Preparation method of biodegradable polyurethane gene transfection reagent
A polyurethane and group technology, applied in the field of nano-biological materials, can solve the problems of unreported, unreported synthesis of cationic polyurethane, and achieve the effects of low cost, low cytotoxicity and low cytotoxicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] Embodiment 1: Synthesis of dithiodiethanol p-nitrophenyl carbonate (DTDE-PNC)
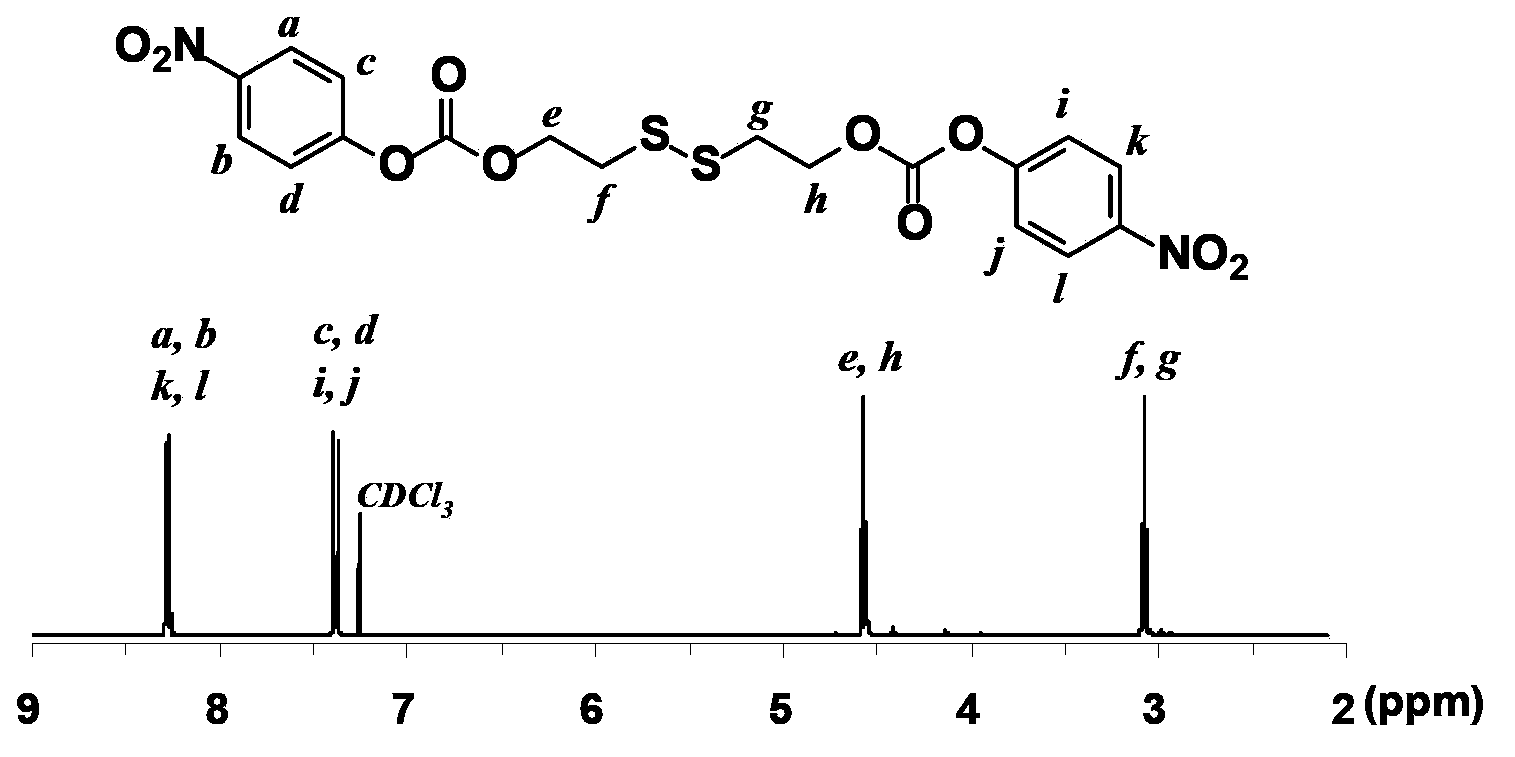
[0058] (1) Add dithiodiethylene glycol (DTDE, 4g) and pyridine (7.4g) at a molar ratio of 1:1, add 40ml of anhydrous dimethylformamide and stir to dissolve for 10-30 minutes, then slowly add p-Nitrophenyl chloroformate (PNC, 10.3g) The molar ratio of p-nitrophenyl chloroformate (PNC) to dithiodiethylene glycol (DTDE) is 1:1.5, react at room temperature for 24 hours ;
[0059] (2) Wash the reaction finished mixture once with disodium hydrogen phosphate solution, then wash with deionized water, and remove the solvent by rotary evaporation; the reaction crude product is separated and purified by silica gel strain to obtain pure light yellow product dithiodiethyl-p-nitrate phenyl carbonate (7.4 g, 58% yield). 1 HNMR (300MHz, CDCl 3 , ppm): δ8.26 (aromatic protons, 4H); 7.37 (aromatic protons, 4H); 4.57 (2×SSCH2CH2, 4H); 3.08 (2×SSCH2CH2, 4H) (see figure 1 ).
Embodiment 2
[0060] Example 2: Synthesis of polyurethane containing 1,4-bis(3-aminopropyl)-piperazine
[0061] (1) Put DTDE-PNC (1.21g) prepared in Example 1 and 1,4-bis(3-aminopropyl)-piperazine (0.5g) in a molar ratio of 1:1 into a round bottom flask ; Dissolved with 5ml chloroform, reacted at room temperature for 5 days;
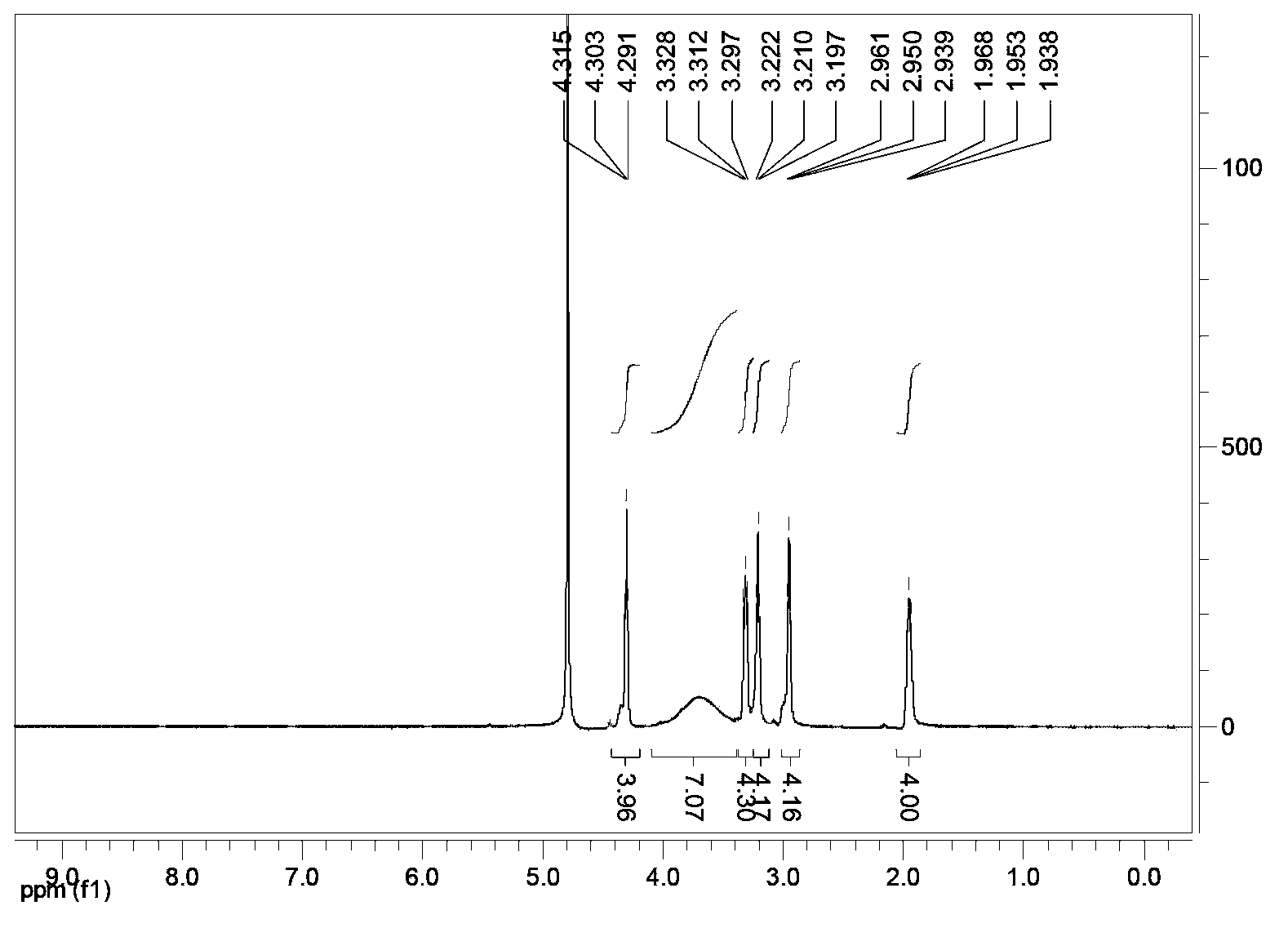
[0062] (2) the reaction product is dissolved in 10ml deionized water; the pH value is adjusted to 6 with hydrochloric acid and the molecular cut-off is 1000g / mol for dialysis bag dialysis; freeze-drying, obtains solid product containing polyurethane (0.7g, producing disulfide bond) rate of 65%). The degree of polymerization n is 300-350.
[0063] The NMR data of the solid product are: 1 HNMR (D 2 O) δ (ppm) = 4.30 (2 × SSCH2CH2, 4H); 3.4-4.0 (2 × NCH2CH2N, 8H); 3.31 (2 × OCONHCH2, 4H); 3.21 (2 × OCONHCH2CH2, 4H); 2.95 (2 × SSCH2CH2 ,4H); 1.95(2×CH2CH2CH2,4H) (see figure 2 ).
Embodiment 3
[0064] Embodiment 3: Synthetic polyurethane containing three (2-aminoethyl) amines
[0065] (1) DTDE-PNC (1.83g) and two (2-aminoethyl) 2-(tert-butoxycarbonylamino) ethylamine (0.93g) of equimolar ratio are put into flask;
[0066] (2) Dissolve with 5ml dimethylformamide and react at room temperature for 5 days;
[0067] (3) After the reaction is over, add 20ml of trifluoroacetic acid to react for 6h, and depressurize and rotary evaporate the trifluoroacetic acid;
[0068] (4) The reaction product was dissolved with 10ml deionized water, and the pH value was adjusted to 6;
[0069] (5) Dialysis with a dialysis bag with a molecular cut-off of 1000 g / mol;
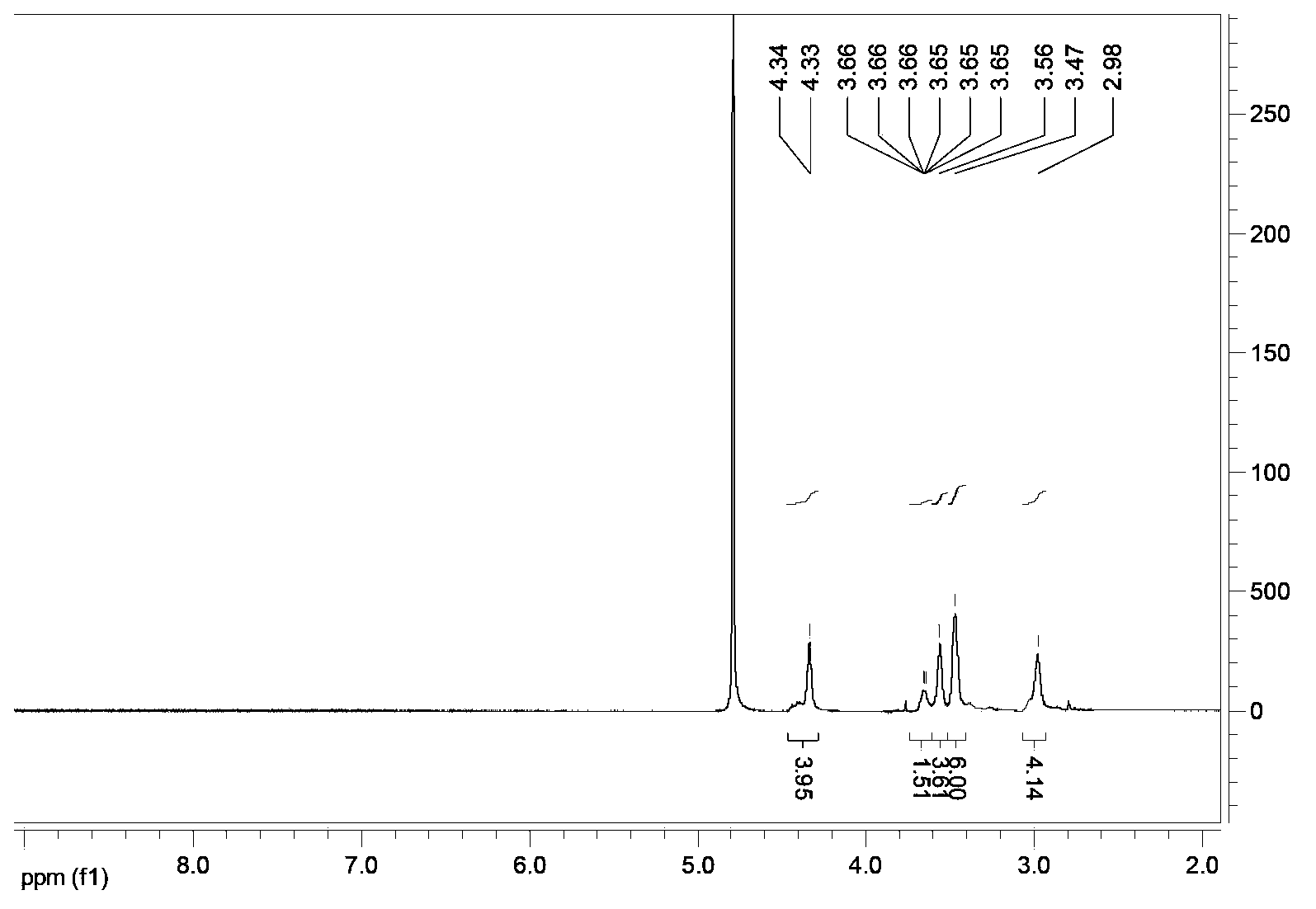
[0070] (6) Freeze drying to obtain a solid product (0.25 g, yield 18%). The degree of polymerization n is 200-250; 1 HNMR (D 2 O)δ(ppm)=4.33(2×SSCH2CH2,4H); 3.65(CH2CH2NH2,2H); 3.56(2×OCONHCH2,4H); 3.47(CH2N(CH2)CH2,6H); 2.98(2×SSCH2CH2,4H )(See image 3 ).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of polymerization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of polymerization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com