Farmland test method of grading index of soil nutrient
A soil nutrient and field test technology, applied in the field of agricultural science and technology, can solve the problems of arranging many test points, low test accuracy, long time consumption, etc., and achieves the effects of high test accuracy, avoiding test errors and improving reliability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
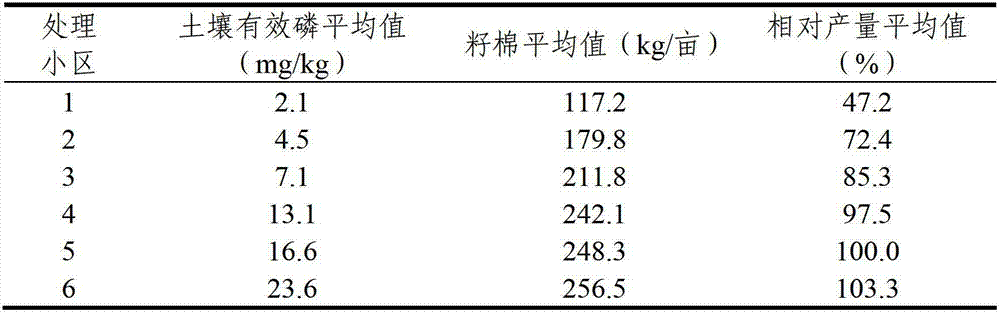
[0030] In this example, the following method was used to obtain the grading index of soil available phosphorus in cotton fields in northern Henan.
[0031] 1. By planting cotton for one year without applying phosphorus fertilizer, the available phosphorus consumption in the soil of the test site is reduced to a lower level
[0032] The annual soil available phosphorus content in the test site was 7.2mg / kg. In order to meet the test requirements, no phosphorus fertilizer was applied to the test site in the previous year to plant cotton; after one year of cotton planting, the available soil phosphorus content in the test site was reduced to 2.1mg / kg.
[0033] 2. According to theoretical calculation, for every increase of 1mg / kg in the soil available phosphorus content in the 0-20cm soil layer, 0.15kg P should be applied per mu (that is, P 2 o 5 0.34kg), considering factors such as the fixation of phosphorus in the soil, 0.22kg P (that is, 0.5kgP 2 o 5 )calculate. The random ...
Embodiment 2
[0045] In this example, the following methods are used to obtain the grading index of soil available potassium in cotton fields in eastern Henan.
[0046] 1. By not applying potassium fertilizer and using wheat-cotton interplanting, the available potassium consumption in the soil of the test site is reduced to a lower level
[0047] The soil available potassium content in the test site last year was 53 mg / kg. In order to meet the test requirements, no potassium fertilizer was applied to the test site in the previous year. Wheat was planted and cotton was interplanted. After harvesting, all straws were removed from the test site; The soil available potassium content in the test field was reduced to 42mg / kg in the same year.
[0048] 2. According to theoretical calculation, for every 1mg / kg increase in the available potassium content in the soil in the 0-20cm soil layer, 0.15kg K (that is, 0.18kgKK) should be applied per mu. 2 o). The random block arrangement of the experiment...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com