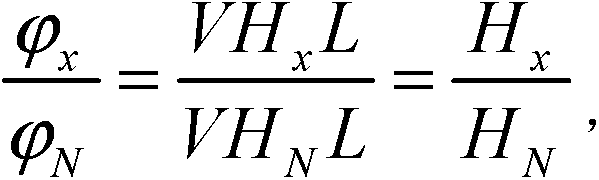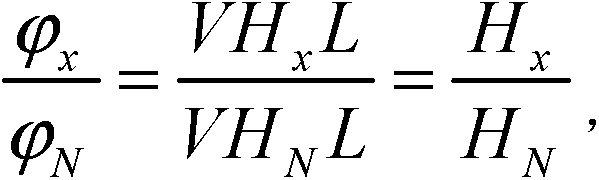Optical current sensor and current measurement method based on comparative measurement structure
A current sensor, comparative measurement technology, applied in the direction of measuring current/voltage, measuring electrical variables, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problem of inaccurate measurement results of wire current, eliminate the influence of Feld's constant, reduce Feld's constant, etc. Constant error, the effect of avoiding errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
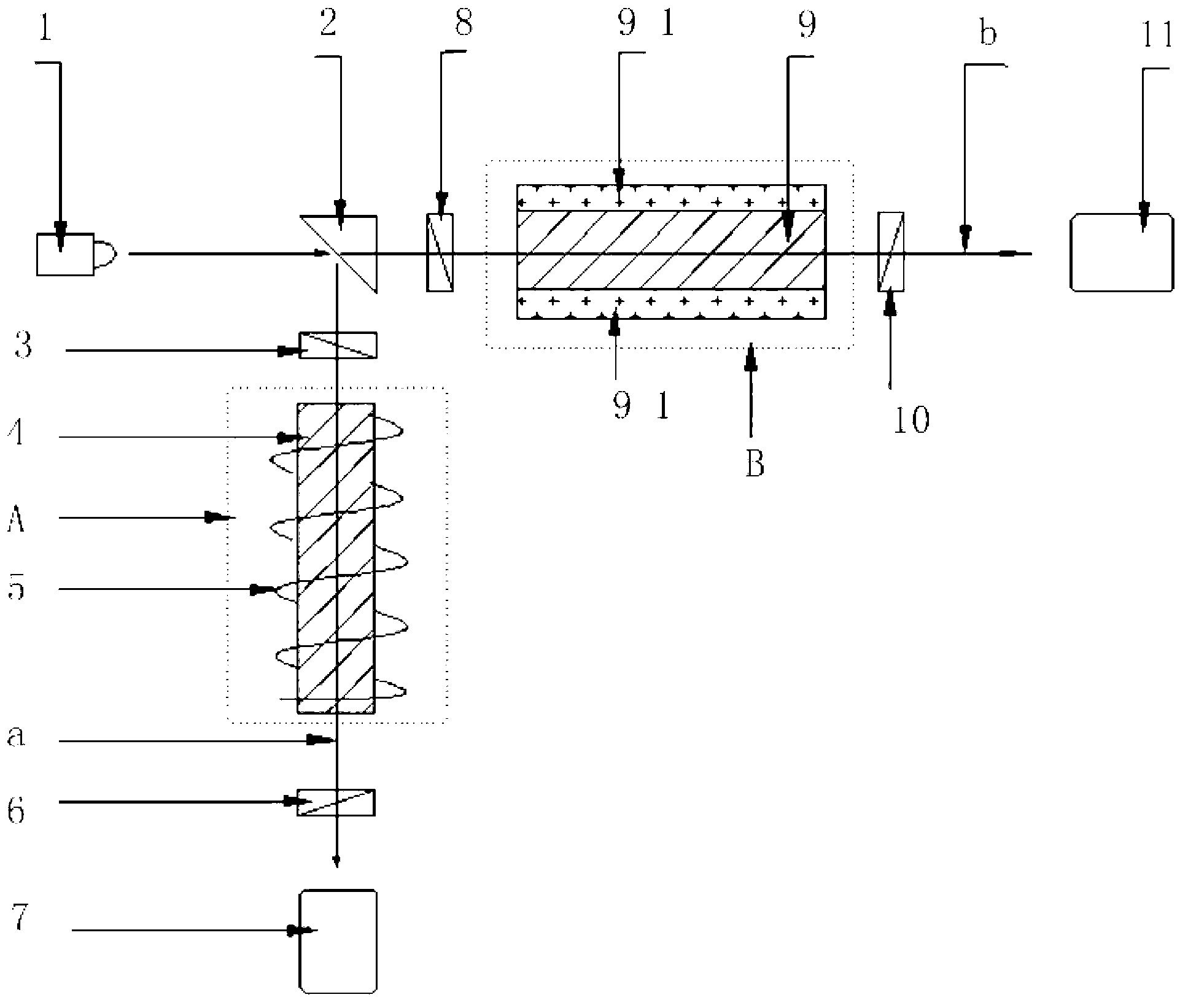
[0021] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination figure 1 Describe this embodiment, the optical current sensor based on the comparative measurement structure described in this embodiment, it includes laser generator 1, beam splitter 2, first polarizer 3, first magneto-optical glass 4, energized coil 5, first detector Polarizer 6, first photodetector 7, second polarizer 8, second magneto-optical glass 9, second analyzer 10 and second photodetector 11,
[0022] The energized coil 5 is helically wound on the outer surface of the first magneto-optic glass 4 to form the measuring arm B of the sensor; the upper surface and the lower surface of the second magneto-optic glass 9 are provided with a flat permanent magnet 9-1, the second The magneto-optical glass 9 and the flat permanent magnet 9-1 form the reference arm A of the sensor, and the reference arm A and the measuring arm B are vertically arranged, and the reference arm A is perpendicular to the upper surface...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0028] Embodiment 2: This embodiment further describes Embodiment 1. The first magneto-optical glass 4 and the second magneto-optic glass 9 in this embodiment are the same magneto-optic glass 9 .
[0029] In this embodiment, the constituent materials of the first magneto-optical glass 4 and the second magneto-optic glass 9 are exactly the same, that is, the constituent substances have the same concentration and the same size.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0030] Specific implementation mode three: this implementation mode is a method for measuring current using the optical current sensor based on the comparative measurement structure described in the first or second implementation mode,
[0031] From the Faraday deflection angle of the first magneto-optical glass 4 in the measuring arm B
[0032] Wherein V is the Verdet constant of the first magneto-optical glass 4 and the second magneto-optic glass 9, H x Be the magnetic field intensity of the first magneto-optical glass 4, L is the length of the first magneto-optic glass 4 and the second magneto-optic glass 9,
[0033] Faraday deflection angle through the second magneto-optical glass 9 in the reference arm A
[0034] h N Be the magnetic field strength of the second magneto-optical glass 9,
[0035] Divide the above two equations to get:
[0036]
[0037] By the Faraday deflection angle of the first magneto-optical glass 4 The Faraday deflection angle of the secon...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com