Light emitting module
A light-emitting module and light-emitting element technology, which is applied in the direction of electrical components, electric solid-state devices, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as poor performance, easy accumulation of heat energy in semiconductor light-emitting elements, and influence of semiconductor light-emitting elements on luminous efficiency and luminous life, so as to avoid light Fading, reliability and service life improvement effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
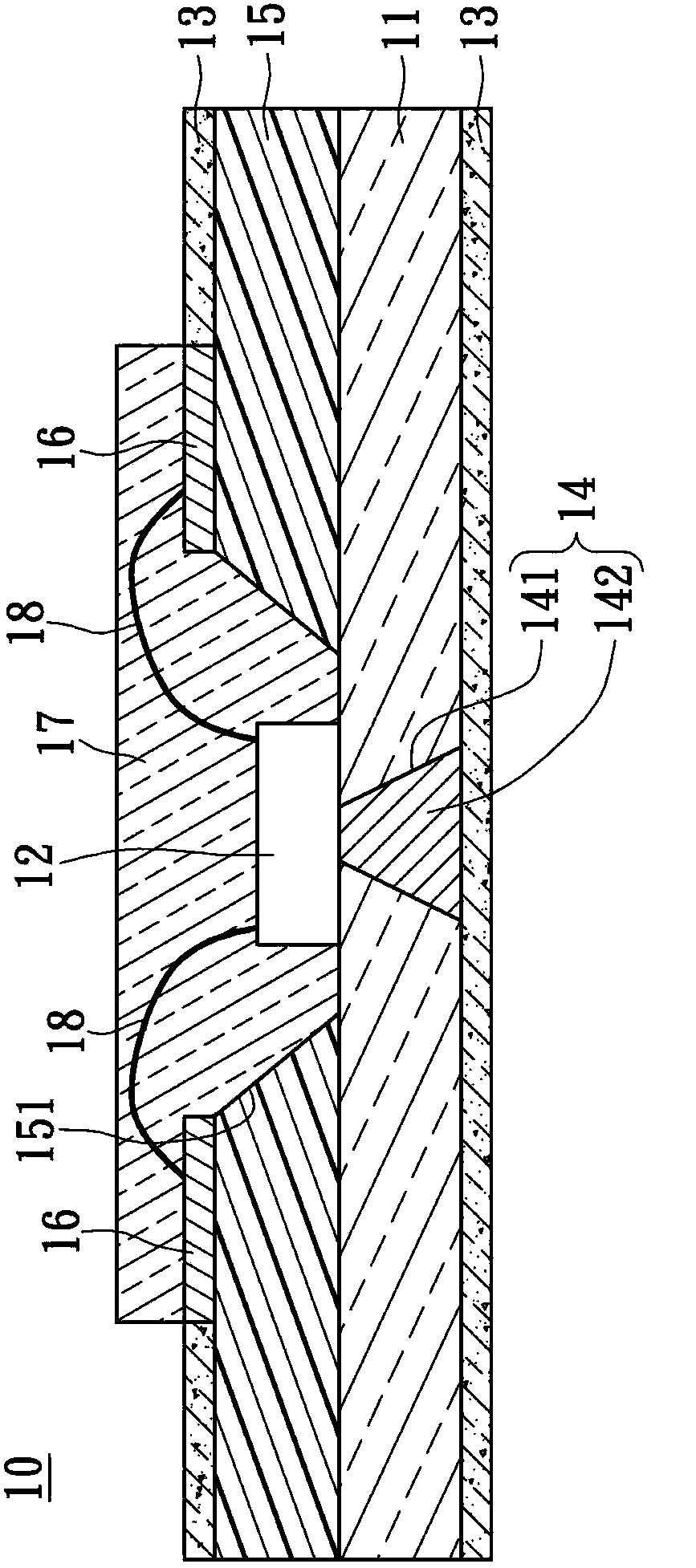
[0045] see figure 1 , figure 1 It is a cross-sectional view of the light emitting module 10 according to the first embodiment of the present invention. The light-emitting module 10 includes a transparent and flexible light-guiding substrate 11 , at least one light-emitting element 12 , a light-guiding and heat-dissipating layer 13 , and at least one vertical heat-conducting structure 14 .
[0046] The transparent flexible light guide substrate 11 has an upper surface and a lower surface, and the transparent flexible light guide substrate 11 has a first refractive index. The light emitting element 12 is disposed on the upper surface of the transparent flexible light guide substrate 11, so that the light emitting element The light emitted by 12 is projected toward the upper surface and the lower surface. The light guide and heat dissipation layer 13 is arranged on the lower surface of the transparent and flexible light guide substrate 11, and the light guide heat dissipation la...
Embodiment 2
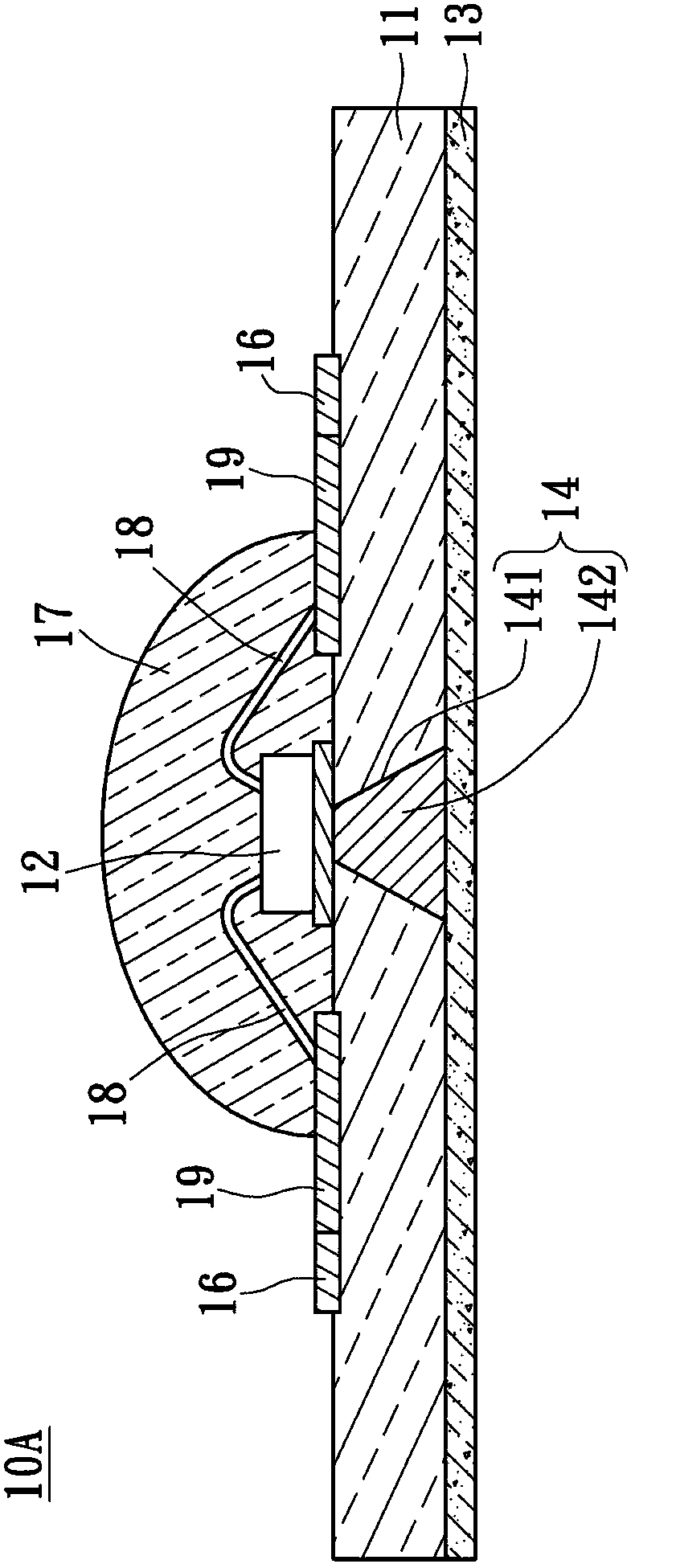
[0058] see figure 2 , figure 2 This is a cross-sectional view of the light-emitting module 10A according to the second embodiment of the present invention. The difference from the previous embodiment is that, in order to make the light-emitting module 10A have a wide range of lighting effects, the light-emitting module 10A does not have a reflective base (not shown), but the outer surface of the lens layer 17 is a convex curved surface. In addition, the light emitting module 10A further includes a plurality of metal pads 19 . The circuit layer 16 and the plurality of metal pads 19 are disposed on the upper surface of the transparent flexible light guide substrate 11 and are electrically connected to each other.
[0059] Accordingly, the light emitting element 12 is disposed on the upper surface of the transparent flexible light guide substrate 11 , and is electrically connected to the metal pad 19 and the circuit layer 16 through the metal wire 18 , so that the circuit desi...
Embodiment 3
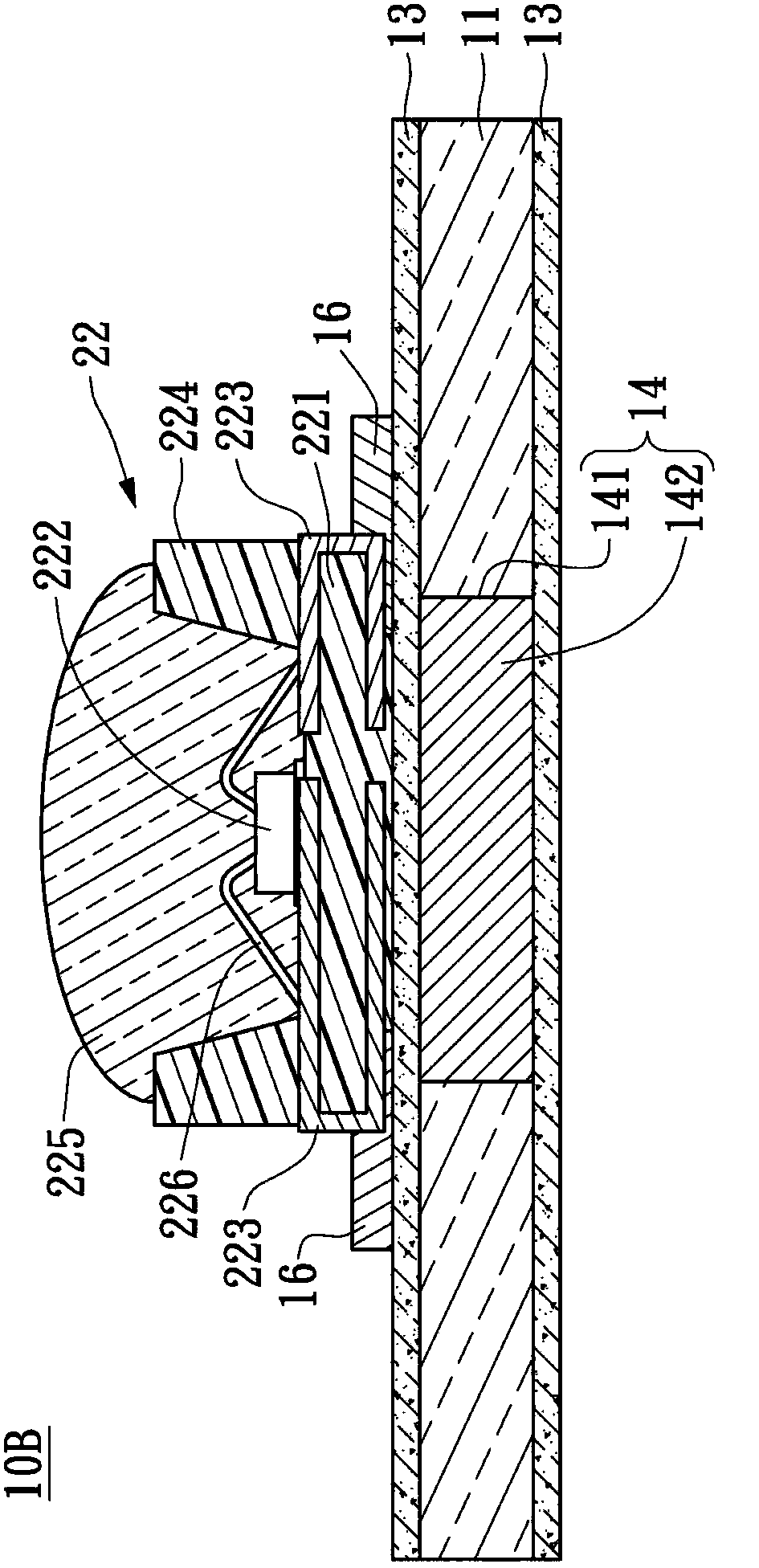
[0061] see image 3 , image 3 It is a cross-sectional view of the light-emitting module 10B according to the third embodiment of the present invention. The difference from the previous embodiment is that the light-emitting element 22 is an LED package, which includes a reflective base 221, a light-emitting diode chip 222, A plurality of metal brackets 223 , a reflection cup 224 and a lens layer 225 are provided.
[0062] The light-emitting diode chip 222 and a plurality of metal pads 223 are fixed on the reflection base 221, wherein each metal bracket 223 is U-shaped, and is respectively connected to the top, surface and one side of the reflection base 221. The light-emitting diode The chip 222 is electrically connected to the metal bracket 223 by means of metal wires 226 . The reflector cup 224 is disposed on the heat dissipation layer 221 and surrounds the LED chip 222 . The lens layer 225 covers the LED chip 222 , some metal pads 233 and metal wires 226 .
[0063] In add...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com