Method for carrying out non-invasive measurement on mitochondrial DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) based on high-flux gene sequencing
A gene sequencing and mitochondrial technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of cumbersome operation, difficult clinical diagnosis, and limited detection methods to detect gene loci, and achieve the effects of accurate detection results, rigorous experimental design, and strong scalability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] The technical solutions of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments. However, the present invention is not limited to the following examples.
[0032] The specific steps of the experimental process of the present invention are as follows.
[0033] 1. Extraction of total genomic DNA from oral cells
[0034] The total genomic DNA of oral cells was extracted strictly according to the operating instructions of the Genomic DNA Purification Kit (Fermentas K0512).
[0035] 2. Design of PCR primers and in vitro enrichment and amplification of mitochondrial DNA
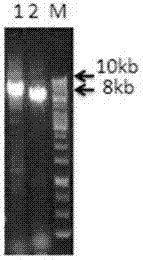
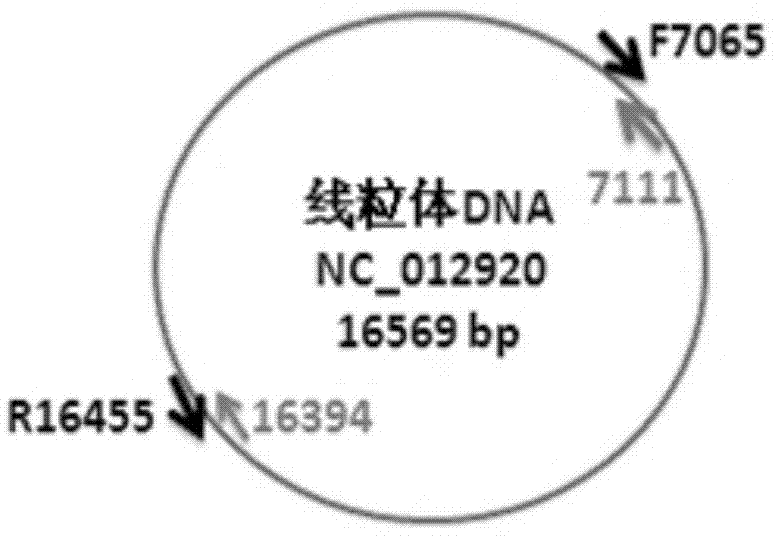
[0036]Two pairs of PCR amplification primers were designed to carry out complete enrichment and amplification of mitochondrial DNA in vitro on the extracted total genomic DNA. The lengths of the amplified products are 9391bps and 7287bps respectively, and the amplified products can cover the entire complete mtDNA sequence at...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com