Method for preparing semiconductor sub-micron band on flexible substrate, and flexible optical waveguide
A flexible substrate and semiconductor technology, applied in the field of flexible optical waveguides, can solve the problems of film surface tension damage, agglomeration into clusters, disordered ordering, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Such as Figure 1~Figure 8b As shown, this embodiment provides a method for preparing a semiconductor sub-micron belt on a flexible substrate based on an edge transfer method, which at least includes the following steps:
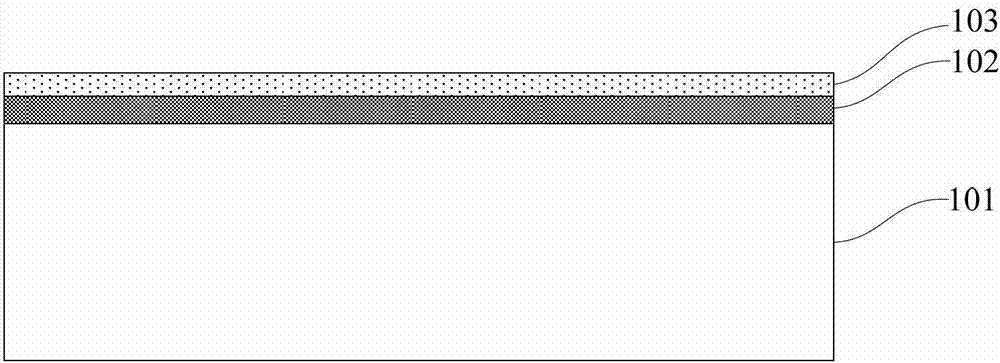
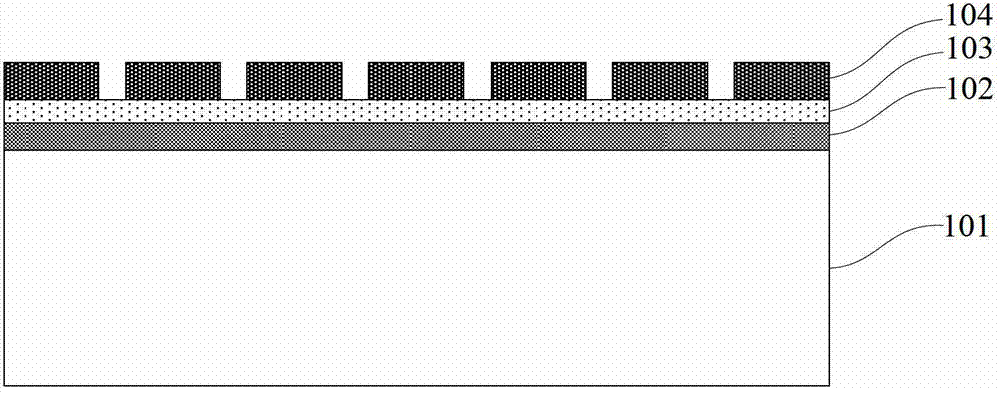
[0040] Such as Figure 1~Figure 2 As shown, step 1) is first performed to provide a semiconductor-on-insulator substrate including a silicon substrate 101, a buried oxide layer 102, and a top semiconductor 103, and a plurality of strips are formed on the surface of the top semiconductor 103 in a photolithography 胶图104。 Glue graphics 104.
[0041] In this embodiment, the semiconductor-on-insulator substrate is an SOI substrate, and the top-layer semiconductor 103 can be used to transfer a microbelt structure of any material to a flexible substrate according to material requirements in actual applications, such as Germanium, three-five group compound semiconductor materials, etc.
[0042] Specifically, a semiconductor-on-insulator substrate including a silico...
Embodiment 2
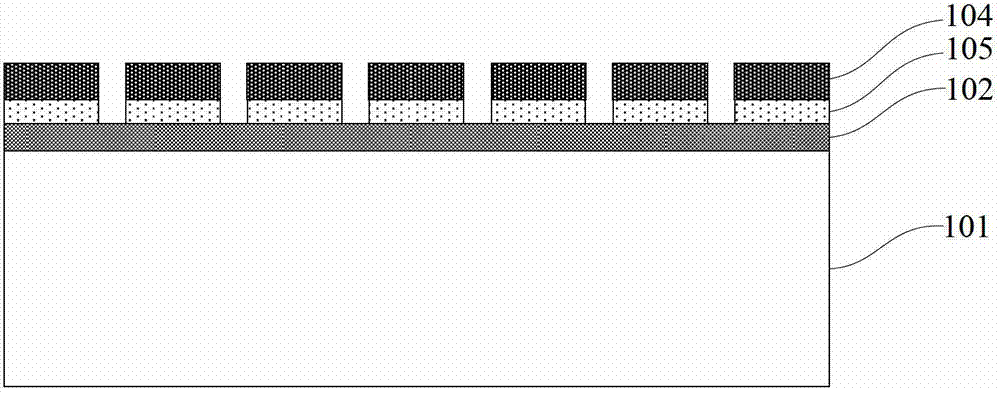
[0055] Such as Figure 1~Figure 8b As shown, this embodiment provides a flexible optical waveguide prepared based on the edge transfer method, when the semiconductor-on-insulator substrate is an SOI substrate, that is, the top semiconductor is silicon, and the strips are rectangular strips. The semiconductor sub-micron tape on the flexible substrate prepared by the method for preparing the semiconductor sub-micron tape on the flexible substrate based on the edge transfer method described in Example 1 can be directly used as a flexible optical waveguide material, so the basic steps are as in the example 1. Of course, it is also possible to obtain a flexible optical waveguide with required functions by performing certain processing on the semiconductor sub-micron strip on the flexible substrate.
[0056] In summary, the present invention provides a method for preparing semiconductor submicron bands on a flexible substrate based on the edge transfer method and a flexible optical wave...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com