All-degradable biological material and preparation method thereof
A biomaterial and fully degradable technology, applied in the field of fully degradable biomaterials and their preparation, can solve the problems of inducing Alzheimer's disease, ignoring the potential harm of acidic degradation products, and accelerating the degradation of magnesium alloy substrates.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
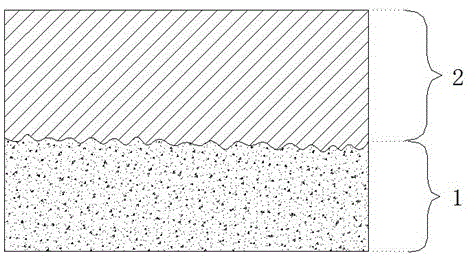
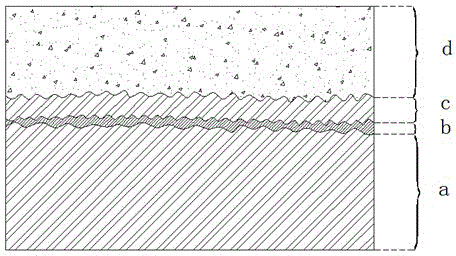
[0053] The sample of high-purity magnesium as cast metal was taken as the research object. Select 100-mesh glass shot, and use a commercially available general-pressure manual sandblasting machine (3 atmospheres, 500kg / h injection volume) to perform 30sec shot peening on the sample. As a result, the surface of the sample has an obvious and uniform sand surface effect. Use the homogeneous mixture of epichlorohydrin and acetone (mixing volume ratio 2:1) as the solvent to first prepare 35.0g / LPLLA solution (liquid), then add 10.0g / L magnesium oxide (solid dispersed phase), stir evenly to obtain a suspension , labeled solution S 01 . Perform 15 rounds of dip-coating on the washed and dried shot-peened sample according to the following specifications: Dip the sample into the solution S 01 , Take it out after 15sec, and wait until the coating is cured. Results A uniform magnesium oxide / PLLA composite coating (functional film) was obtained on the surface of the sample.
[0054] T...
Embodiment 2
[0056] The sample of AZ31 magnesium alloy in mold casting state was taken as the research object. Shot peening process condition control and result are the same as embodiment 1. In addition to changing the concentration of PLLA to 75.0g / L, the concentration of magnesium oxide to 0.377g / L (accounting for 0.5% of the total content of magnesium oxide and PLLA), and changing the solvent to chloroform, solution S 01The preparation is with embodiment 1. Perform 10 rounds of dip-coating on the washed and dried shot-peened sample according to the following specifications: Dip the sample into the suspension S 01 , Take it out after 30sec, and wait until the coating is cured. Results A uniform magnesium oxide / PLLA composite coating (functional film) was obtained on the surface of the sample. The in vitro biodegradability test of the material was carried out the same as in Example 1, and the results showed that the substrate of the sample began to have visible corrosion marks after ab...
Embodiment 3
[0058] The sample of AZ91 magnesium alloy in mold casting state was taken as the research object. Shot peening process condition control and result are the same as embodiment 1. In addition to changing the concentration of PLLA to 0.2g / L, the concentration of magnesium oxide to 0.133g / L, and the solvent to methylene chloride, solution S 01 The preparation is with embodiment 1. Perform 10 rounds of dip-coating on the washed and dried shot-peened sample according to the following specifications: Dip the sample into the suspension S 01 , Take it out after 7sec, and wait until the coating is cured. Results A uniform magnesium oxide / PLLA composite coating (functional film) was obtained on the surface of the sample. The in vitro biodegradability test of the material was carried out the same as in Example 1, and the results showed that the substrate of the sample began to have visible corrosion marks after about 17 days, indicating that the functional film had a certain biodegrada...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com