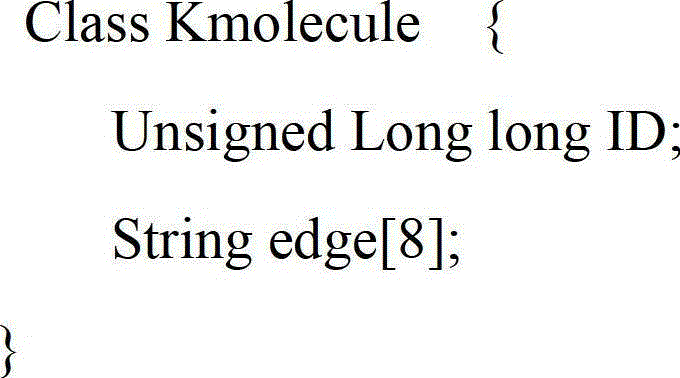Compression storage and construction method of bidirectional multi-step debruijn graph
A compression storage, two-way multi-step technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., to achieve the effect of improving the speed of splicing and reducing the memory consumption of a single machine
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] A method for compressing, storing and constructing a bidirectional multi-step deBruijn graph provided by an embodiment of the present invention includes the following steps:
[0059] Compression storage steps, specifically
[0060] S11. Read a sequence s;
[0061] S12. Cut the sequence s into multiple segments t using a sliding window of length k; wherein 0
[0062] S13. For each fragment t, use the nucleic acid encoding table {A:00, C:01, G:10, T:11} to encode, and represent it as a 64-bit integer a;
[0063] S14. Reverse the string of the segment t, and use the symmetric complementation table {A->T, C->G, G->C, T->A} to change each character in the reversed string to its Complementary characters, obtain a string v of complementary characters, and use the nucleic acid encoding table in step S13 again to encode the string v, and represent it as a 64-bit integer b;
[0064] S15, take the maximum number of integer a and integer b as the sig...
Embodiment 2
[0078] Another embodiment of the present invention provides a method for compressing, storing and constructing a bidirectional multi-step deBruijn graph, comprising:
[0079] Compression storage steps, specifically
[0080] S11. Read a sequence s;
[0081] S12. Cut the sequence s into multiple segments t using a sliding window of length k; wherein 0
[0082] S13. For each fragment t, use the nucleic acid encoding table {A:00, C:01, G:10, T:11} to encode, and represent it as a 64-bit integer a;
[0083] S14. Invert the fragment t, use the symmetric complementation table to complement the inverted fragment to obtain a complementary fragment, and use the nucleic acid encoding table in step S13 again to encode the complementary fragment and express it as a 64-bit integer b ;
[0084] S15, take the maximum number of integer a and integer b as the sign number of k molecules of fragment t and complementary fragment v;
[0085] S16. Repeat steps S11-S1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com