Gene sequencing data reading method and system
A gene sequencing and data reading technology, applied in the field of bioinformatics, can solve problems such as the sharp increase of gene sequence fragments, and achieve the effect of uniform size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
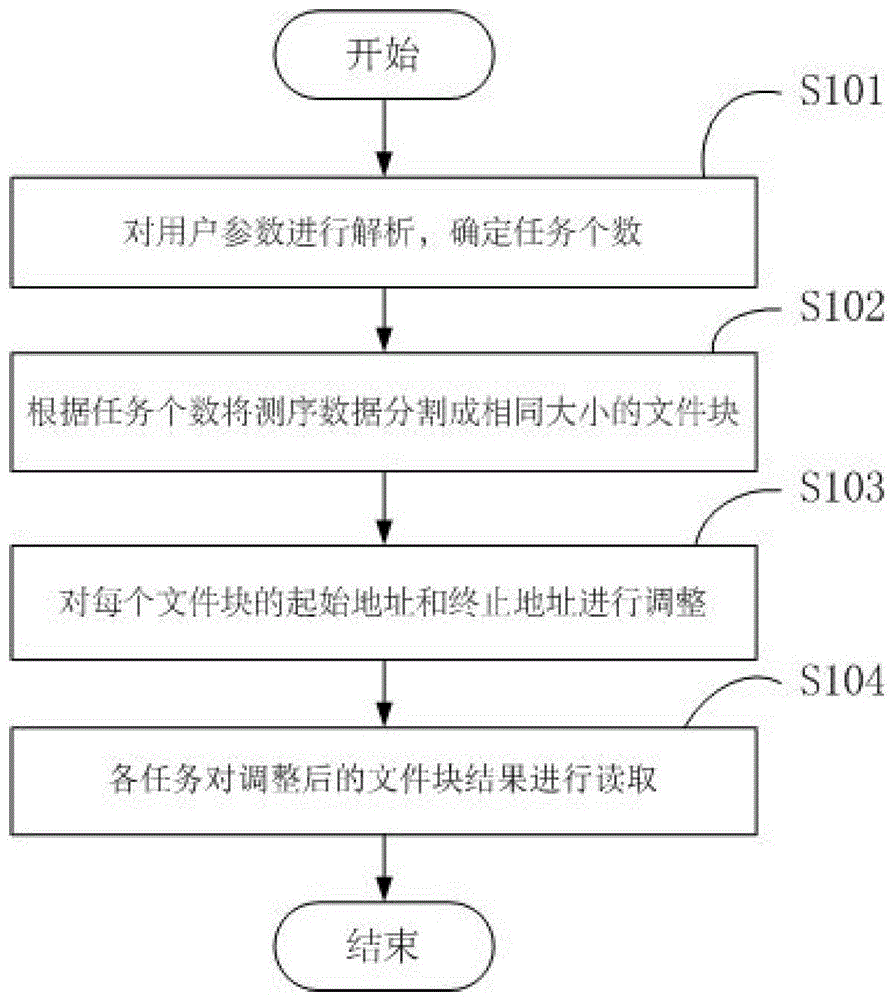
[0037] Embodiment 1 of the present invention provides a method for reading gene sequencing data. Such as figure 1 As shown, the method includes the following steps:
[0038] Step S101: Analyze user parameters to determine the number of tasks. The user parameters described in this embodiment include hard performance, the total size of gene sequencing data, the length of the homologous gene reference sequence, etc., and the number of required tasks is reasonably selected according to the user parameters. The tasks in this embodiment are MPI processes.
[0039] Step S102: Divide the sequencing data into file blocks of the same size according to the number of tasks. Specifically, in this embodiment, the sequencing data is divided into file blocks of the same size according to the number of tasks, and the start position and end position of each file block are obtained. If the number of tasks is n and the total size of gene sequencing data is S, then the starting position of the...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Embodiment 2 of the present invention provides a method for reading gene sequencing data. Such as Figure 4 As shown, the method includes the following steps:
[0047]Step S201: Initialize tasks, establish connections between all nodes, and collect statistics on node information and process information. In this embodiment, task initialization is performed, and the information of all computer nodes involved in computing, task identification numbers communicated with the group, and the number of all potential tasks capable of participating in group communication are obtained for statistics. The tasks in this embodiment are MPI processes.
[0048] Step S202: Analyze the user parameters to determine the number of tasks.
[0049] Step S203: Divide the sequencing data into file blocks of the same size according to the number of tasks.
[0050] Step S204: Adjust the start address and end address of each file block.
[0051] The above steps have been described in detail in...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Embodiment 3 of the present invention provides a method for reading gene sequencing data. In this embodiment, a high-performance mainframe utilizes different threads in the program to complete the reading of gene sequencing data. The method includes the following steps:
[0063] Step S301: Analyzing user parameters to determine the number of threads of the program.
[0064] Step S302: Divide the sequencing data into file blocks of the same size according to the number of program threads.
[0065] Step S303: Adjust the start address and end address of each file block.
[0066] Step S304: each thread reads the file from the adjusted file block result.
[0067] Steps S302 to S304 have been described in detail in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com