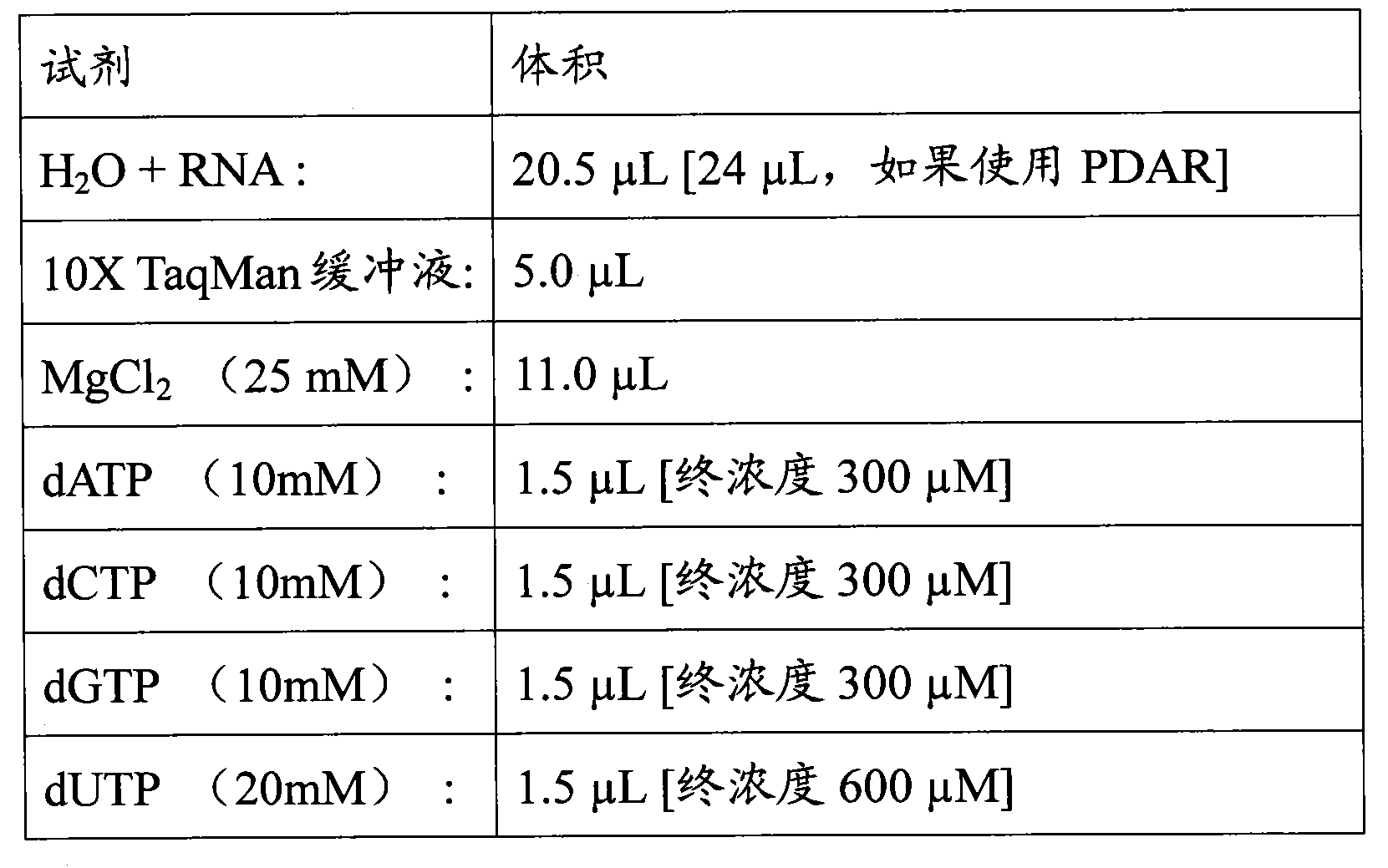
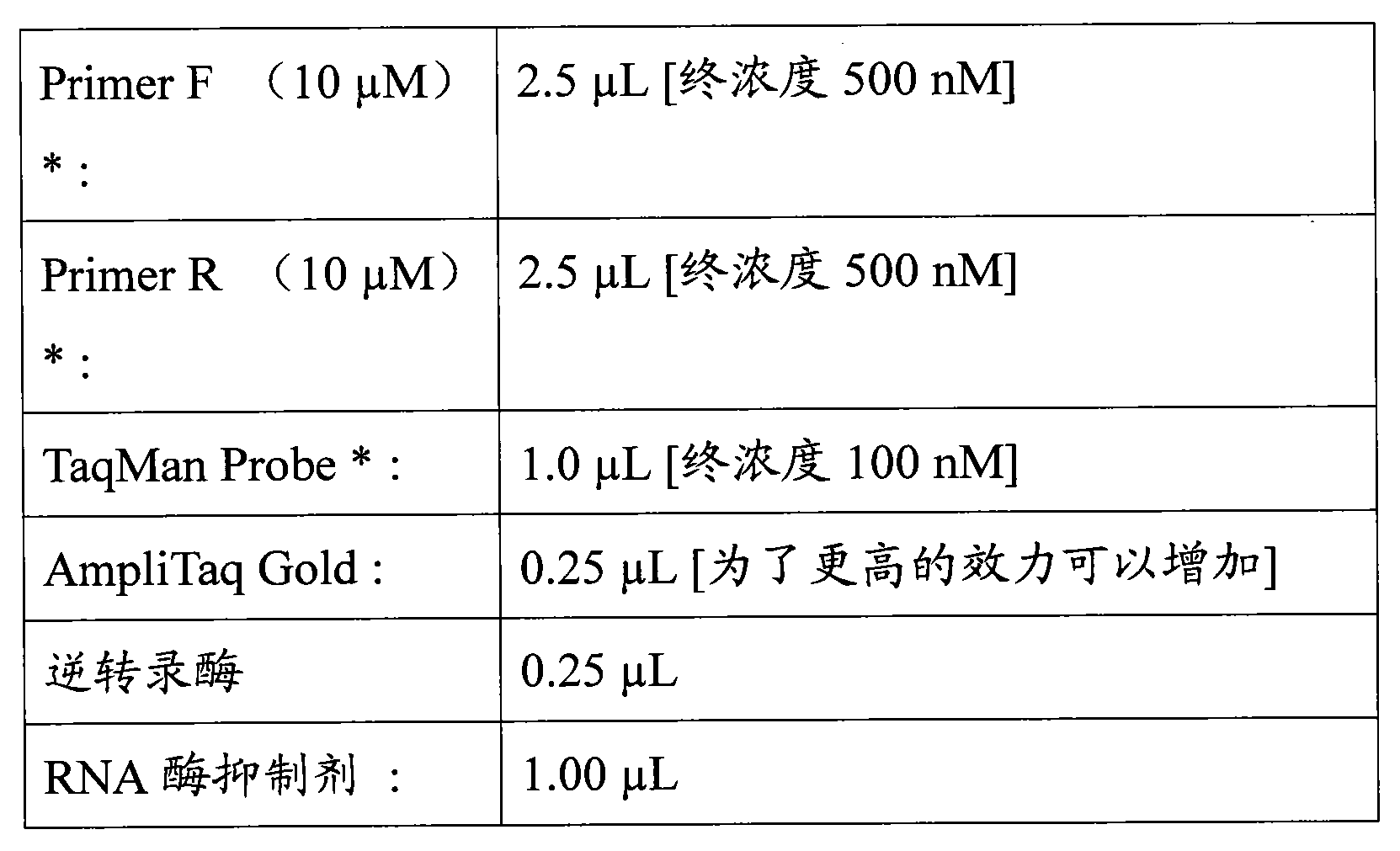
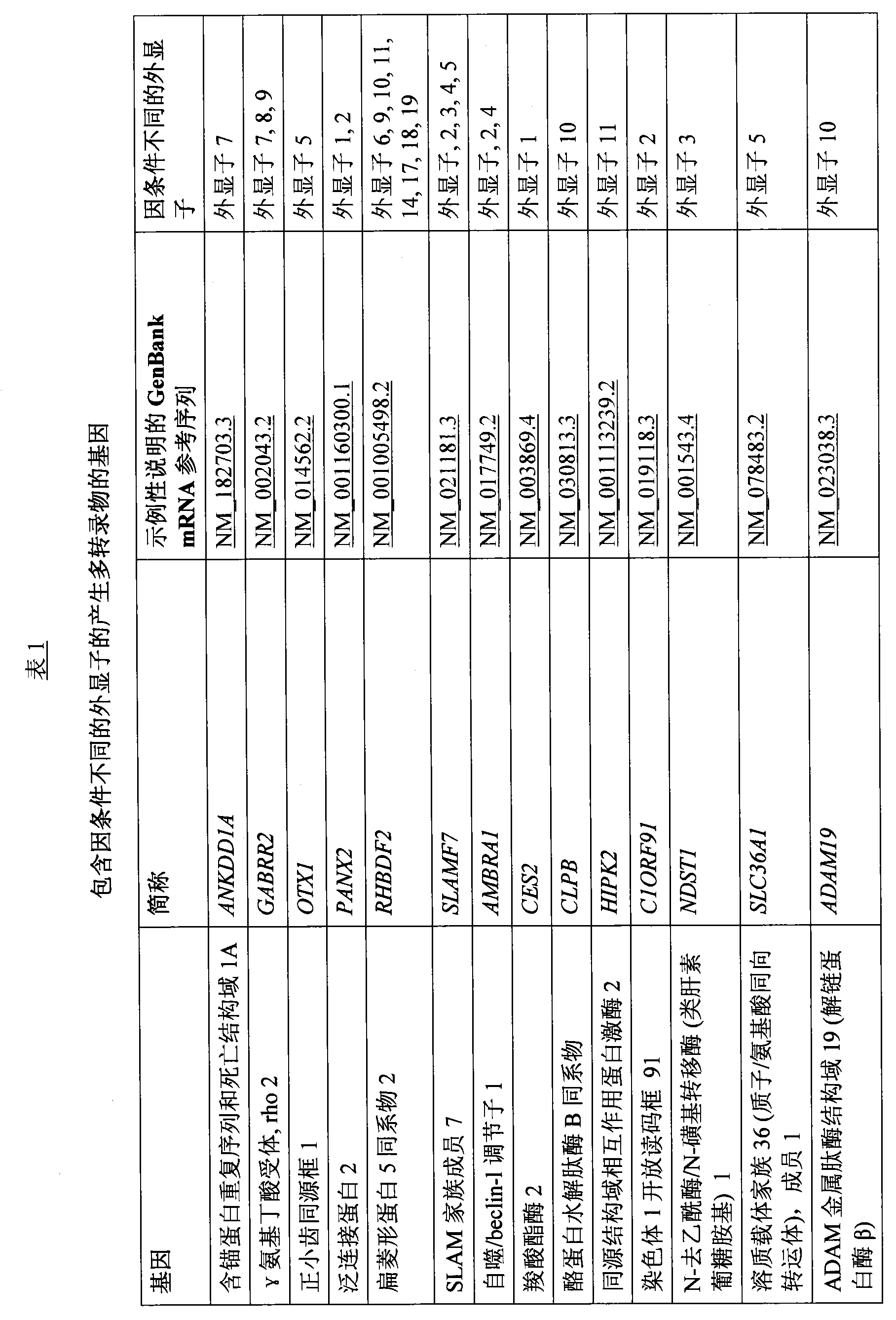
Diagnostic and/or screening agents and uses therefor
A technology of selection, gene, applied in the field of diagnosis and/or screening agent and its use, which can solve the problem of inability to clear primary infection, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0236] Identification of diagnostic genes that differ between postoperative inflammation, sepsis, and inSIRS
[0237] Experimental Disease Trial Design
[0238] A clinical trial was conducted to determine whether the gene's transcript could differentiate patients with sepsis, inSIRS, and post-surgical inflammation.
[0239]Blood samples were collected at various time points to provide time course data and Affymetrix exome assay (Affymetrix HuEx-1.0) analysis of these data (see "Identification of Diagnostic Marker Genes" below) was used to analyze gene expression showing 235 specific genes Evidence of splicing changes was shown, which also differed in expression between sepsis-positive, inSIRS-positive, and post-operative patients. Of these 235 only a limited number (57) were identified that could be used as classifiers to distinguish these patient groups, the 57 genes resulting in between postoperative inflammation and inSIRS, between postoperative inflammation and sepsis, ...
Embodiment 2
[0423] Identify splice variants
[0424] For a given gene, splice variants were detected using ANOVA. The method used is similar to the Affymetrix MIDAS method. In the exon-level data, for each subject, there is the intensity of each probe set. The sample model for strength would be the population mean of genes, plus probeset effects plus subject effects plus error. where i is the probeset index and j is the subject index.
[0425] Yij=α+βi+γj+εij
[0426]This model is only applicable when there is no alternative splicing. If probeset i maps to exon e(i) and subject j is in class c(j), then alternative splicing will be represented in the model by the presence of the term δe(i)c(j). In the X:Map annotation, the probe sets matched multiple exons. This is related to the alternate exon layout in the gene, so a test for δic(j), which is the classically responsive probe set, was performed. For simplicity, the subject effect is ignored (this variation becomes part of the noise...
Embodiment 3
[0428] Gene transcripts distinguish sepsis from postoperative inflammation
[0429] Any of the gene transcripts in Table 7 are capable of distinguishing sepsis from postoperative inflammation (signs on values in column logFC indicate competitive up- or down-regulation. For example, transcripts of ankddla are expected to be relative to postoperative in sepsis relative to upregulated whereas OXT1 transcripts are expected to be relatively downregulated in sepsis relative to post-surgery).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com