Digital-to-analog convertor
A digital-to-analog converter technology, applied in the field of digital-to-analog converters, can solve problems such as monotony
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
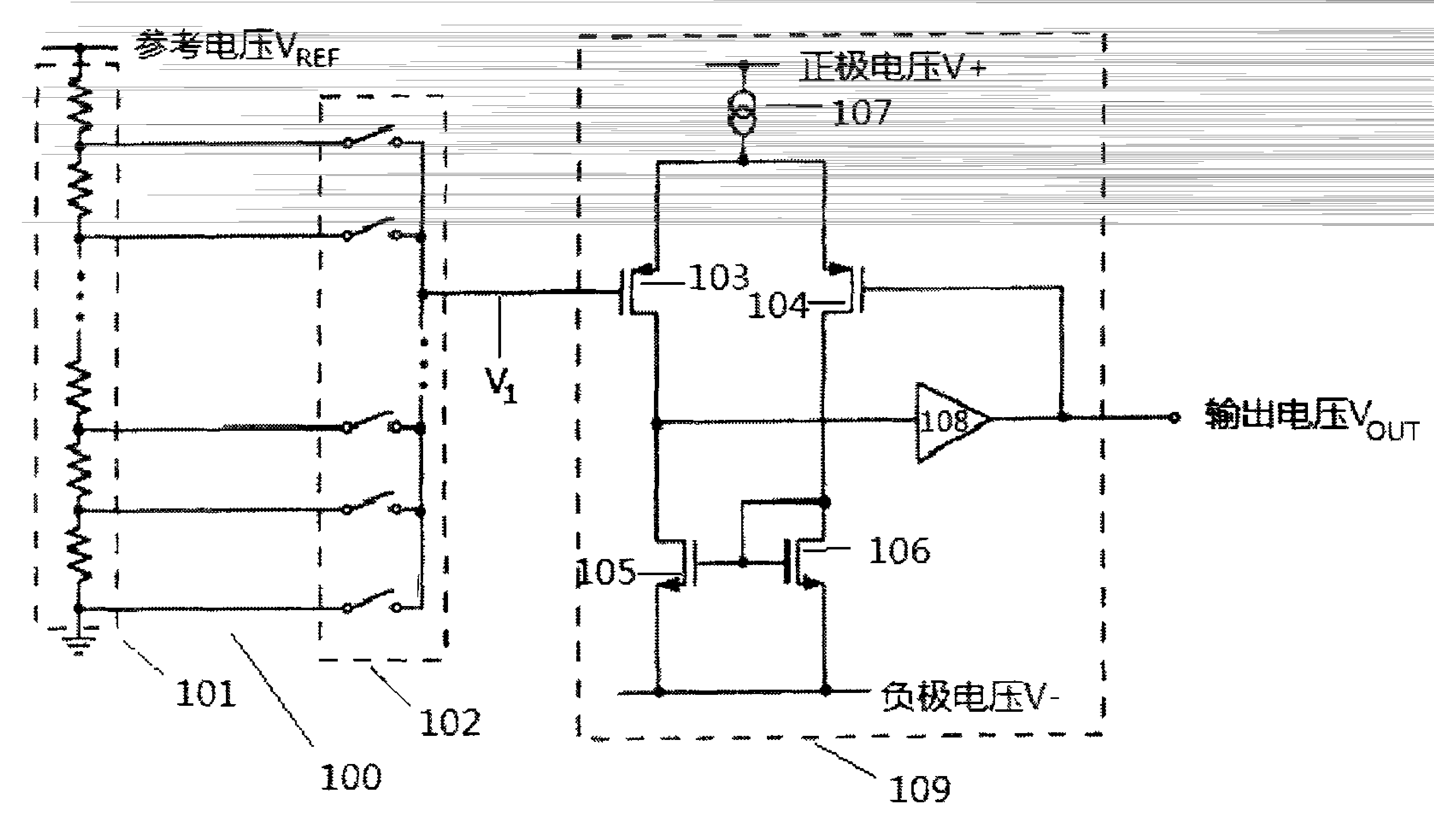
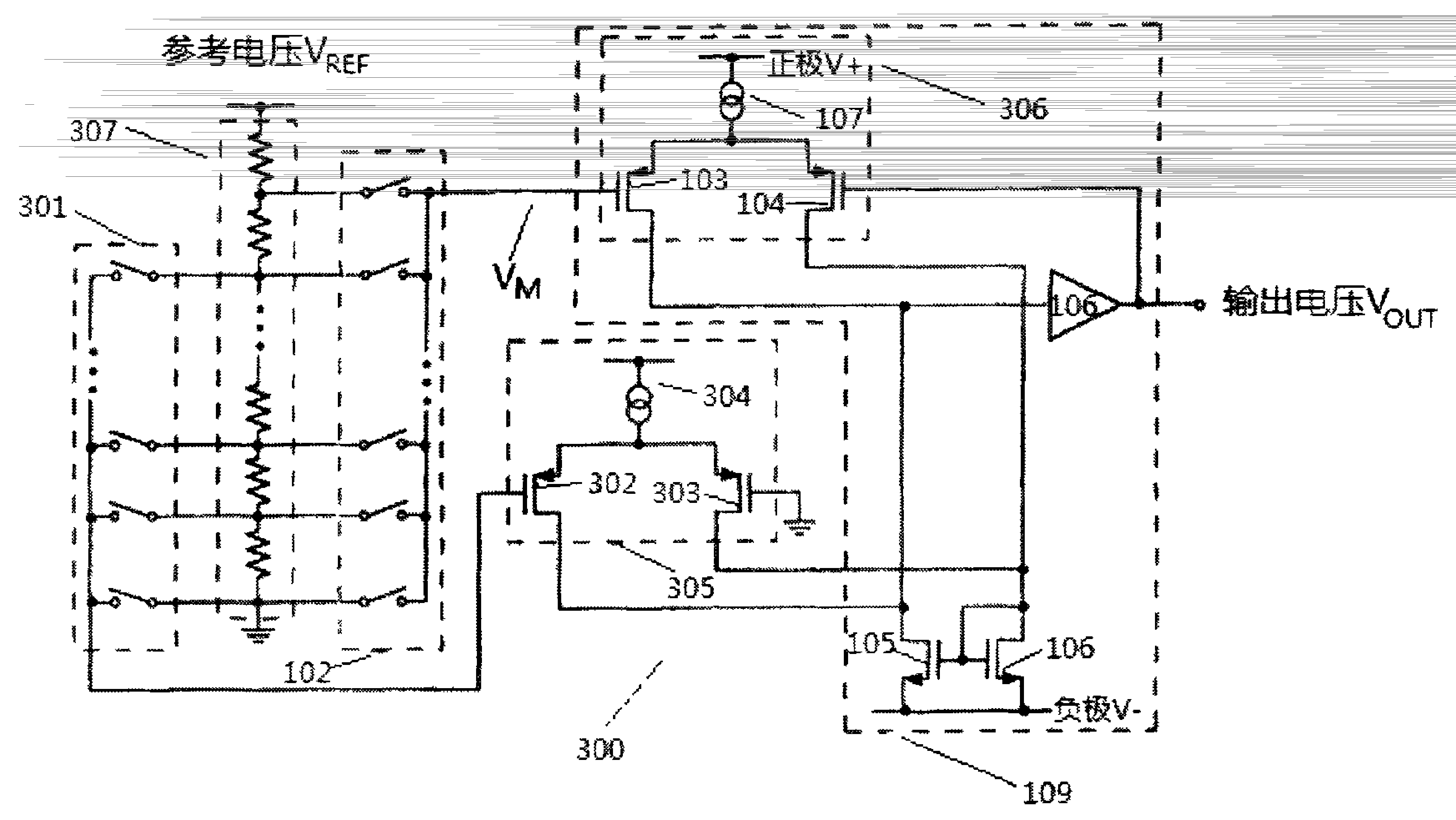
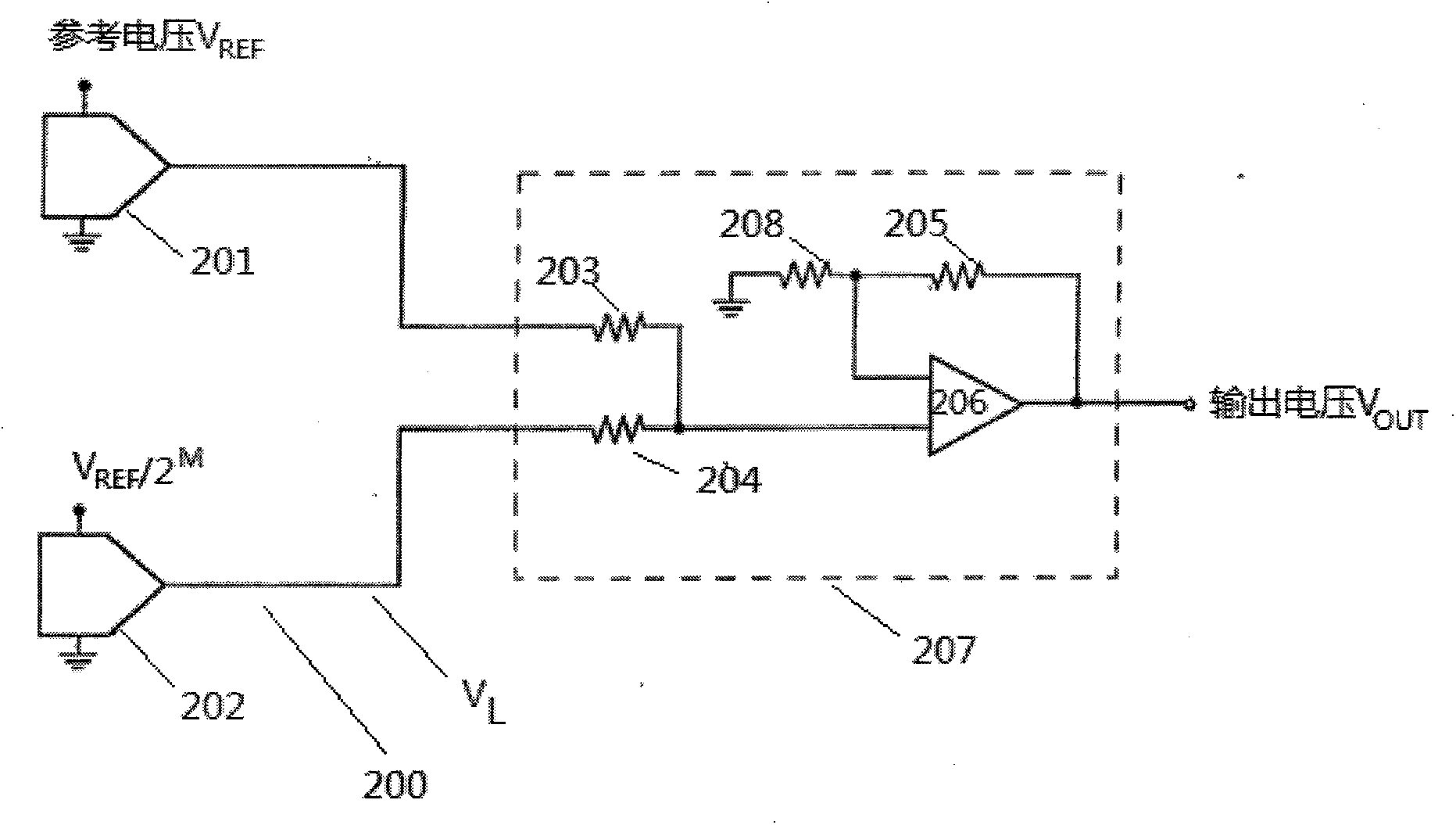
[0022] A typical example of a conventional N-bit DAC providing a guaranteed monotonic conversion is shown in simplified schematic form in figure 1 explained in. DAC100 consists of a set of 2 N node connected resistive element 101 with a set of 2 N A switching device 102 is coupled to the input of a unity gain buffer 109 , directly to element 103 and through element 108 . Although a specific instance of buffer 109 is illustrated, any conventional buffer may be used. Current source 107 in buffer 109 drives the sources of PMOS transistors 103 and 104 . The drains of transistors 103 and 104 are coupled to the drains of NMOS transistors 105 and 106 . Transistors 105 and 106 form a current mirror. The high-gain inverting amplifier 108 provides negative feedback through the drain of the transistor 103 and the gate of the transistor 104 . This feedback ensures that the drain currents of transistors 105 and 106 are substantially equal. In turn, this ensures that the gate voltage...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com