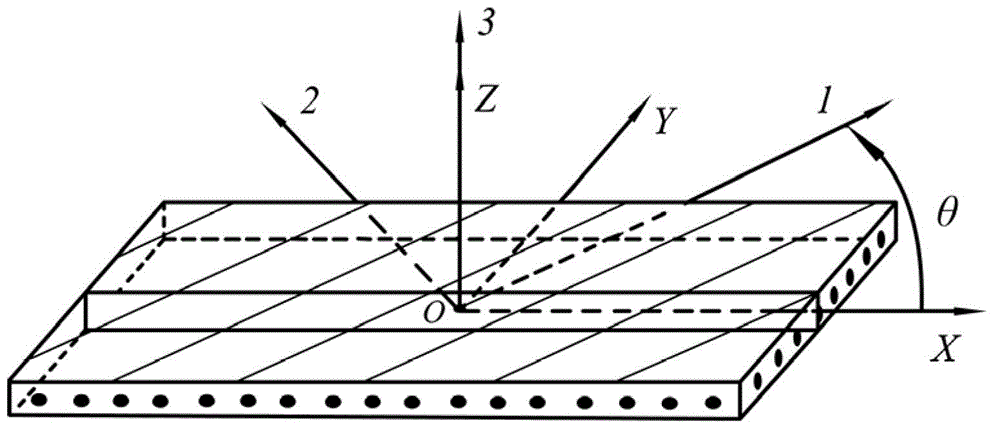
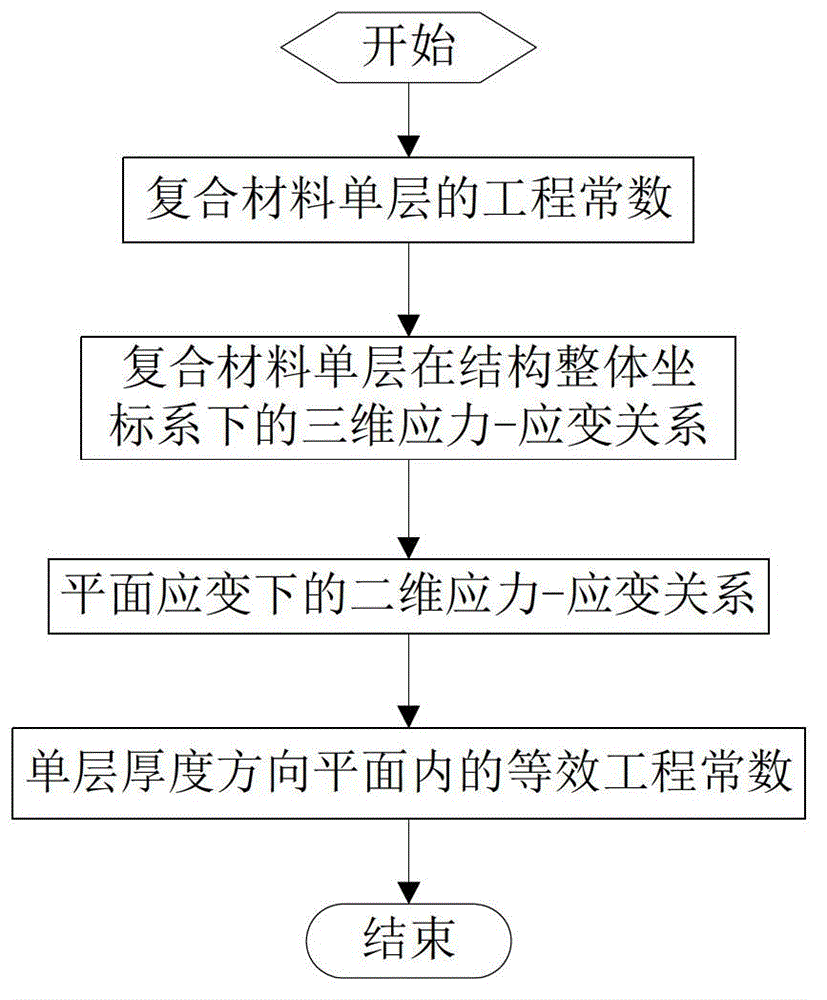
Method for determining equivalent engineering constants in planes of compound materials in thickness direction
A technology of composite materials and engineering constants, which is used in electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., and can solve problems such as limiting the application of two-dimensional finite element analysis of mechanical responses.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
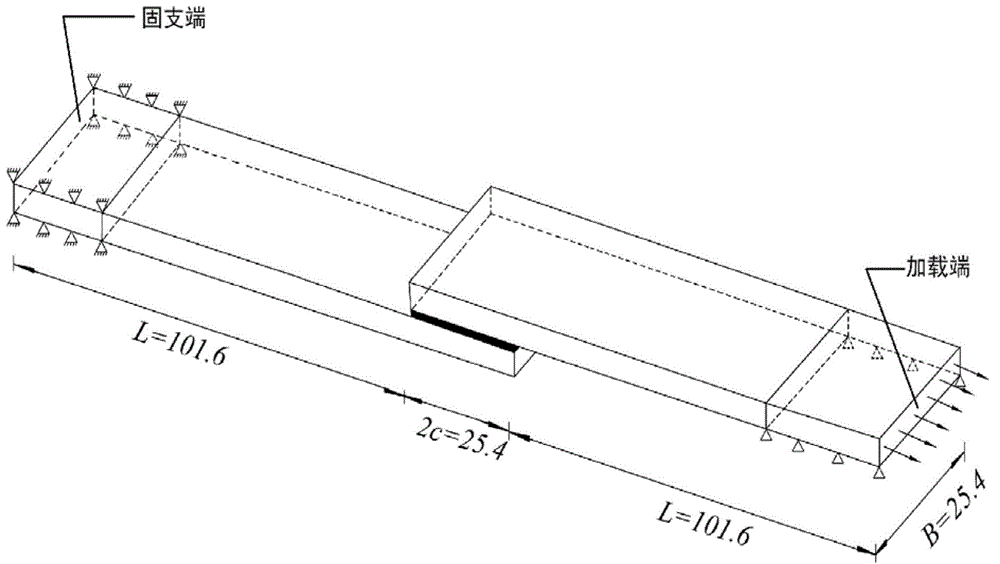
[0052] Example: Shear Stress Analysis of the Middle Surface of the Adhesive Layer of a Composite Single Lap Bonded Joint Subjected to a Tensile Load
[0053] 1. Geometric description;
[0054] Such as image 3 As shown, the composite material single-lap adhesive joint to be studied is composed of two identical upper and lower lap plates and an intermediate adhesive layer. The transverse dimension of the joint is: B=25.4mm. The overlapping board is made of composite material laminated board, the length L is 101.6mm, the height h is 2mm, and the length 2c of the glued part is 25.4mm.
[0055] (1) The upper and lower composite material lap plates:
[0056] Lap-up form of lap joint board is [0 / 45 / -45 / 0] s , the thickness of each composite single layer is 0.25mm;
[0057] (2) Adhesive layer material:
[0058] The thickness of the glue layer is 0.13mm;
[0059] (3) Loads and boundary conditions:
[0060] The lower lap plate on the left side of the joint is fixed with a 20mm l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com