Linear Motor
A linear motor and coil technology, applied in the direction of electrical components, electromechanical devices, electric components, etc., can solve the problems of limiting vertical thrust and horizontal thrust, limiting vertical magnetic density and horizontal magnetic density, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
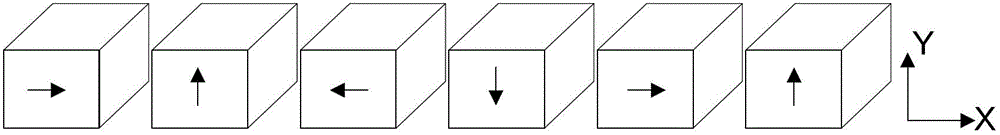
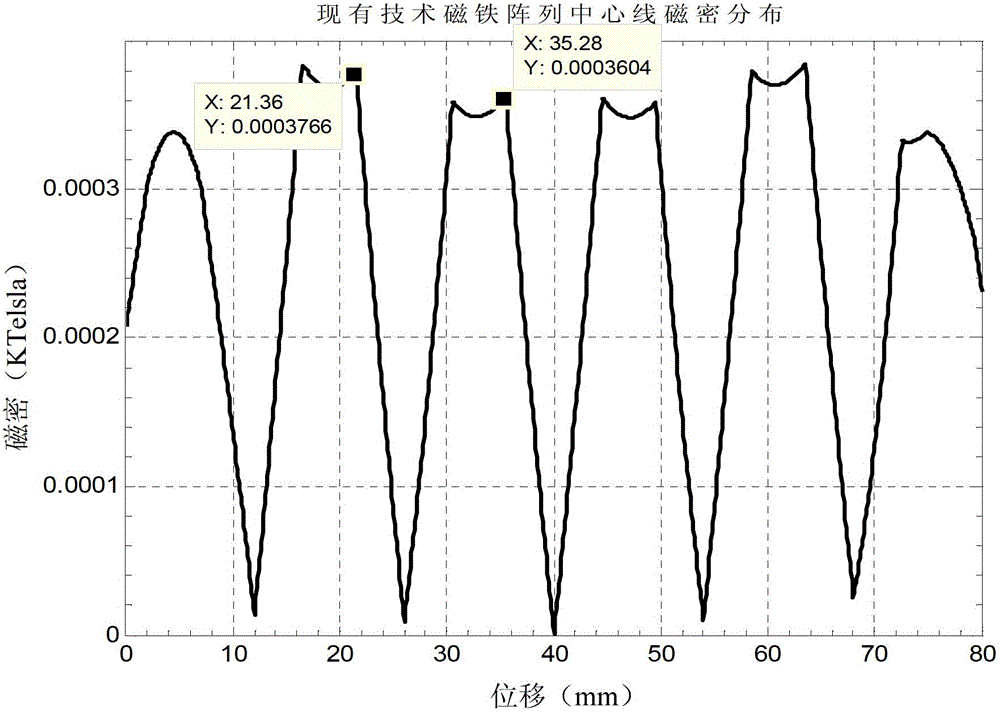
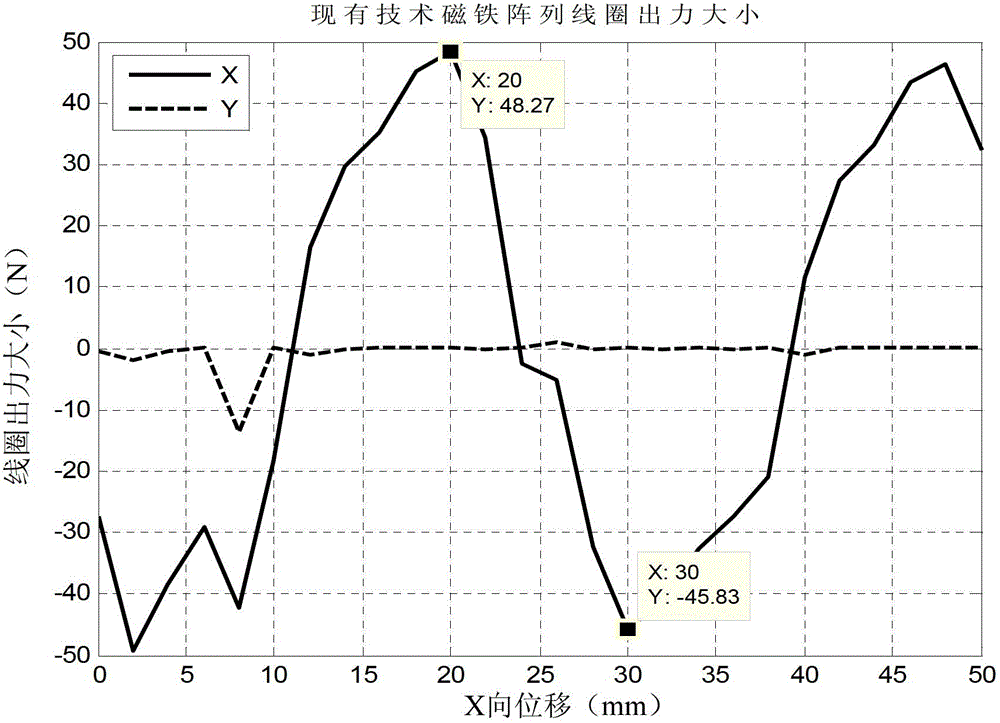
[0037] see Figure 4 and Figure 5 , Figure 4 A schematic structural view of the linear motor in Embodiment 1 of the present invention is given, wherein the magnet array is a cross-sectional view along the X axis, Figure 5 gives Figure 4 Schematic diagram of the three-dimensional structure of the magnet array. The linear motor provided in this embodiment includes a coil unit and a magnet unit. The magnet unit includes two groups of relatively parallel and symmetrical magnet arrays located on the yoke 100 . The coil unit is inserted between two sets of magnet arrays, the coil unit includes a coil 202 and a corresponding iron core 201 that can move relative to it, and the coil unit is close to but not in contact with the magnet array, that is, the coil unit is in contact with the magnet array. There are gaps between the magnet arrays. The magnet array is composed of first type magnets 111, second type magnets 112 and third type magnets 113 between them along the X axis ...
Embodiment 2
[0045] see Figure 8 , Figure 8 A schematic structural diagram of the linear motor according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention is given, wherein the magnet array is a cross-sectional view along the X axis. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that in the third type of magnet 123, the cross-sections along the XY plane of the first prism magnet 123a, the second prism magnet 123b and the third prism magnet 123c are right triangles respectively. , an isosceles trapezoid and a right triangle, wherein the magnetization direction of the first prism magnet 123a enters the second prism magnet 123b through its opposite surface with the second prism magnet 123b, and the magnetization direction of the second prism magnet 123b is parallel to the X axis And point to the first type of magnet 123a, the magnetization direction of the third prism magnet 123c is away from the second prism magnet 123b through its opposite surface with the second prism magnet 123b, o...
Embodiment 3
[0047] see Figure 9 , Figure 9 A schematic structural diagram of the linear motor according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention is given, wherein the magnet array is a cross-sectional view along the X-axis. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the cross-sections along the XY plane of the first prism magnet 133a, the second prism magnet 133b and the third prism magnet 133c of the third type magnet 133 are right-angled trapezoid, isosceles triangle and right-angle respectively. trapezoidal, wherein the magnetization direction of the first prism magnet 133a enters the second prism magnet 133b through its opposite surface with the second prism magnet 133b, and the magnetization direction of the second prism magnet 133b is parallel to the X axis and points to the first type of magnet 133a, the magnetization direction of the third prism magnet 133c is away from the second prism magnet 133b through its opposite surface with the second prism magnet 1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com