Method for detection of subsurface seismic events in vertically transversely isotropic media
An event, surface technique, applied in seismology for well logging, seismology for areas covered by water, seismology, etc., can solve problems such as bias
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
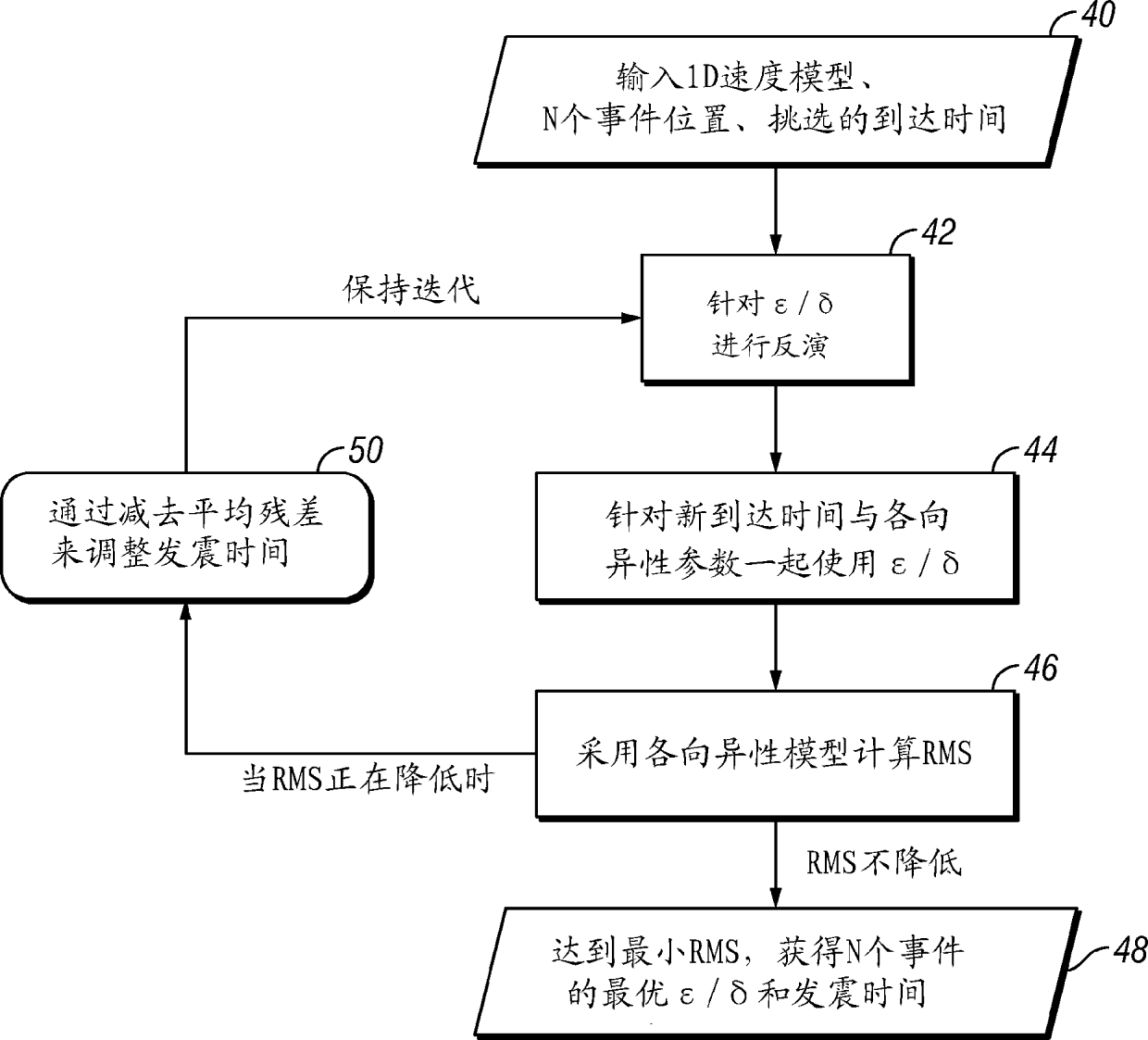
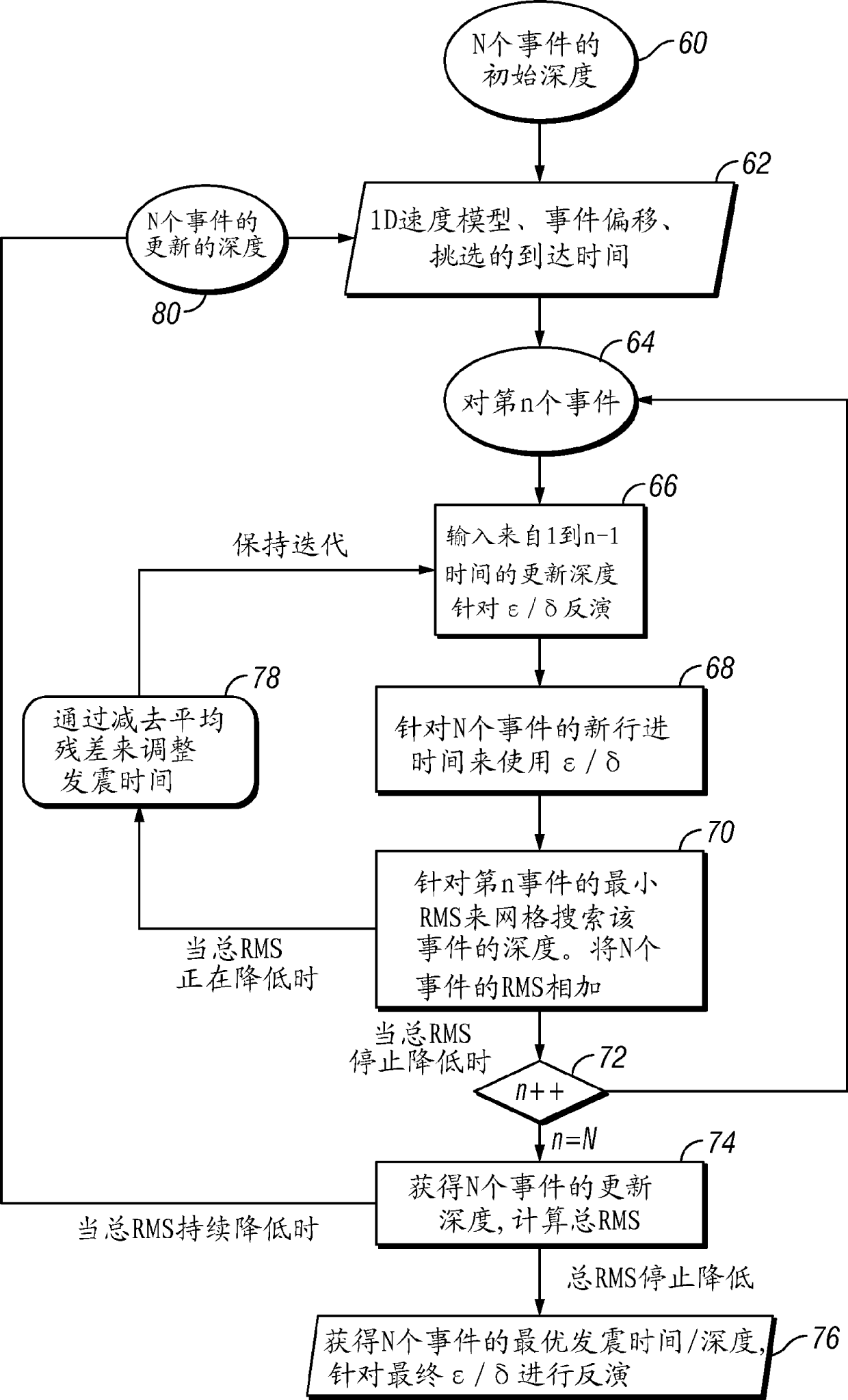
[0017] The method according to the invention will be described generally, with particular reference to the example of its use in monitoring the progress of a subsurface fracturing treatment of a rock formation. Subsequently, a specific case study of an example implementation will be described. In the described case study, the initial velocity model was a layered 1D isotropic model derived from a surface seismic check blast survey, however, the technique is generally applicable to 3D media. Because check blast surveys typically only provide seismic information from a single offset (source to sensor distance), the velocity model has to be smoothed to represent a 1D isotropic layered model of the rock formation. In this example case study, such models had to be artificially multiplied by a factor of 1.25 to locate a calibration shot (ie, a drilling munition detonated at a known time and location). However, this approach is inconsistent with what is known about the physics of sou...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com