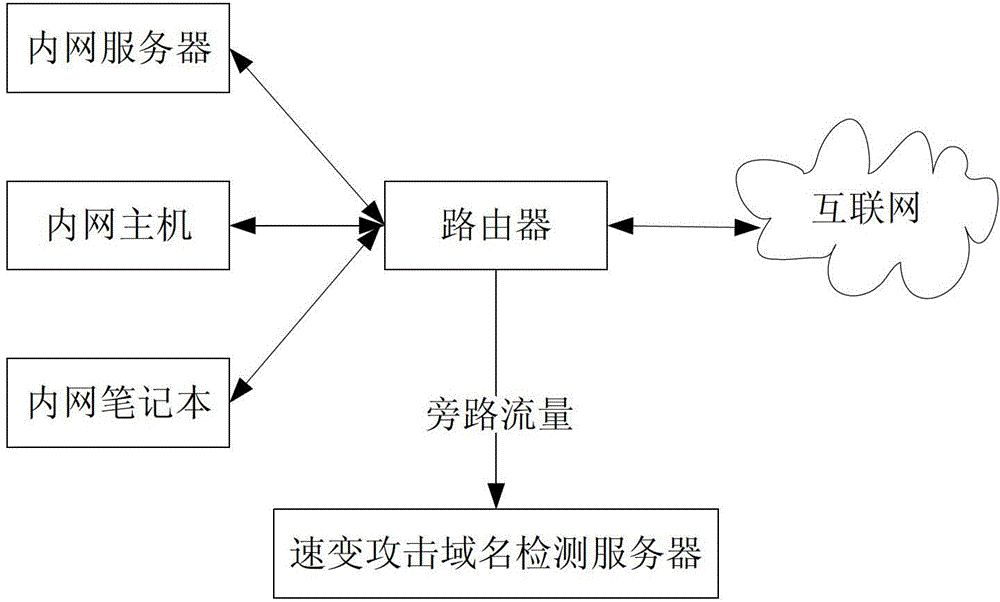
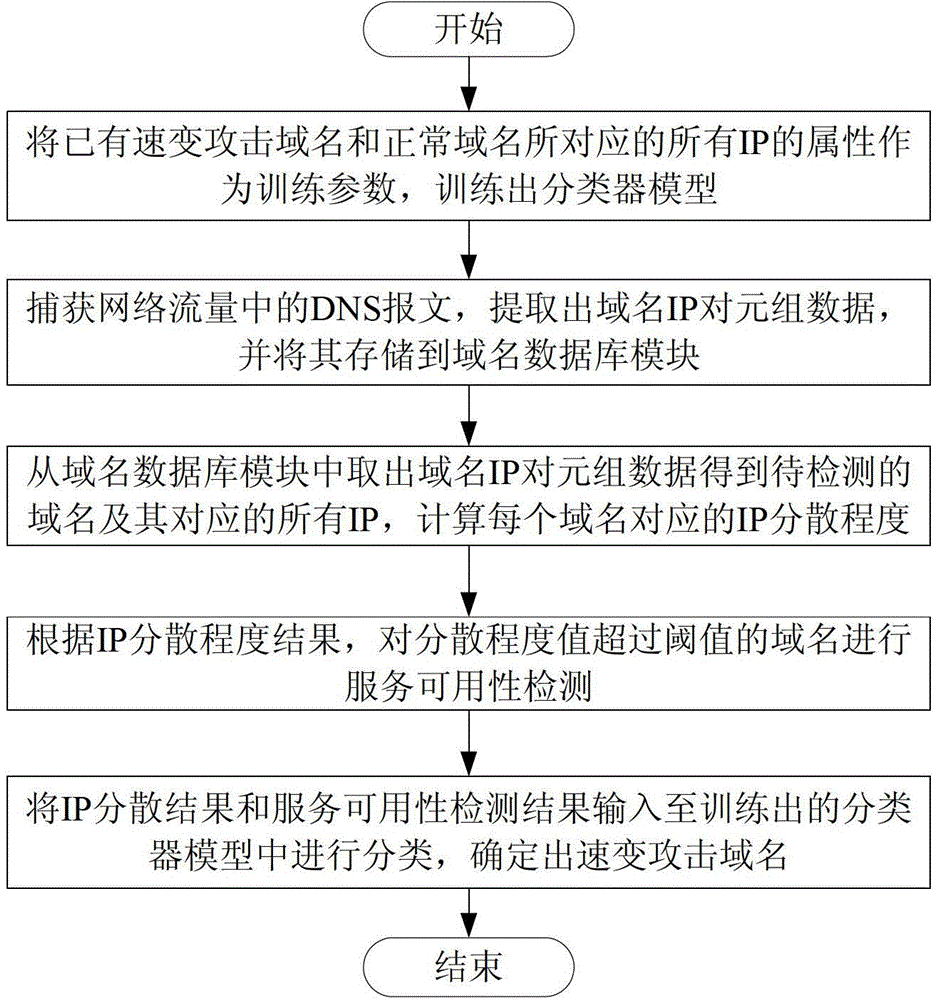
Method for detecting quick-changing attack domain name based on host group characteristics
A technology of fast-changing attacking domain names and domain names, which is applied to digital transmission systems, electrical components, transmission systems, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty in timely discovery and control of fast-changing attacking network domain names, long detection cycles, and large error results, and achieve detection The effect of short cycle, large data set and accurate results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
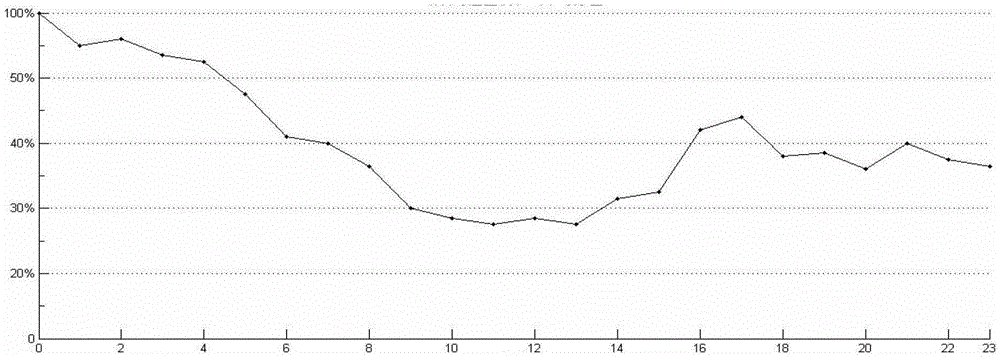
[0060] Embodiment 2 is based on the technical solution described in Embodiment 1. Its training data set comes from the fast-changing attack domain names and normal domain names announced by major websites, and the test data set comes from DNS messages of the entire LAN mirrored from the gateway in a certain research institute. , which has about 50,000 records per working day. According to the tuple recorded in the IN message returned by the recorded DNS, calculate the degree of dispersion of the host group IP corresponding to the domain name, detect and calculate the service availability of the host group corresponding to the domain name, and use these two indicators to determine the domain name For classification, the timing diagram of the online rate of the host group corresponding to the rapidly changing attack domain name detected in the second embodiment is as follows: image 3 As shown, the vertical axis represents the online rate, and the horizontal axis represents the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com