A kind of Lactobacillus plantarum strain jp-8 and application thereof
A technology of Lactobacillus plantarum and JP-8, which is applied in the field of food microbiology and food processing, can solve problems such as difficult long-term storage, and achieve the effect of retaining flavor and nutrients, high nutritional value, and unique flavor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1, the process of using Lactobacillus plantarum (Lactobacillus plantarum) JP-8 to ferment sea asparagus puree
[0035] Take the glycerol-preserved strain of Lactobacillus plantarum JP-8 of the present invention, inoculate it on a fresh MRS solid plate by streaking and inoculate it on a fresh MRS solid plate, activate and cultivate it at 25°C for 48 hours; use a sterilized toothpick to pick a single colony of JP-8 and inoculate it into a In a 10mL MRS liquid culture test tube, culture at 30°C for 36 hours; take the cultured bacteria solution and transfer it to a 100mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 50mL MRS liquid medium at a ratio of 5% (v / v), 35 Cultivate statically for 24 hours under the condition of ℃, and use it as seed bacterial liquid for future use.
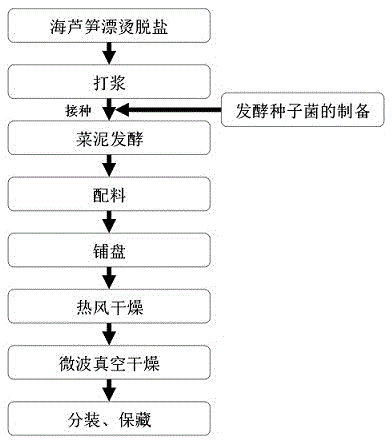
[0036] Such as figure 1 As shown, fresh sea asparagus twigs were selected, blanched at 95°C for 4 minutes, and then put into tap water for desalination for 8 hours. During this period, the water was changed ev...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2, the process of using Lactobacillus plantarum (Lactobacillus plantarum) JP-8 to ferment sea asparagus puree
[0039] Take the glycerol-preserved strain of Lactobacillus plantarum JP-8 of the present invention, inoculate it on a fresh MRS solid plate by streaking and inoculate it on a fresh MRS solid plate, activate and cultivate it at 30°C for 36 hours; use a sterilized toothpick to pick a single colony of JP-8 and inoculate it into a In a 10mL MRS liquid culture test tube, culture it statically at 25°C for 48 hours; take the cultured bacteria solution and transfer it to a 100mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 50mL MRS liquid medium at a ratio of 1% (v / v), 30 Cultivate statically for 36 hours under the condition of ℃, and use it as seed bacterial liquid for future use.
[0040] Such as figure 1 As shown, select fresh sea asparagus twigs, blanch at 100°C for 3 minutes, then put them into tap water for desalination for 6 hours, change the water every 2 hours during...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Example 3, the process of using Lactobacillus plantarum (Lactobacillus plantarum) JP-8 to ferment sea asparagus puree
[0043] Take the glycerol-preserved strain of Lactobacillus plantarum JP-8 of the present invention, inoculate it on a fresh MRS solid plate by streaking, and activate and cultivate it at 35°C for 24 hours; use a sterilized toothpick to pick a single colony of JP-8 and inoculate it into a In a 10mL MRS liquid culture test tube, culture it statically at 35°C for 24 hours; take the cultured bacteria solution and transfer it to a 100mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 50mL MRS liquid medium at a ratio of 2.5% (v / v), 25 Cultivate statically for 48 hours under the condition of ℃, and use it as seed bacterial liquid for future use.
[0044] Such as figure 1 As shown, fresh sea asparagus twigs were selected, blanched at 90°C for 6 minutes, then put into tap water for desalination for 10 hours, during which time the water was changed every 2 hours, and finally the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com