Method for tolerating malicious nodes in wireless sensor network
A technology of wireless sensor and sensor network, applied in the field of wireless communication and network security, can solve the problems of inability to achieve the purpose of attack, impossible to achieve unlimited energy and resources, not established, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0028] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
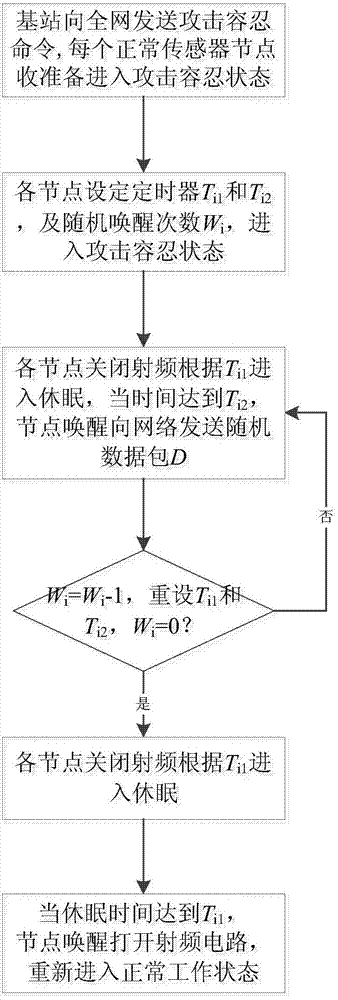
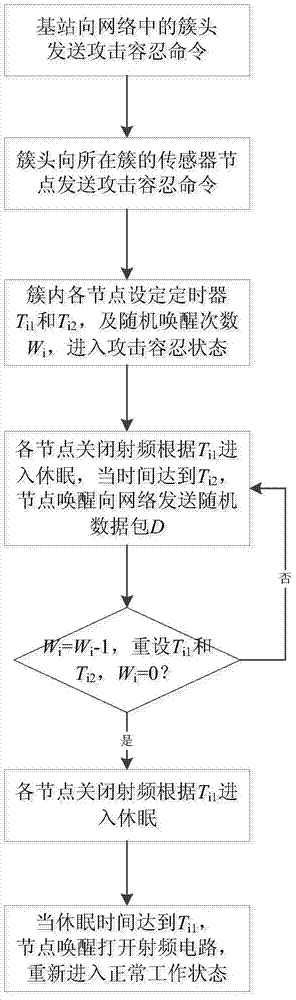
[0029] Such as figure 1 Shown is a flow chart of a malicious node tolerance method in a wireless sensor network in a clustering network, including the following steps:
[0030] (1) The base station sends an attack tolerance command to the entire network, and the command message is transmitted in the network in a flooding manner, and each normal node in the sensor network is ready to enter the attack tolerance state from the normal working state after receiving the command;
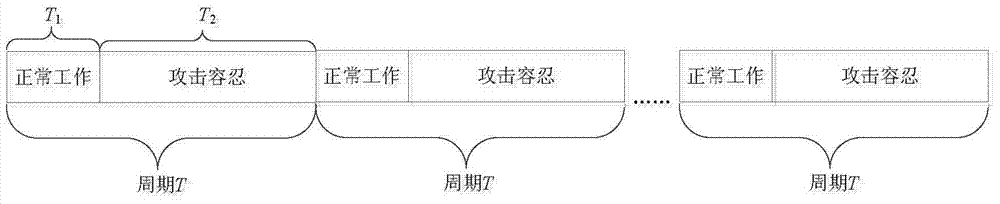
[0031] (2) The normal node i (i=1,2,...N) enters the attack tolerance state, and N represents the number of nodes in the wireless sensor network. Node i sets two timers T respectively i1 and T i2 , and a random number of wake-ups W i , where W i Determined according to the number of attacking nodes in the network, when the attacking nodes are uncertain, set W i = 3, W i As the number of atta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com