A Sparse Node Location Algorithm
A node positioning and sparse technology, applied in transmission monitoring, electrical components, transmission systems, etc., can solve the problems of HADO algorithm with a large amount of calculation, MAP algorithm positioning accuracy easily affected by string azimuth accuracy, and high moving path , to achieve convenience, improve reliability, and simple positioning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
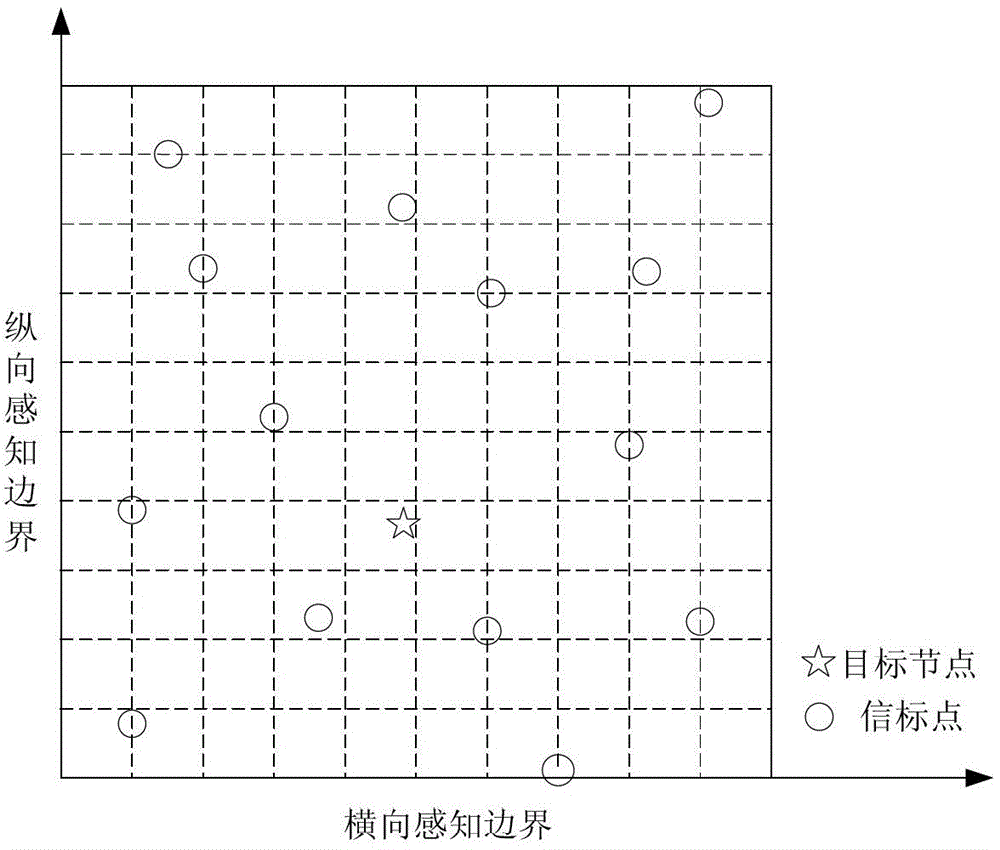
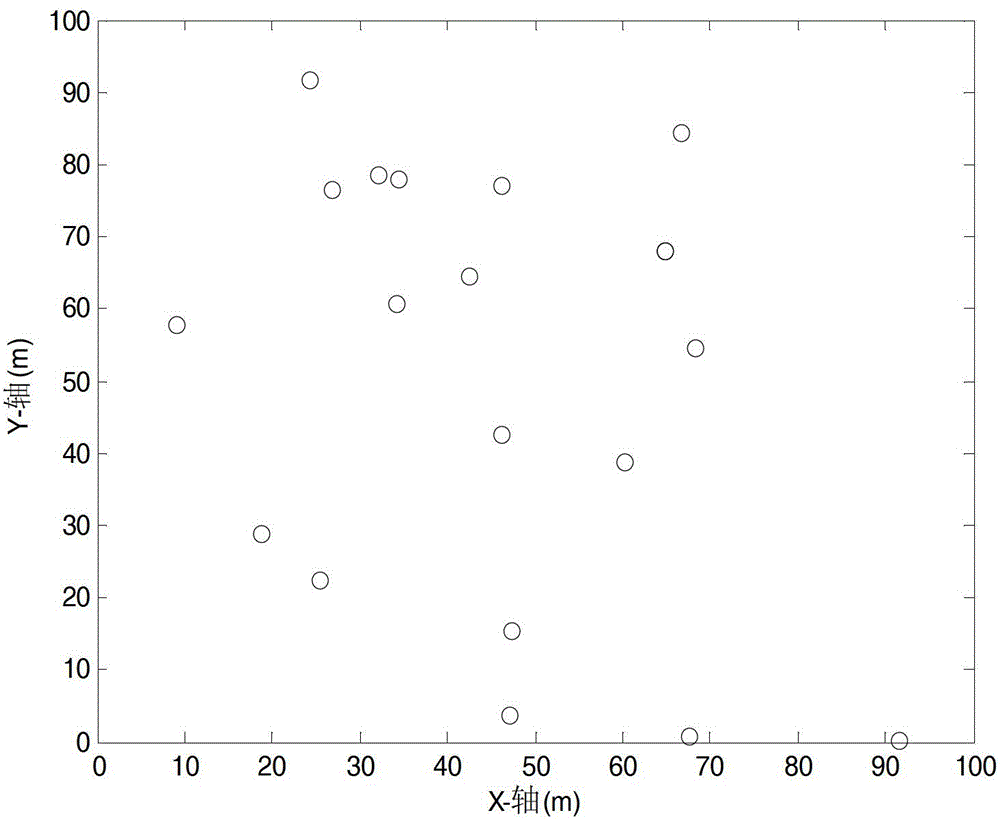
[0070] refer to Figure 5 , Figure 6 , 1000 common nodes are randomly distributed in a square area of 100m×100m. The communication radius of all ordinary nodes and beacon nodes in the area is 20m, and the maximum moving speed of the beacon node is 20m / s, and its moving path follows the RWP model. Among them, the algorithm divides the node sensing area into a grid of 15×15, and the signal strength P t =-40dBm, the signal-to-noise ratio is 20dB. When the number of beacon points perceived by the node is less than 8, M takes the actual number of beacon points; when it is greater than or equal to 8, take the 8 beacon points with the strongest signal strength for positioning, that is to say, M=8 . In the algorithm, the beacon node is set to broadcast a beacon signal every 1 second, broadcasting 400 times (the following simulation experiment parameters are the same as this parameter). Figure 5 and Figure 6 Respectively described in the ideal environment ( image 3 ) and i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com