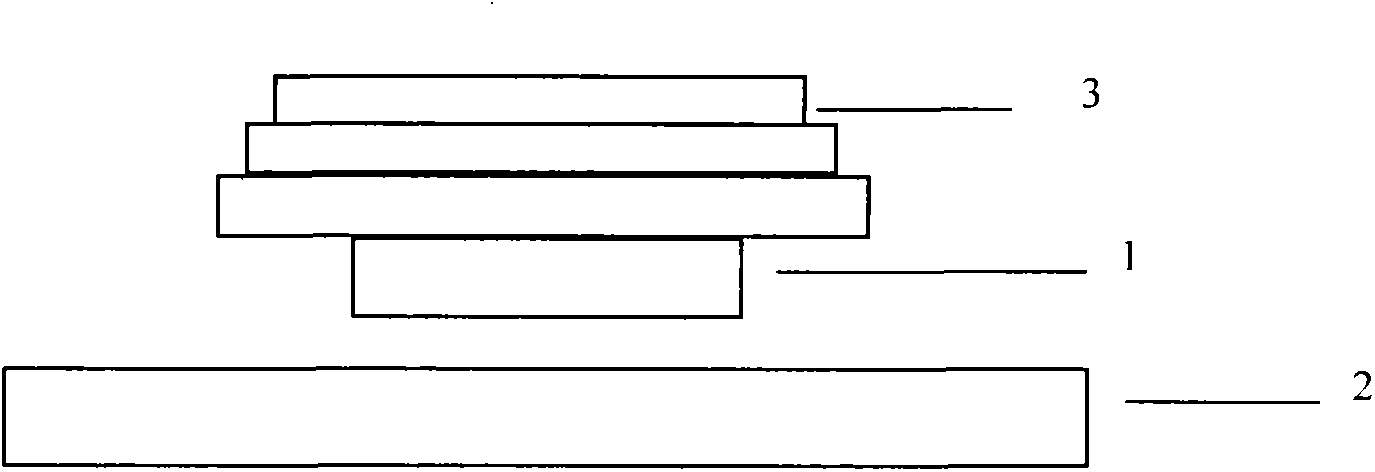
Experimental instrument capable of demonstrating superconductive magnetic levitation phenomenon and testing magnetic levitation force
A magnetic levitation and instrument technology, applied in the field of teaching instruments, can solve the problems of high cost, easy damage of the measured object, and damage of the measured object, and achieve the effect of low cost, simple structure, and easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Place the heat preservation container flat on the table, put the superconducting ring in the heat preservation container, and add an appropriate amount of liquid nitrogen to the heat preservation container. To ensure safety, try to avoid liquid nitrogen splashing. In the process of liquid nitrogen cooling the superconducting ring and the heat preservation container, violent boiling will occur due to a large amount of heat absorption. When the boiling basically stops, the superconducting ring drops to the same temperature as liquid nitrogen (minus 196°C), that is, it enters the superconducting state. At this point the preparations are ready and the experiment can begin. This way of cooling the superconducting ring in an environment without a magnetic field is called zero-field cooling.
[0041] Use tweezers to clamp the superconducting ring out of the heat preservation container, put it on the guide rail, and adjust the position so that the plane of the superconducting ...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Put the magnetic guide rail upside down, take out the superconducting ring from the heat preservation container with tweezers, and use a ruler with the other hand to make the superconducting ring stick to the surface of the magnetic guide rail. The tweezers and ruler are removed, and the superconducting ring hangs below the magnetic rail. Gently move the superconducting ring with tweezers, and the superconducting ring can be suspended under the magnetic rail for reciprocating motion.
Embodiment 3
[0045] Place the superconducting ring in the insulated container so that it is in close contact with the inner diameter of the insulated container. Place the spacer on the magnetic rail, put the foam insulation container on the spacer, and add liquid nitrogen to cool it. This way of cooling the superconducting ring in a magnetic field environment is called field cooling.
[0046] In the process of liquid nitrogen cooling the superconducting ring and the heat preservation container, violent boiling will occur due to a large amount of heat absorption. When the boiling basically stops, the superconducting ring drops to the same temperature as liquid nitrogen (minus 196°C), that is, it enters the superconducting state. At this point the preparations are ready and the experiment can begin.
[0047] Remove the spacer, at this time the foam insulation container and the superconducting ring are suspended above the magnetic guide rail as a whole, and the insulation container can be r...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com