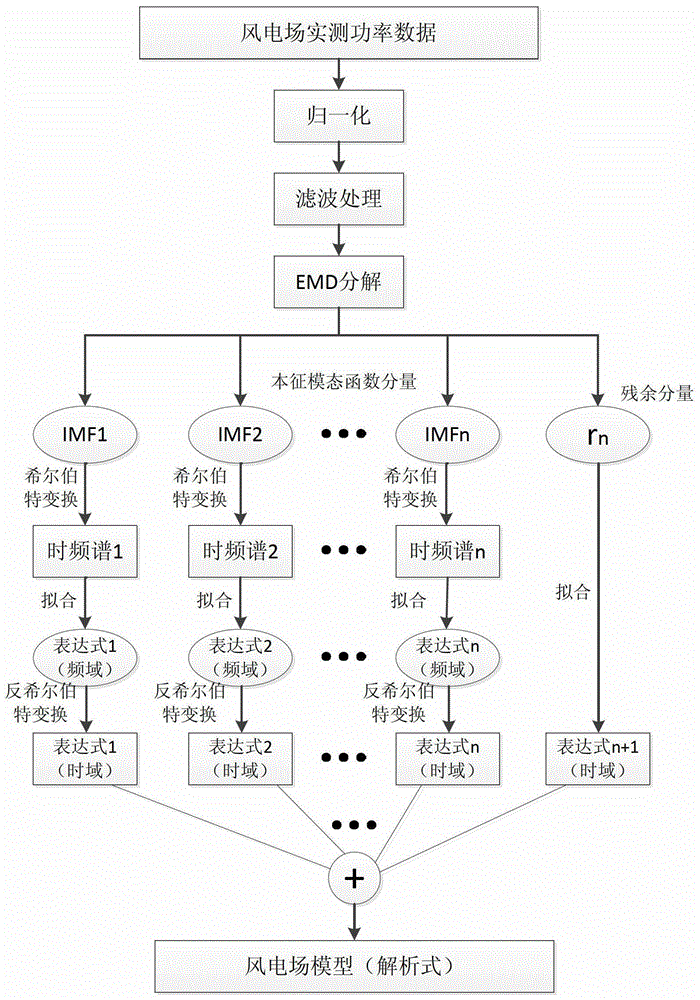
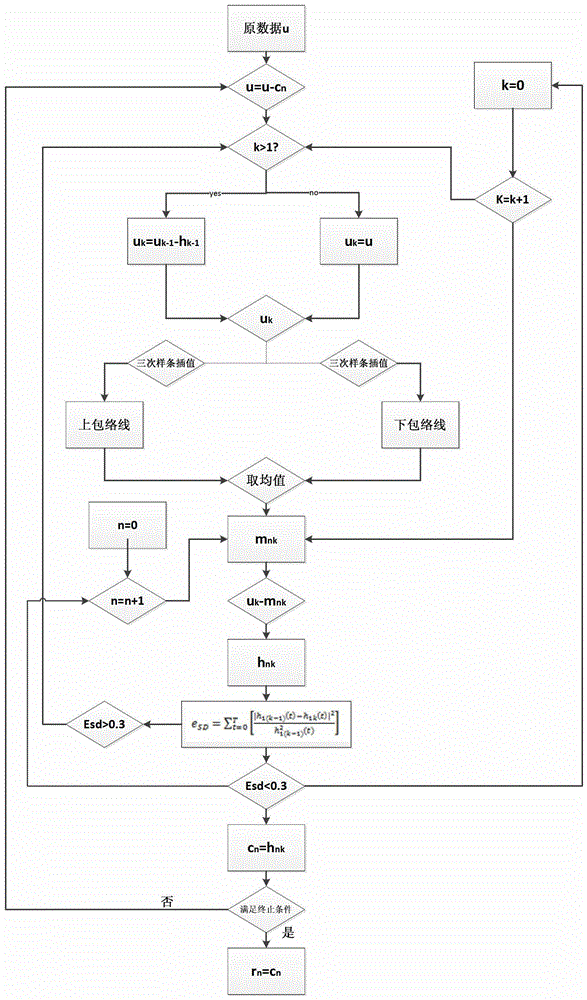
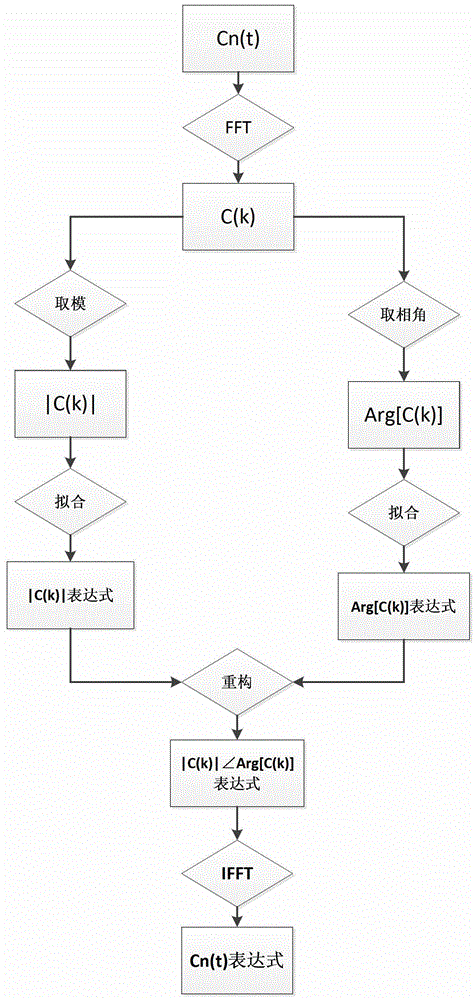
[0047] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
[0048] The concrete steps of modeling method of the present invention are as follows:
[0049] 1. Acquisition of wind farm active power data
[0050] Collect the output power P of each unit in a wind farm in a wind farm wind_i (t), and summed up, the result is the total output power P of the wind farm wind_f (t), namely:
[0051]
[0052] 2. Normalization processing
[0053] Select the total rated output power Pe(t) of the wind farm as the base value, for the P obtained in step 1 wind_f (t) Perform normalization processing to obtain data
[0054] 3. Data filtering processing
[0055] For the discrete sequence P obtained in step 2 or (t) Generating the power spectrum by a numerical method, observing P or (t) Frequency distribution, select a reasonable low-pass digital filter pair P or (t) is filtered to filter out the interference ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com