Method for obtaining 3D imaging image from single 2D image
An image and 3D technology, applied in image communication, electrical components, stereo system, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
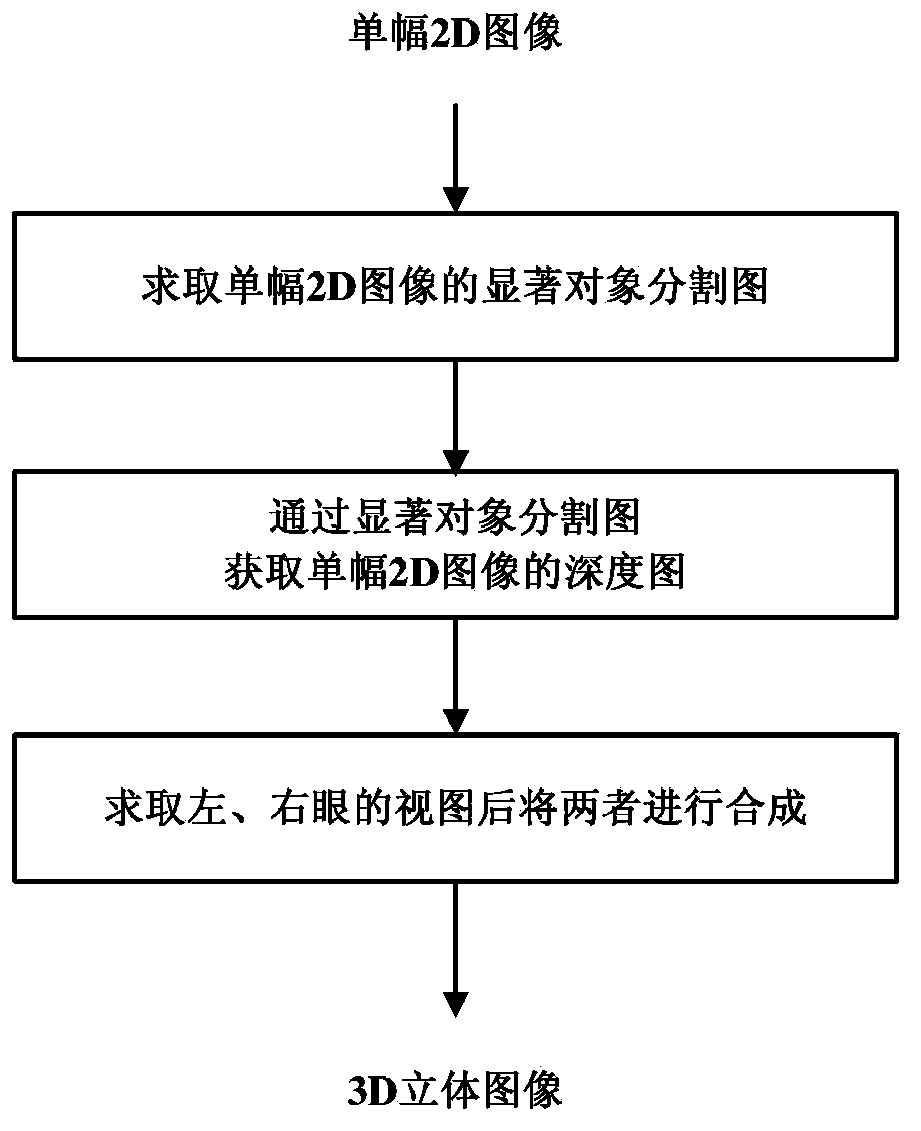
[0072] This embodiment is for a single 2D image, such as figure 1 As shown in the method for obtaining a 3D imaging image from a single 2D image, the process of obtaining the corresponding left-eye view and right-eye view is carried out in the following three steps:
[0073] Step A: Obtain a salient object segmentation map of a single 2D image
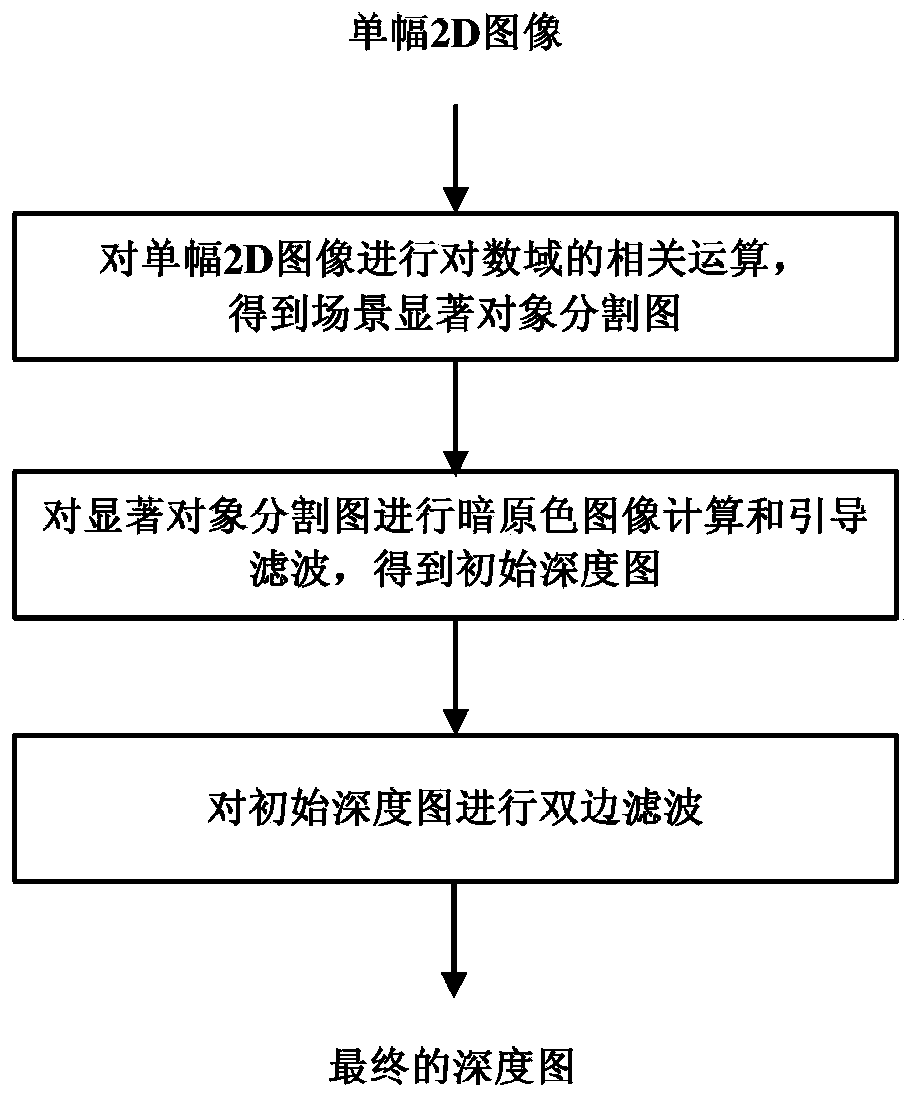
[0074] The calculation of the salient object segmentation map is as follows: figure 2 The first step in the specific process of depth map estimation shown includes the following steps:
[0075] Step A1: Convolute the single 2D image with a Gaussian low-pass smoothing function to obtain the luminance component image of the single 2D image
[0076] L ^ c ( x , y ) = I c ( x , y ) ...
Embodiment 2
[0114] For a single 2D image Figure 4 (a) (size 800×500) for 3D conversion processing. First, the original 2D image is convoluted with a Gaussian low-pass smoothing function to obtain the brightness component image of the original image. Among them, the standard deviation σ of the Gaussian low-pass smoothing function is 9, the smoothing window size w is set to 55, and the center m of the window is set to 28. Then use formula 4 to get a new brightness component image, where ω 1 Set to 3. Finally, the correlation operation in the logarithmic domain is carried out to obtain Figure 4 Salient object segmentation of (a) Figure 4 (b).
[0115] Then, the salient objects are segmented Figure 4 (b) On the three color channels of R, G, and B, use a window with a size of 3×3 to perform minimum value filtering, and use the minimum value of the corresponding pixel points of the three images obtained after filtering as the pixel of the corresponding point of the dark primary color ...
Embodiment 3
[0118] For a single 2D image Figure 5 (a) (size 470×500) for 3D conversion processing. First, a single 2D image is convolved with a Gaussian low-pass smoothing function to obtain the brightness component image of the original image. Among them, the standard deviation σ of the Gaussian low-pass smoothing function is 5, the smoothing window size w is set to 31, and the center m of the window is set to 16. Then use formula (4) to get a new brightness component image, where ω 1 Set to 2. Finally, the correlation operation in the logarithmic domain is carried out to obtain Figure 5 Salient object segmentation of (a) Figure 5 (b).
[0119] Then, the salient objects are segmented Figure 5 (b) On the three color channels of R, G, and B, use a window with a size of 3×3 to perform minimum value filtering, and use the minimum value of the corresponding pixel points of the three images obtained after filtering as the pixel of the corresponding point of the dark primary color ima...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com