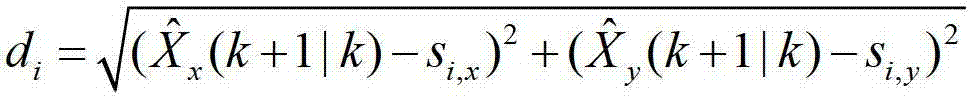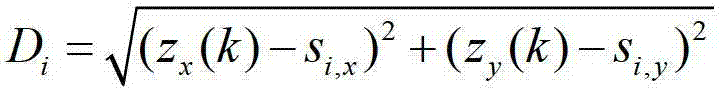Underwater wireless sensor network target tracking method based on sensor node strategy selection
A sensor node and wireless sensor technology, applied in network topology, wireless communication, advanced technology, etc., can solve the problems of reducing sensor working time, useless information encroaching on underwater channel spectrum resources, node energy waste, etc., to reduce energy consumption and Effect of communication load
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0027] Step 101: Initialize the underwater wireless sensor network, spread the wireless sensor network nodes evenly in the underwater environment, all nodes have uniform specifications, such as communication distance, detection distance, etc., all nodes are in working state, and maintain the detection function, but The communication function can be turned off, all nodes must know the location data.
[0028] Step 102: At time k=0, set the estimated initial position of the target and the estimated variance of the initial target according to the initial distribution of the target.
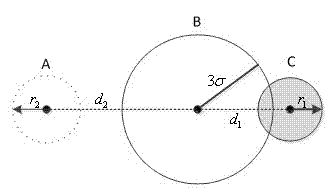
[0029] Step 103: At time k, there is an elliptical area estimated for the target position. The ellipse area of target position estimation at this moment can be obtained through the Kalman filter prediction process at the last moment. Select the node closest to the center of the ellipse area as the processing node, and the processing node at the previous moment will transmit the target motion inform...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com