Downlink physical control channel sending method and receiving method and corresponding devices
A physical control channel and sending device technology, applied in wireless communication, communication between multiple stations, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as limited bandwidth, inability to fully receive control information, and no solution proposed, to reduce cost, improve spectrum efficiency, and promote the effect of evolution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042]This embodiment describes the sending method of the downlink physical control channel, such as Figure 4 shown, including the following steps:
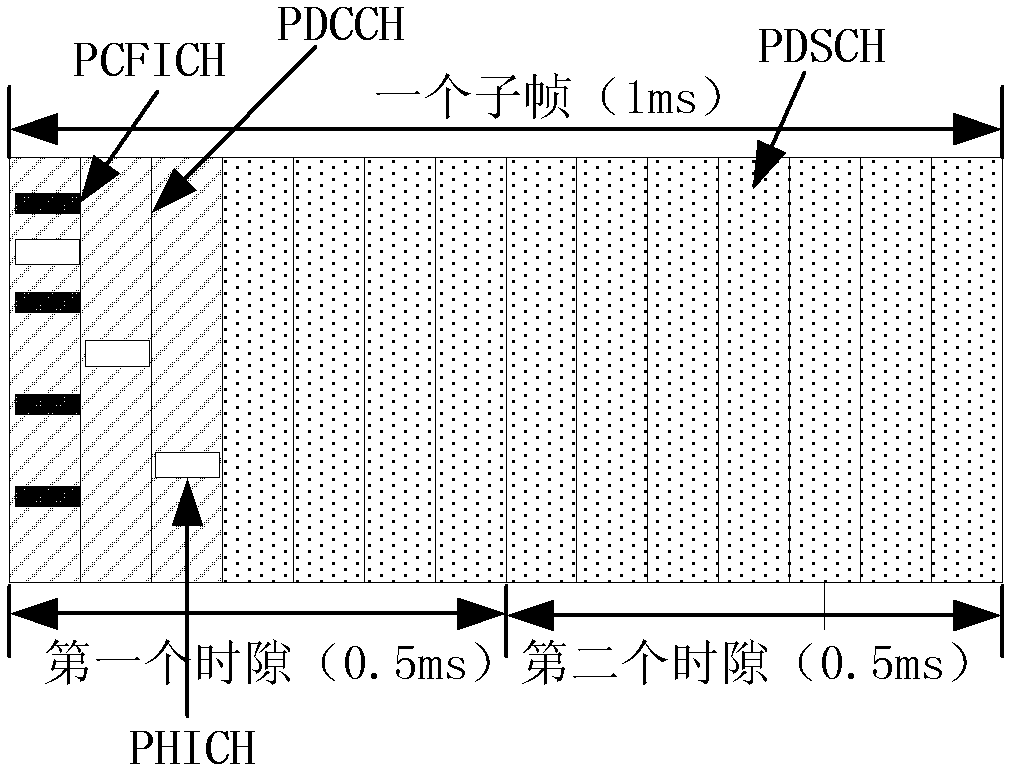
[0043] Step 101, the base station (eNodeB) maps the downlink physical control channel of the UE to the center frequency domain position of the system bandwidth of the second time slot of the subframe when sending the downlink physical control channel of the user equipment (UE);
[0044] Preferably, the UE includes an MTC UE, specifically, a low-cost MTC UE with limited bandwidth.
[0045] Preferably, when sending the downlink physical control channel of the UE, the eNodeB first judges whether the system bandwidth is greater than the first predefined bandwidth, and if so, maps the downlink physical control channel of the UE to the system bandwidth of the second time slot of the subframe If not (less than or equal to), send the downlink physical control channel (PCFICH, PDCCH, PHICH) of the UE according to the prior art. The wid...
Embodiment 2
[0073] This embodiment describes the receiving method of the downlink physical control channel, such as Figure 6 shown, including the following steps:
[0074] Step 201, UE judges whether the system bandwidth is greater than the first predefined bandwidth, if yes, execute step 202, otherwise execute step 203;
[0075] Preferably, the UE includes an MTC UE.
[0076] Step 202, the UE detects the downlink physical control channel at the central frequency domain position of the system bandwidth in the second time slot of the subframe; the width of the central frequency domain is the second predefined bandwidth, and the first predefined bandwidth is greater than or equal to the second predefined bandwidth. define the bandwidth;
[0077] The first predefined bandwidth is the maximum receiving bandwidth of the UE, and the second predefined bandwidth is the downlink control area bandwidth of the UE (or the system receiving bandwidth of the UE). Preferably, the first predefined ban...
application example 1
[0097] This example describes the case where the downlink physical control channel includes M-PCFICH, M-PHICH and M-PDCCH. In this example, the system bandwidth is 10MHz, while the transmit-receive bandwidth of the MTC UE is 1.4MHz, with 6 RBs.
[0098] The process of sending the channel on the eNodeB side is as follows: Figure 4 As shown, first, the eNodeB makes a judgment and compares the system bandwidth with the bandwidth predefined by the MTC UE. In this example, the system bandwidth is obviously greater than the bandwidth predefined by the MTC UE, so the Figure 8 The shown channel time-frequency mapping position sends the downlink physical control channel of the low-cost bandwidth-limited MTC UE:
[0099] The frequency domain position of the entire control region is located in the center 6 RBs of the system bandwidth, and the time domain is the first 3 OFDM symbols in the second slot of the subframe. in:
[0100] The value of M-PCFICH is 2, 3 or 4. For each antenna...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com